- 有料閲覧
- 文献概要
- 1ページ目
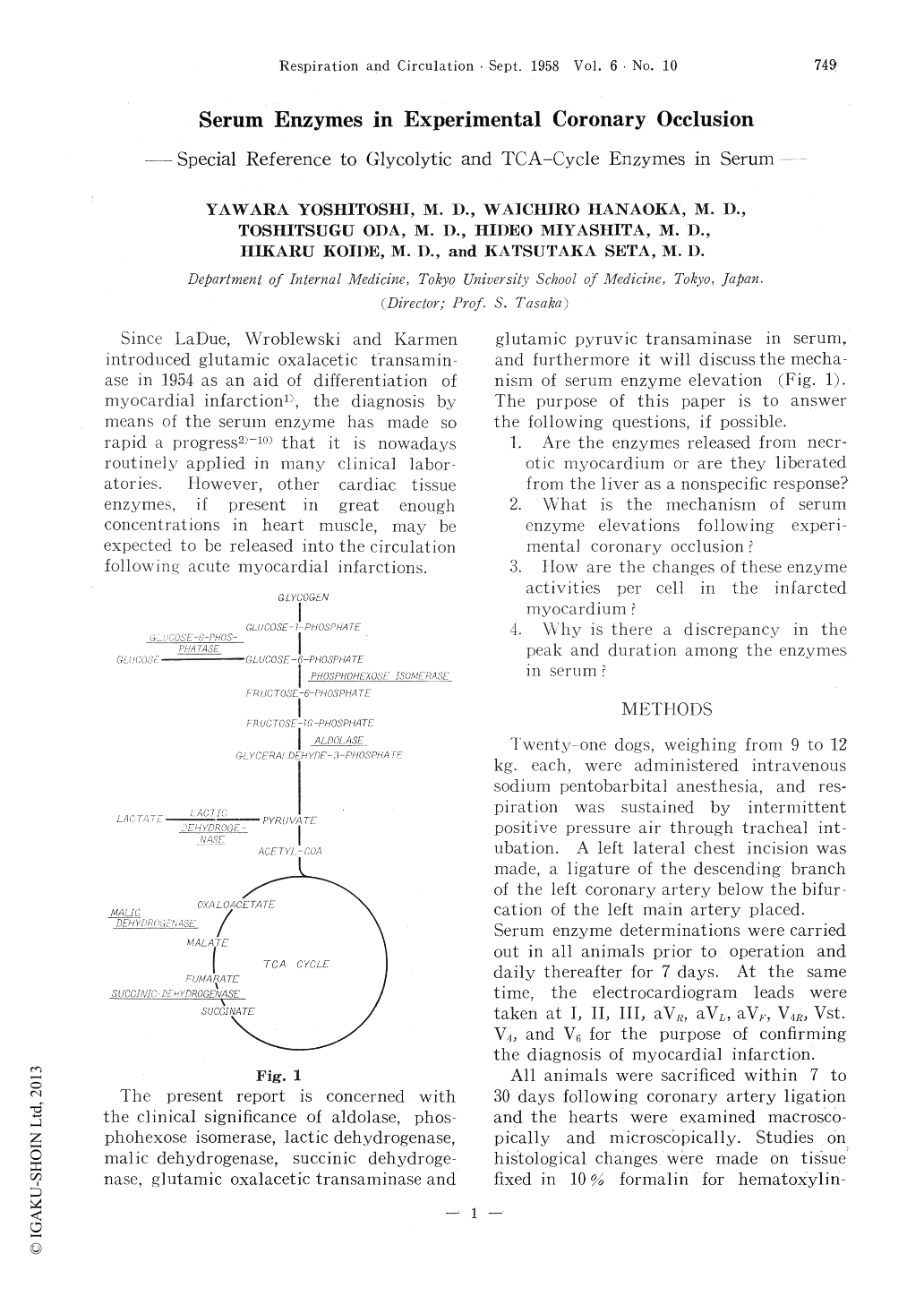
1. Serial determinations of aldolase, phosphohe—xose isomerase, lactic dehydrogenase, malicdehydrogenase, succinic dehydrogenase, glutamic oxalacetic transaminase and glutamic pyruvic transaminase in serum were carried out in ex—perimental coronary occlusion. Each enzyme level reached a peak 24 hours to fourth days and returned to normal levels two days to more than seven days following ligation of the coro—nary artery. And there is a discrepancy of the peak and duration between glycolytic enzymes and TCA-cycle enzymes in serum. Therefore the former is suitable for early diagnosis and the latter for later stage diagnosis of myocardial in—farction.
2. The fact that the activity of the enzymes in the coronary sinus blood is all higher than that in arterial blood, together with the observation that serum glucose—6—phosphatase activity does not increase in myocardial infarction at all, suggests that elevation of enzyme activities is due to the release of intracellular enzymes into blo—od stream.
3. The enzyme activities in infarcted heart muscle are decreased if based on wet weight, but they do not change at all if based on deoxyribonu—cleic acid.
4. The alterations of intracellular distribution of enzymes were observed in experimentally induced myocardial infarcts.
Copyright © 1958, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


