Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
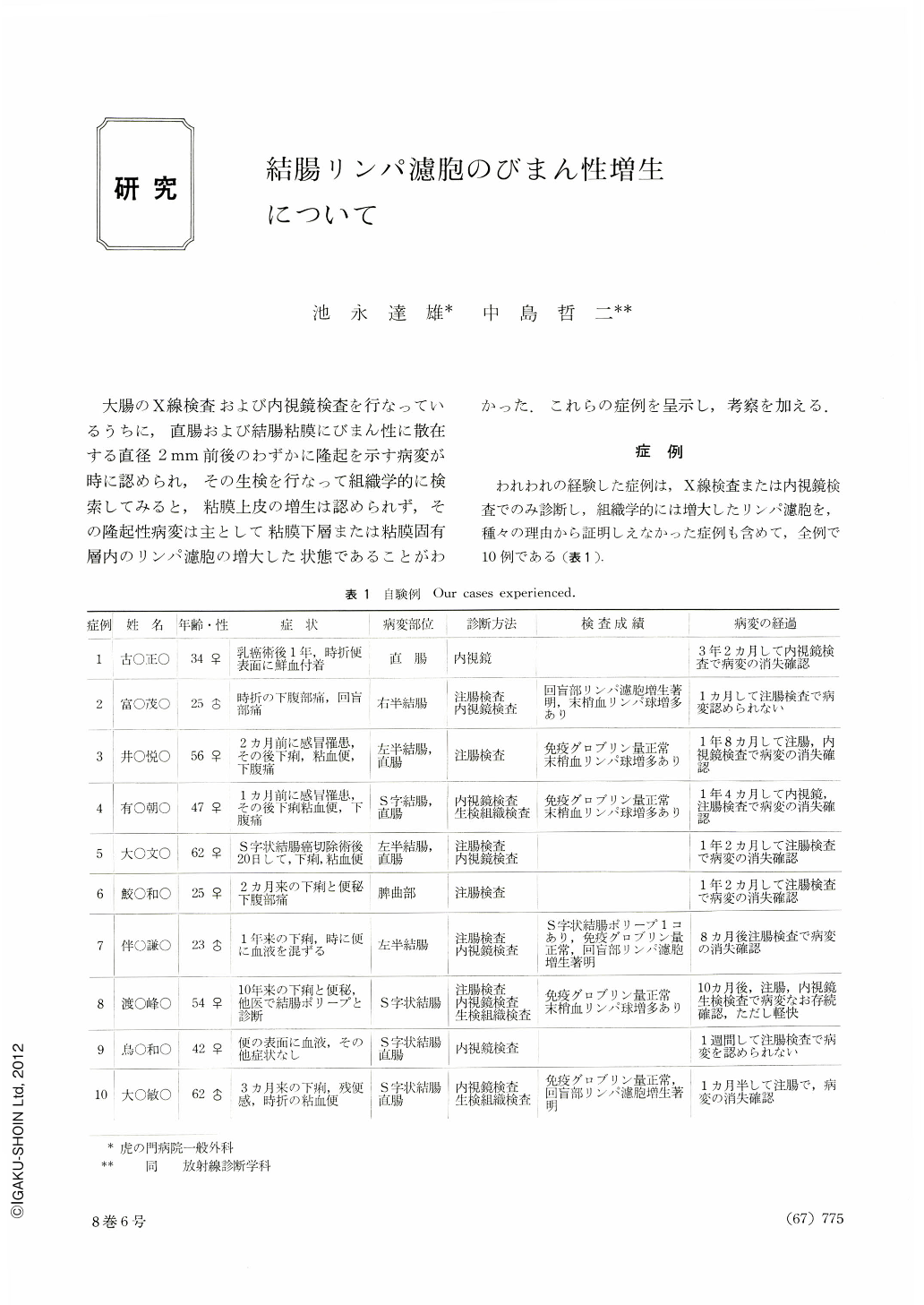
大腸のX線検査および内視鏡検査を行なっているうちに,直腸および結腸粘膜にびまん性に散在する直径2mm前後のわずかに隆起を示す病変が時に認められ,その生検を行なって組織学的に検索してみると,粘膜上皮の増生は認められず,その隆起性病変は主として粘膜下層または粘膜固有層内のリンパ濾胞の増大した状態であることがわかった.これらの症例を呈示し,考察を加える.
症例
われわれの経験した症例は,X線検査または内視鏡検査でのみ診断し,組織学的には増大したリンパ濾胞を,種々の理由から証明しえなかった症例も含めて,全例で10例である(表1).
While performing barium enema and endoscopic examinations of the colon and rectum, we happened to notice numerous, diffusely scattered and slightly elevated lesions of about 2 mm in diameter. Their biopsies revealed enlarged lymph follicles in the tunica submucosa or in the lamina propria mucosae without proliferation of the overlying mucosal epithelium.
We have experienced ten cases in total, three males and seven females, whose ages ranged from the third to seventh decade. Their previous and family history showed nothing relevant. They came to us with symptoms of bouts of diarrhea, unpleasant feelings in the lower abdomen, excretion of mucous stools occasionally tinged with a small amount of blood for a few months. Physical examinations revealed no superficial lymph node enlargement, no palpable liver or spleen. Hematological studies disclosed no pathological findings except relative lymphocytosis in peripheral blood in four cases. Laboratory studies on serum showed total protein levels of normal range and nothing suggestive of malabsorption syndrome or of protein losing gastroenteropathy.
Endoscopic examinations of the colon and rectum revealed numerous, uniform, slightly elevated and round or elliptical excrescences of about 2 mm in diameter with smooth, glistening and somewhat pale or pinkish surfaces scattered over the mucoua of the colon and rectum. Barium enema examinations showed numerous, uniform, round or elliptical and radiolucent foci of about 2~3 mm in diameter scattered throughout the entire colon or limited mainly to the left half of the colon. These foci resembled roentgenologically those described by Ichikawa in cases of lymph follicle hyperplasia of the terminal ileum.
Pathological examinations on biopsy specimens disclosed large lymph follicles with germinal centers in the tunica submucosa or within the lamina propria mucosae. Neither proliferation of the overlying mucosal epithelium nor its neoplastic changes were observed. Histological findings also resembled those observed in cases of lymph follicle hyperplasia of the terminal ileum described by Ichikawa.
As to the clinical courses, the symptoms disappeared usually within several months after their onsets and it has also been confirmed that the lesions disappeared without treatment in nine cases out of ten on whom reexaminations were performed from two months to three years and two months after their initial examinations. The lesions are considered to be transient.
The lesions should be differentiated from multiple polyposis, inflammatory polyposis of ulcerative colitis and tuberculosis of the colon, several types of lymphatic tissue hyperplasia of the alimentary tract such as lymph follicle hyperplasia of the terminal ileum by Ichikawa (nonsclerosing ileitis of Golden), dysgammaglobulinemia with nodular lymphoid hyperplasia by Hermans, benign lymphoma of the rectum, benign lymphoid polyps of the colon in children and so forth. Multiple lymphomatous polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract and multiple colonic polyps of leukemic origin should also be ruled out.
Copyright © 1973, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


