Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
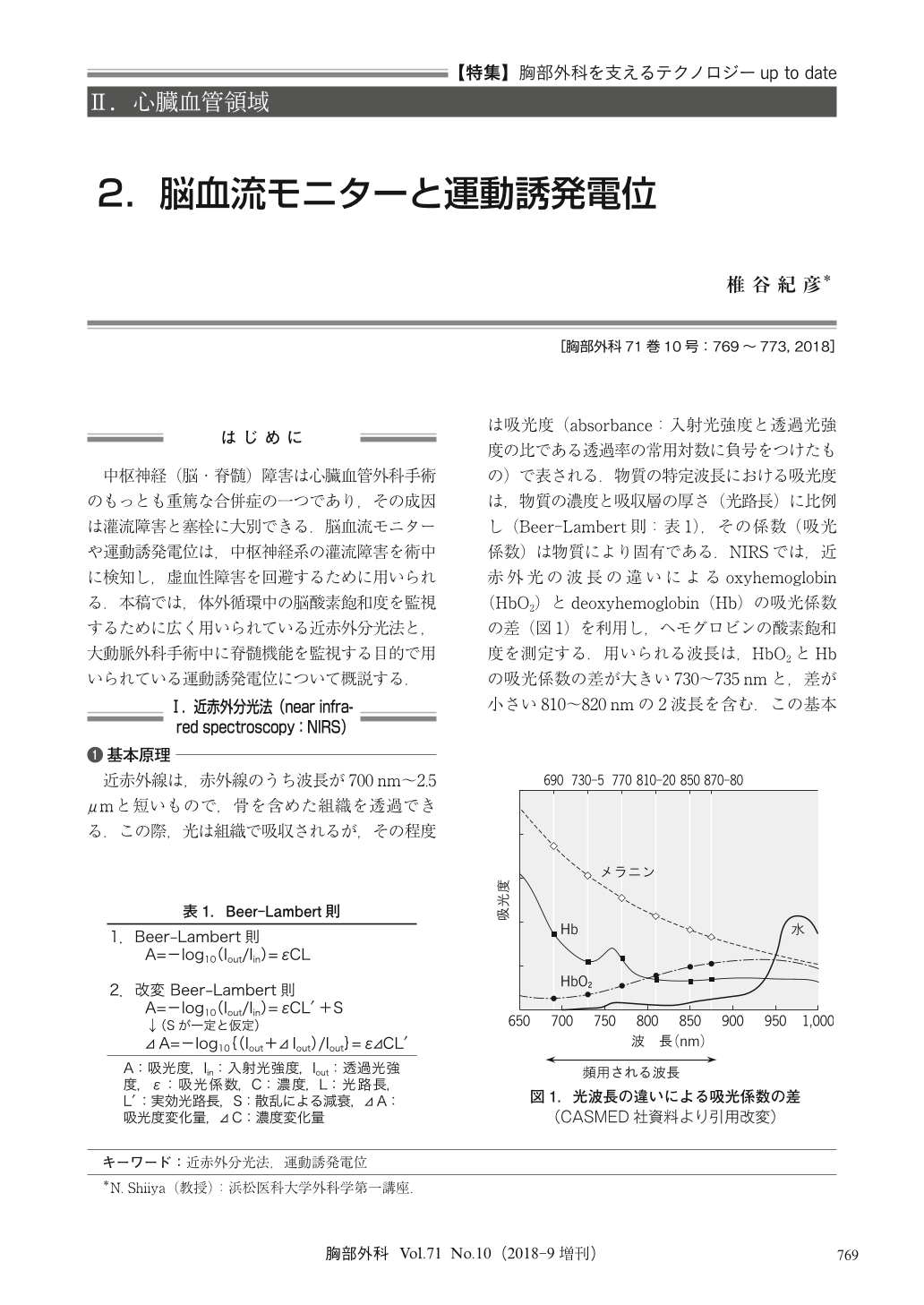
中枢神経(脳・脊髄)障害は心臓血管外科手術のもっとも重篤な合併症の一つであり,その成因は灌流障害と塞栓に大別できる.脳血流モニターや運動誘発電位は,中枢神経系の灌流障害を術中に検知し,虚血性障害を回避するために用いられる.本稿では,体外循環中の脳酸素飽和度を監視するために広く用いられている近赤外分光法と,大動脈外科手術中に脊髄機能を監視する目的で用いられている運動誘発電位について概説する.
Near infra-red spectroscopy (NIRS) and motor evoked potentials (MEP) have been used to monitor brain and spinal cord ischemia. NIRS calculates oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, based on the modified Beer-Lambert law. It correlates with the change in regional tissue blood flow. However, the technology is not matured enough for the measured value to be used as an index of tissue oxygenation, so that relative change should be carefully followed. Myogenic MEP has widely been used to monitor spinal cord ischemia, since the introduction of pulse train transcranial electrical stimulation. It evaluates motor pathways from the cortex to the muscle. Therefore it is influenced by non-spinal cord factors such as peripheral nerve ischemia. It is highly sensitive and shows changes in the early phase of spinal cord ischemia. On the other hand, its vulnerability to anesthesia requires special anesthetic consideration, and baseline amplitude fluctuation is common. Specificity is thus low, and the results should be interpreted together with the operative findings.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2018


