Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
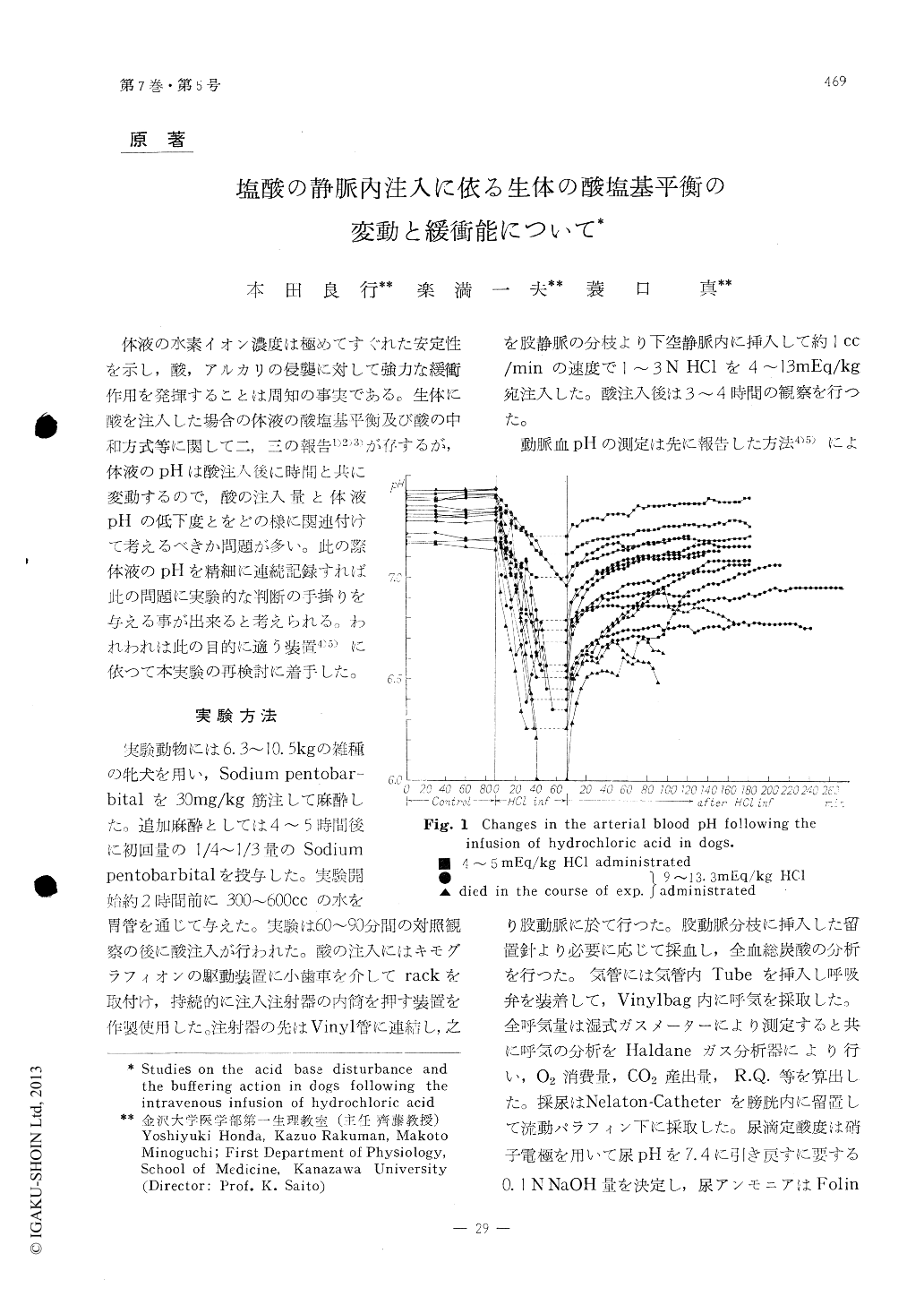
体液の水素イオン濃度は極めてすぐれた安定性を示し,酸,アルカリの侵襲に対して強力な緩衝作用を発揮することは周知の事実である。生体に酸を注入した場合の体液の酸塩基平衡及び酸の中和方式等に関して二,三の報告1)2)3)が存するが,体液のpHは酸注入後に時間と共に変動するので,酸の注入量と体液pHの低下度とをどの様に関連付けて考えるべきか問題が多い。此の際体液のpHを精細に連続記録すれば此の問題に実験的な判断の手掛りを与える事が出来ると考えられる。われわれは此の目的に適う装置4)5)に依つて本実験の再検討に着手した。
In order to investigate the acid base balance and the buffer capacity of the living body, measu-rements were performed on the blood pH, pulmonary CO2 elimination and urinary acid excretion of dogs after the intravenous injection of HCl of 4 to 13.3 mEq per Kg weight.
Following results were obtained:
1) After the intravenous injection of HC1, as shown in Fig. 1, the arterial pH reached an equi-librium in 2 to 3 hours.
The lowest equilibrium value of the arterial pH was, according to our observation, 6.8 which appeared to be the critical limit of the acidity of the blood for maintaining life.
2) Of the total amount of the acid injected, 44.2% was excreted through the lungs, 4.0 th-rough the kidneys and remaining 51.3 % was neutralized by the tissue substance in the body. The blood was found to contribute to the neutralization of about one seventh in amount of the acid inje-cted. (Table 1)
3) The buffer value of the body mass, (the amount of acid remaining neutralized in the body per Kg weight)/(the decrement of the arterial pH), increased gradually for 1 to 3 hours after the injection and attained a final equilibrium, the value of which was, on an average, 20 mEq/pH/Kg.(Fig. 6 and Table 2)
From this value, the total buffering capacity of the living body capable of responding to the acid introduced not only with neutralization but also with excretion was estimated, on an average, at 39.0 mEq/pH/Kg.
4) If it is admitted to estimate the buffering capacity of the human body from that of the dog, a human subject weighing 60 Kg will be able to tolerate about 1.4 Eq of the strong acid introduced into the body.
Copyright © 1959, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


