Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
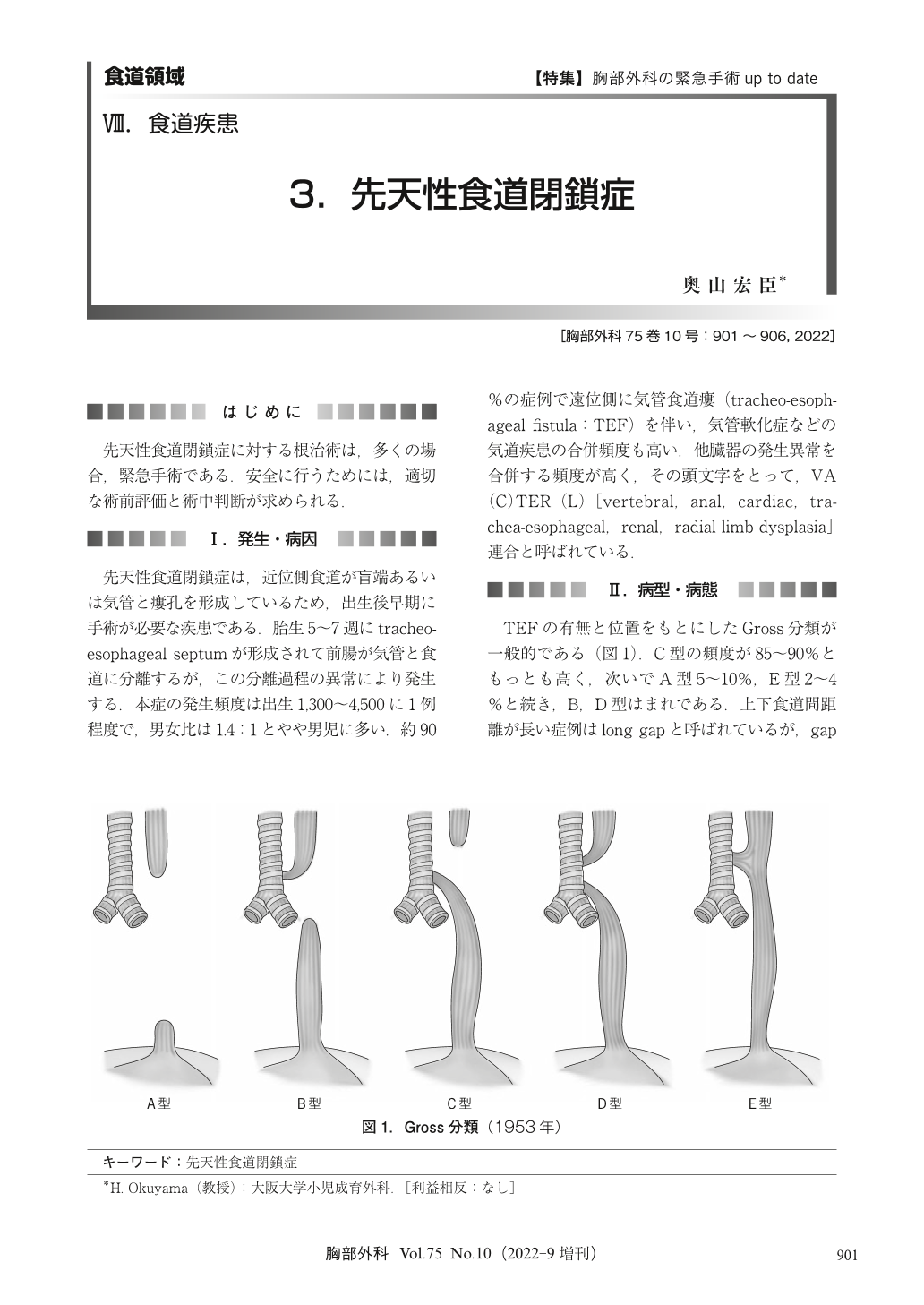
先天性食道閉鎖症に対する根治術は,多くの場合,緊急手術である.安全に行うためには,適切な術前評価と術中判断が求められる.
Congenital esophageal atresia, in which the proximal esophagus forms a blind end, results in respiratory failure due to aspiration of saliva. When accompanied by a distal tracheoesophageal fistula, increased intragastric pressure causes gastric juice to reflux into the trachea, resulting in severe pneumonia. Because of the above conditions, surgery should be performed early in life once the diagnosis is made. Conventionally, a two-stage radical operation was performed after gastrostomy. Recently, if the patient is in good general condition, a one-stage radical operation is preferred without gastrostomy.
The patient is positioned in the left lateral recumbent position. The tracheoesophageal fistula is double ligatured near the tracheal junction by extra-pleural approach. After dissection of the upper esophageal blind end, the upper and lower esophagus are anastomosed using a single-layer intermittent suture. In cases of a long gap in which one-stage anastomosis is difficult, two-stage esophageal anastomosis is performed. As the long-term prognosis of esophageal reconstruction using the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine in children is not always good, it is desirable to reconstruct the esophagus using autologous esophagus.
Recently, thoracoscopic repair has been performed for esophageal atresia, and its results have been reported to be comparable to those of open repair.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2022


