Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
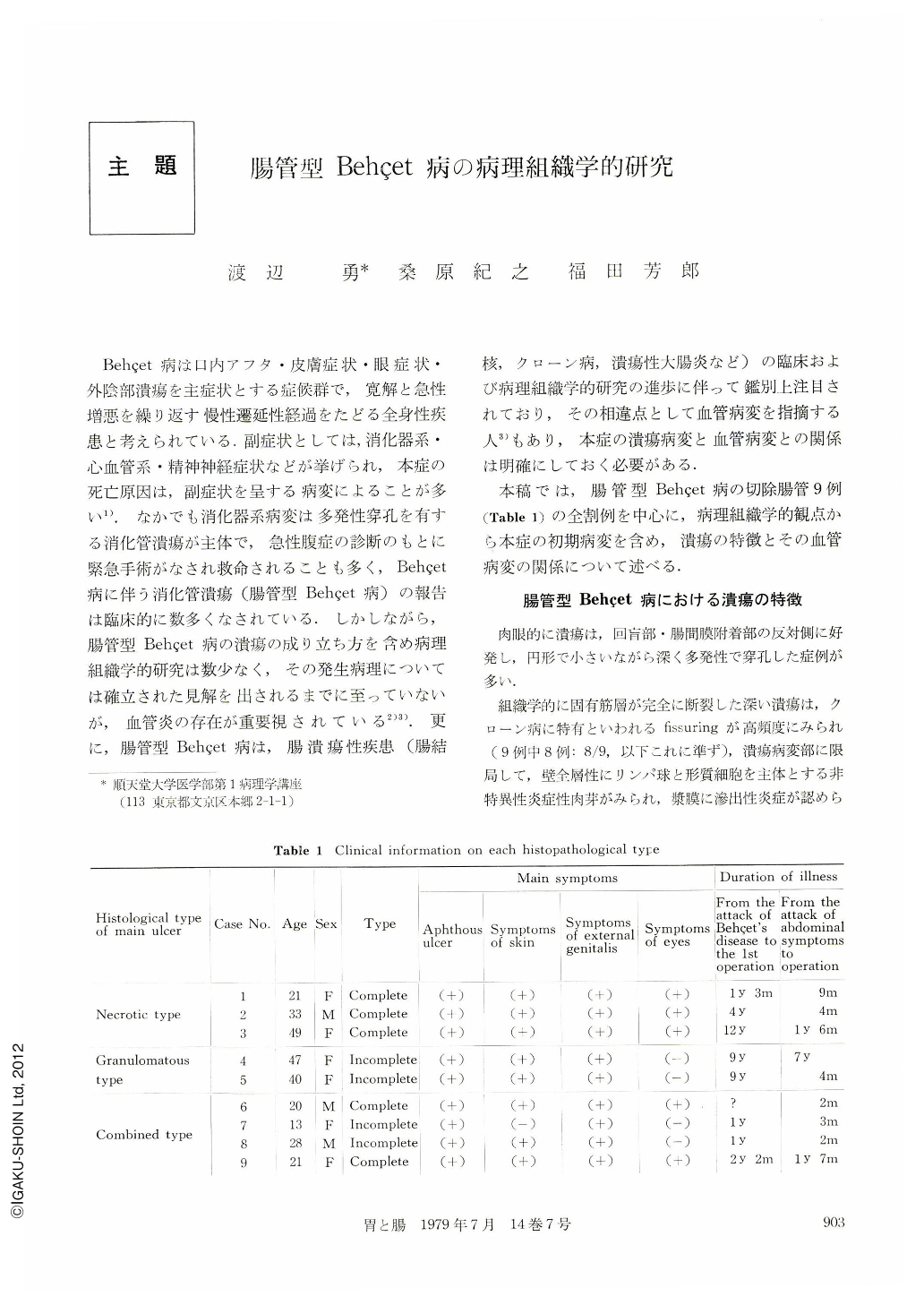
Behcet病は口内アフタ・皮膚症状・眼症状・外陰部潰瘍を主症状とする症候群で,寛解と急性増悪を繰り返す慢性遷延性経過をたどる全身性疾患と考えられている.副症状としては,消化器系・心血管系・精神神経症状などが挙げられ,本症の死亡原因は,副症状を呈する病変によることが多い1).なかでも消化器系病変は多発性穿孔を有する消化管潰瘍が主体で,急性腹症の診断のもとに緊急手術がなされ救命されることも多く,Behcet病に伴う消化管潰瘍(腸管型Behcet病)の報告は臨床的に数多くなされている.しかしながら,腸管型Behcet病の潰瘍の成り立ち方を含め病理組織学的研究は数少なく,その発生病理については確立された見解を出されるまでに至っていないが,血管炎の存在が重要視されている2)3).更に,腸管型Behcet病は,腸潰瘍性疾患(腸結核,クローン病,潰瘍性大腸炎など)の臨床および病理組織学的研究の進歩に伴って鑑別上注目されており,その相違点として血管病変を指摘する人3)もあり,本症の潰瘍病変と血管病変との関係は明確にしておく必要がある.
本稿では,腸管型Behcet病の切除腸管9例(Table 1)の全割例を中心に,病理組織学的観点から本症の初期病変を含め,潰瘍の特徴とその血管病変の関係について述べる.
Ulcerations in intestinal Bechet's disease are multiple, round, deep and located on the opposite side of mesentery in the ileocaecum. Histopathologically, they show fissuring and non-specific inflammatory reaction with weak collagen fiber reaction. Vascular changes have been reported by many authors. The histopathological mechanism of ulcer formation in intestinal Bechet's disease has been attributed to arteritis obliterans (Nagasu, K.), phlebitis (Nagao, K.), while some authors have questioned whether ulcers have a relationship to vascular disease (Smith, G.E., Sakamoto, K.) And Nagao reported that the presence of vasculitis was important in differentiating intestinal disease from other enterelcoses (tuberculosis of the intestine, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis). At the present, the mechanism of ulcer formation is not clearly understood.
Nine cases of intestinal Bechet's disease (Table 1) are studied histopathologically to clarify the characteristic findings of ulcerative and vascular changes and compared with tuberculosis of the intestine (nine cases), Crohn's disease (four cases) and ulcerative colitis (three cases) using the surgically resected intestinal materials.
Main ulcers (2cm~ Table 2) are histologically classified into three types; necrotic, granulomatous and combined. Ulcerating lesions of the necrotic type are seen in three cases, showing necrosis as a main change, no elevating muscular layer and no thickening of the intestinal wall (Fig. 2). Ulcerating lesions of the granulomatous type are seen in two cases and are composed of granulation tissue showing obvious elevating muscular layer and thickening of the wall (Fig. 4). Ulcerating lesions of the combined type are seen in four cases showing characteristic findings of both the necrotic and granulomatous types (Fig. 6). From a pathological point of view, it is belived that the necrotic-type ulcers are acute or subacute and granulomatous type are chronic. Furthermore, the macroscopic finding of the ulcers are compatible with the microscopic.
Small ulcers (~2cm, Table 3) are round or starlike with no fusion, multiple (Fig. 7) and are located on the small intestine (Fig. 11). Although they are less than 2cm in diameter, they are deep (Ul-Ⅱ, Ⅱs, Ⅲ, Ⅲs, Ⅳs). Pathologically, small ulcers are open lesions with fissuring and non-specificimflam matory (Fig. 8), while healing ulcers have weak collagen fiber reaction (Fig. 9).
Venous changes (Fig. 13) are intimal proliferation and thrombus formation. Arterial changes are intimal fibrous thickening. Venous changes (Fig. 12) are severer than arterial. Similar vascular changes are observed in the surrounding of the ulcers in Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and tuberculosis of the intestine. Vascular-change-dependent intestinal ulcers are seen in the surrounding area of the deep ulcers (Ul~Ⅲ over, Tables 4 and 5) in intestinal Behcet's disease. The size of the affected blood vessels range from 100 to 300μ in diameter (Fig. 14). Necrotic type with acute ulcers show slight venous changes as compared with those of the granulomatous and combined types with chronic ulcers, and no arterial changes (Table 4). Except for serosal venous changes, there are no vascular changes in the small ulcers (Ul-Ⅱ, Table 6) in intestinal Bechet's disease. Dilatation of the lymph vessels, venous congestion, edema and edema sclerosis in the submucosa of the area surrounding the ulcers and the non-ulcerative region (Fig. 10) are noted. Vascular changes have a close relation to the depth and duration of the ulceration, but none to the size.
In conclusion, vascular changes in the area surrounding the ulcers in intestinal Behcet's disease are believed to be secondary.
Copyright © 1979, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


