Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
潰瘍性大腸炎の外科治療の歴史
潰瘍性大腸炎の外科治療の歴史は19世紀の後半に始まり,最近30年間で目覚ましい進歩を遂げた.1948年Miller1)らが穿孔を起こした潰瘍性大腸炎患者に対し,一期的に部分的結腸切除と回腸瘻造設術を行ったところ,良好な結果が得られたことから,以後結腸切除,回腸瘻造設術が盛んに行われるようになった.Scarborough(1955)2),Brooke(1954)3),Cooper(1956)4),Goligher(1961)5),Waugh(1964)6),Daly(1968)7)らがその後数多くの良好な成績を報告し,この術式が確立された.この術式は一期的に結腸を切除するため,中毒症や蛋白漏出を防ぎ,全身状態の改善をもたらすということで有用である.しかし,この術式に対してもいろいろな見解が示され,回腸瘻造設と亜全結腸切除を一期的に行い,二期的に直腸切除を行うのがよいとするものや,一期的に全大腸切除と回腸瘻造設がよいとするものもみられた.回腸瘻術式の確立により潰瘍性大腸炎の治療は長足の進歩を遂げたが,反面永久人工肛門の障害が出現してきた.回腸瘻よりの排便のコントロールの困難性,回腸瘻周囲の皮膚びらん,回腸瘻よりの腸脱出などがこれらの障害として取り上げられた.この問題を解決すべく試みられたのがKockのcontinent ileostomy8)である.現在この術式は欧米で多く用いられ良好な成績を収めている.
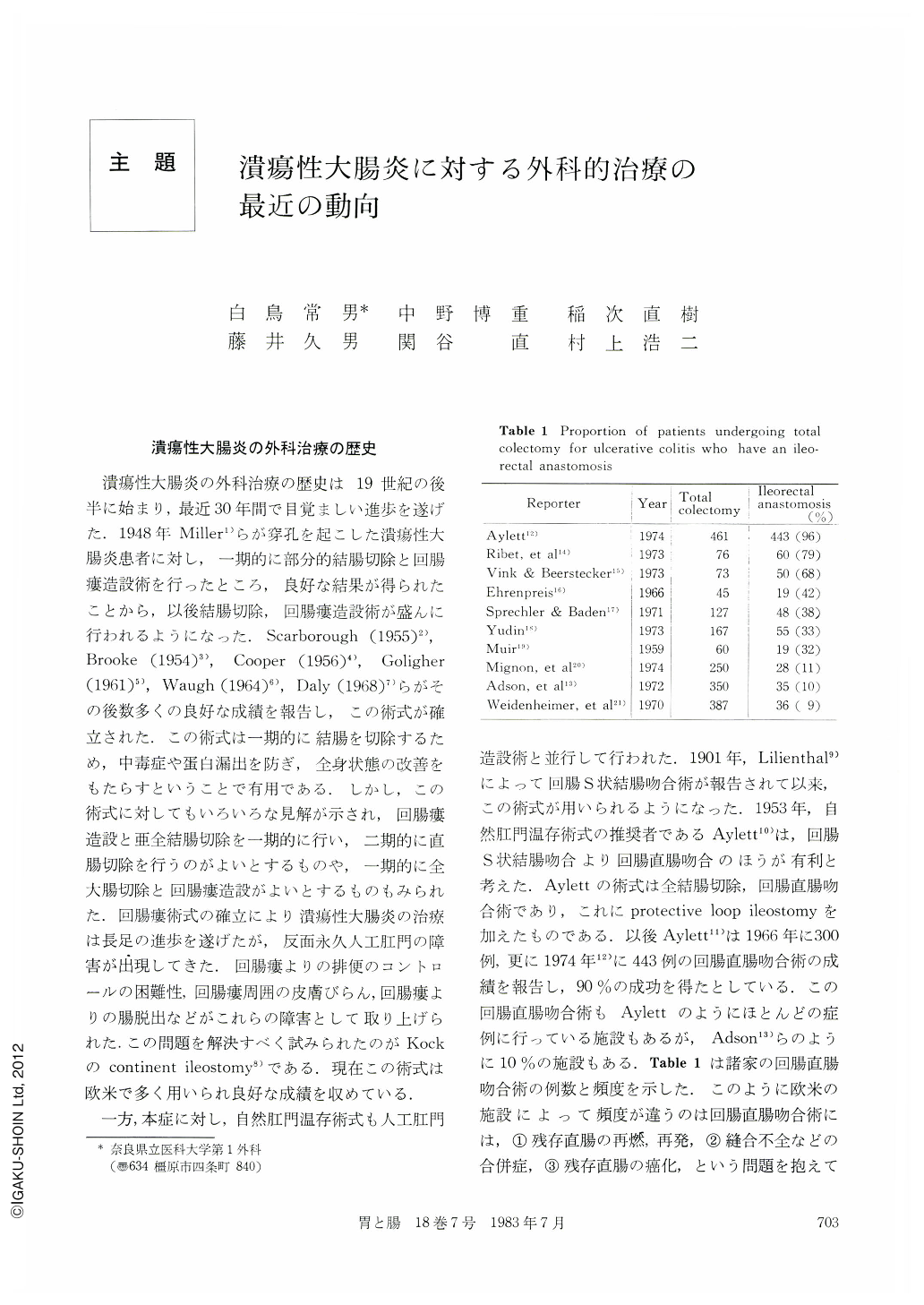
一方,本症に対し,自然肛門温存術式も人工肛門造設術と並行して行われた.1901年,Lilienthal9)によって回腸S状結腸吻合術が報告されて以来,この術式が用いられるようになった.1953年,自然肛門温存術式の推奨者であるAylett10)は,回腸S状結腸吻合より回腸直腸吻合のほうが有利と考えた.Aylettの術式は全結腸切除,回腸直腸吻合術であり,これにprotective loop ileostomyを加えたものである.以後Aylett11)は1966年に300例,更に1974年12)に443例の回腸直腸吻合術の成績を報告し,90%の成功を得たとしている.この回腸直腸吻合術もAylettのようにほとんどの症例に行っている施設もあるが,Adson13)らのように10%の施設もある.Table1は諸家の回腸直腸吻合術の例数と頻度を示した.このように欧米の施設によって頻度が違うのは回腸直腸吻合術には,①残存直腸の再燃,再発,②縫合不全などの合併症,③残存直腸の癌化,という問題を抱えていることによるようである.そこで近年上記の問題,特に直腸粘膜温存による再燃・再発・痛化の問題に対する解決策として直腸粘膜を抜去して回腸肛門吻合を行う術式が注目されてきている.この方法は1948年Ravitch22)により報告されたが,結果はあまり良好でなかった.次いでSoave23)がHirschsprung病の治療に直腸粘膜抜去法を行って良好な成績を上げたことにより,この手技を本症の術式に利用しようとして行われてきた.最近Martin24)は結腸を全摘し,直腸粘膜を肛門側から歯状線口側1cmまで温存し,残りの直腸粘膜を剝離,歯状線より1cm口側にて回腸肛門吻合を行い良好な成績を報告している.以後Peck25),Fonkalsrud26),Telender27),宇都宮28)らにより種々改良がなされ,症例数も増加しつつある.
Surgical treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC) in Japan has been advanced in the past thirty years. In general, for UC, there are two operative methods, which are the ileostomy after proctcolectomy and the sphincter-saving operation after colectomy. These procedures have been popularized in Europe and America, and many long term follow-up studies after these operations have been reported, making clear the merits of both methods and improving the demerits at the same time.
In Japan, however, it has been seldom to study about the result of these methods because of less cases and less follow-up studies of UC than in Europe or in America. In this paper, present status of the surgical treatments of UC in Japan is reported, based on the enquete data from the members of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research Committee, organized by Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare. Two hundreds sixty nine patients underwent surgical treatment. In classification according to the extent of the lesion, there were 179 cases of total colitis. According to the stage at operation, there were 191 cases of active stage and according to the severity at operation, there were 215 cases of moderate or severe stages, which were more than three-fourths of all.
Recurrence rate of 269 cases was 26% and operative mortality rate was 10%.
There were 124 cases of sphincter-saving operation, 143 cases of ileostomy or colostomy and 58 cases of ileostomy after colectomy.
In sphincter-saving operation, there were 58 cases of ileoproctomy. Forty three out of 58 cases were operated on the active stage, and in 58 cases, the operative mortality rate was 10% and the rate of leakage at anastomosis was 12%.
Among 58 patients, 52 are still alive and 24 are with relapsing and 19 in good control with conservative therapy.
From the collected data in Japan, the sphinctersaving operation for UC is increasing year by year, but we must follow-up much more operated cases of UC, considering the indication for sphincter-saving operation.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


