Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
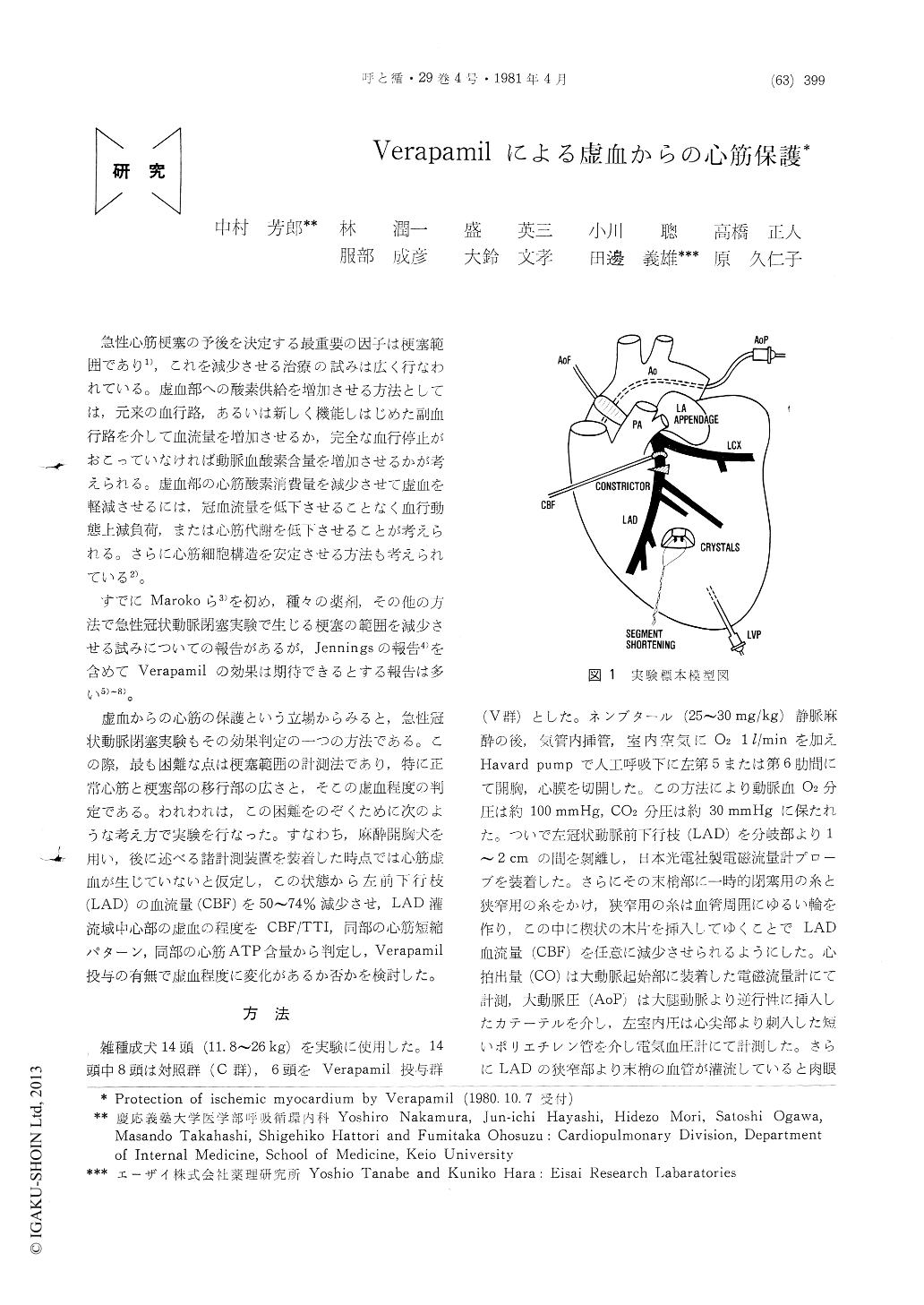
急性心筋梗塞の予後を決定する最重要の因子は梗塞範囲であり1),これを減少させる治療の試みは広く行なわれている。虚血部への酸素供給を増加させる方法としては,元来の血行路,あるいは新しく機能しはじめた副血行路を介して血流量を増加させるか,完全な血行停止がおこっていなければ動脈血酸素含量を増加させるかが考えられる。虚血部の心筋酸素消費量を減少させて虚血を軽減させるには,冠血流量を低下させることなく血行動態上減負荷,または心筋代謝を低下させることが考えられる。さらに心筋細胞構造を安定させる方法も考えられている2)。
すでにMarokoら3)を初め,種々の薬剤,その他の方法で急性冠状動脈閉塞実験で生じる梗塞の範囲を減少させる試みについての報告があるが,Jenningsの報告4)を含めてVerapamilの効果は期待できるとする報告は多い5)〜8)。
The protection of the ischemic myocardium following a reduction of left anterior descending blood flow (CBF) with Verapamil was examined in 14 open-chest dogs. CBF and aortic blood flow were measured by electromagnetic flowmeters. In the area which became ischemic by reduction in CBF, myocardial segment length was measured by a pair of small ultrasonic crystals implanted into the endocardial region. Five minutes after reduction of CBF, measurement of hemodynamics and biopsy of the ischemic myocardium for ATP analysis were performed.
In 8 cases of control group, 52.4±3.9% reduction of CBF resulted in a decrease aortic pressure and a reduction of segment shortening. Myocardial ATP content in the ischemic area was 2.963± 0.190μmol/g wet weight. Six cases, of which hemodynamic data were not different from control group's, were medicated by 0.25 mg/kg of Verapamil. Ten to eleven minutes after the injection, CBF was reduced by 57.3±4.1% of preinjection state. None of the hemodynamic data in ischemic state in Verapamil group was different significantly from the data of control group in ischemic state, however, pattern of myocardial shortening in ischemic area was less affected than that of control group. Myocardial ATP content in the ischemic area in Verapamil group was 3.25±0.354 which was significantly higher than that of control group.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


