Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
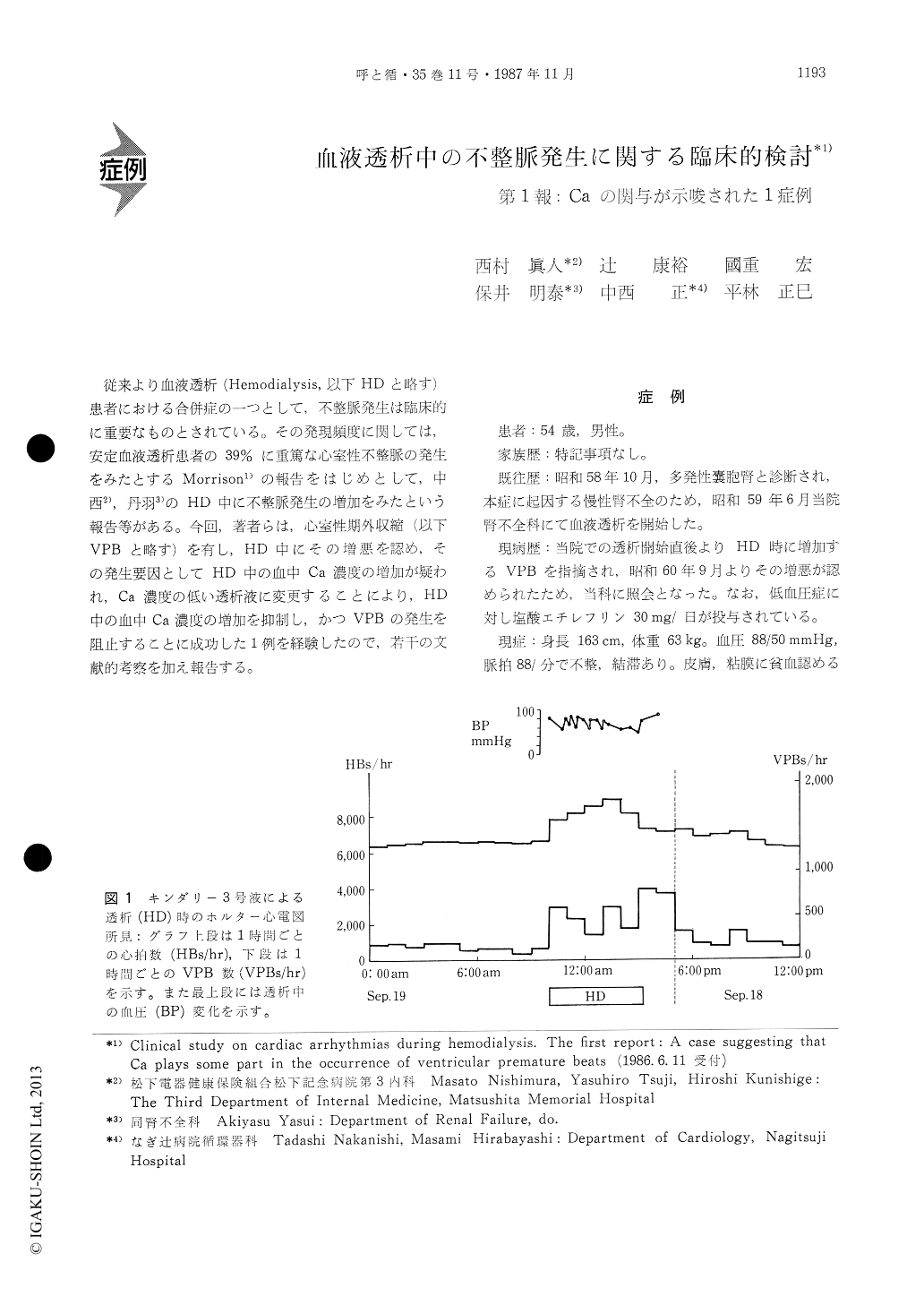
従来より血液透析(Hemodialysis,以下HDと略す)患者における合併症の一つとして,不整脈発生は臨床的に重要なものとされている。その発現頻度に関しては,安定血液透析患者の39%に重篤な心室性不整脈の発生をみたとするMorrison1)の報告をはじめとして,中西2),丹羽3)のHD中に不整脈発生の増加をみたという報告等がある。今回,著者らは,心室性期外収縮(以下VPBと略す)を有し,HD中にその増悪を認め,その発生要因としてHD中の血中Ca濃度の増加が疑われ,Ca濃度の低い透析液に変更することにより,HD中の血中Ca濃度の増加を抑制し,かつVPBの発生を阻止することに成功した1例を経験したので,若干の文献的考察を加え報告する。
We present a case of 54 year old man, with chro-nic renal disease undergoing intermittent hemodialy-sis (HD). During HD the increase of serum Ca concentration and augmenting ventricular premature beats (VPBs) were observed.
It's speculated that the increase of serum Ca con-centration plays a part in the occurrence of VPBsand the dialysis fluid was changed from Kindaly 3 (Ca 3.5 mEq/l) to Kindaly 2 (Ca 2.5m Eq/l). In this manner we could succeed in suppressing the increase of serum Ca concentration, and preventing aggrava-tion of VPBs during HD. As the mechanisms lead-ing to the production of VPBs, it is conceivable that the increase of serum Ca concentration increasesintracellular Ca concentration which causes both triggered activity due to transient depolarization and reentry due to conduction delay and shortening refractory period. These observations indicated the necessity of attention to serum Ca concentration in hemodialysis patients with VPBs.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


