Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
胃の扁平上皮癌,類腺癌(Adenoacanthoma)は稀ながら報告をみ,その大部分は進行癌である.今回表層拡大型浸潤を示すpm癌で粘液細胞型腺癌(Adenocarcinoma mucocellulare)の癌巣中に扁平上皮癌の見られる1例を経験したので,文献的知見を加え報告する.
It is well-known that primary adenoacanthoma of the stomach is a rare disease, and fifty-eight case reported since Rösing (1895) were all “advanced carcinoma”.
Our present case shows primary adenoacanthoma in the so-called pm. cancer with superficial spreading type.
Case report: The patient was a 71-year-old woman and her chief complaint was swelling of the lymphnodes on both sides of her neck.
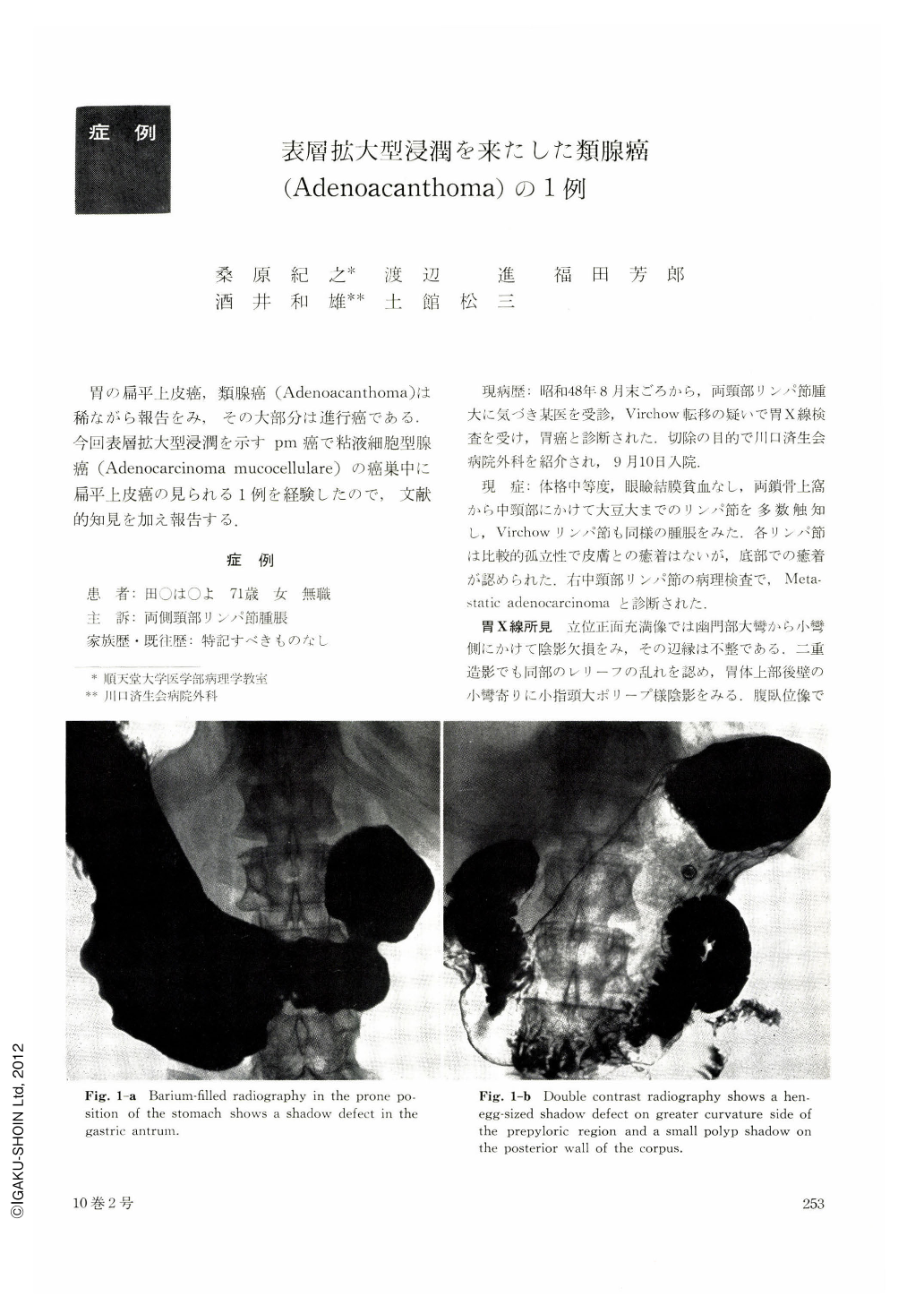
The biopsy of the lymphnode showed “metastatic adenocarcinoma” histologically, so that she underwent an upper-gastrointestinal tract series and endoscopic examinations which revealed carcinoma lesion in the posterior wall of the gastric body region near the greater curvature (suspected Borrmann Ⅲ). She underwent laparotomy and subtotal gastrectomy.
Pathological finding of the resected stomach:
Grossly, it showed so-called superficial spreading type carcinoma, extending to the whole antrum, mid-body of posterior wall and ulcer formation along the greater curvature.
Microscopically, as is shown in Fig. 3, carcinoma was composed of three different cell types, mucocellular adenocarcinoma mainly in the antrum and body regions with two small lesions of squamous cell carcinoma in the surface mucosal layer and muconodular adenocarcinoma along the greater curvature.
Most carcinoma were found in the submucosal layer, partly extending to muscle coat.
There was remarkable carcinoma invasion in the lymph vessels in the submucosal layer and several metastatic lymphnodes at the lesser curvature.
Conclusion: In this case, two lesions of squamous cell carcinoma were found in the superficial mucosal layer and the carcinomatous basal cells were connecting with and changing into the mucocellular adenocarcinoma in multiple foci of deep mucosal layer.
In addition, the epithelium surrounding the surface mucosa of squamous cell carcinoma was well-defined from the intestinal metaplasia of foveolar epithelium and atypical regeneration. For this reason, superficial epithelium cannot be considered as the origin of squamous cell carcinoma.
It was considered that this was the undifferentiated basal cell of squamous cell carcinoma originated from mucocellular adenocarcinoma cells.
Copyright © 1975, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


