Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
Ⅰ.まえがき
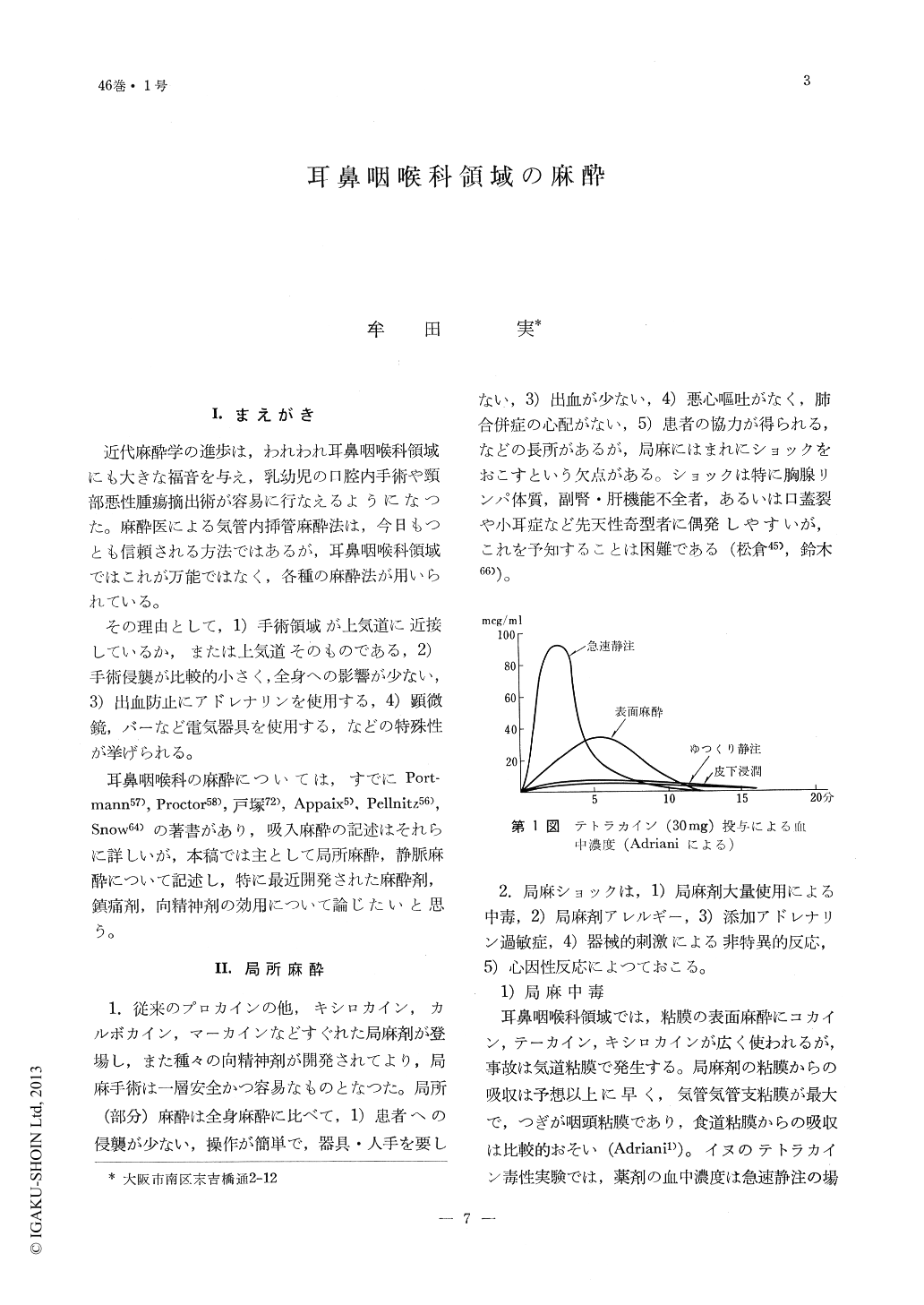
近代麻酔学の進歩は,われわれ耳鼻咽喉科領域にも大きな福音を与え,乳幼児の口腔内手術や頸部悪性腫瘍摘出術が容易に行なえるようになつた。麻酔医による気管内挿管麻酔法は,今日もつとも信頼される方法ではあるが,耳鼻咽喉科領域ではこれが万能ではなく,各種の麻酔法が用いられている。
その理由として,1)手術領域が上気道に近接しているか,または上気道そのものである,2)手術侵襲が比較的小さく,全身への影響が少ない,3)出血防止にアドレナリンを使用する,4)顕微鏡,バーなど電気器具を使用する,などの特殊性が挙げられる。
Principal techniques of anesthesia for ENT surgery are reviewed and discussed. Topical anesthesia in the pharynx and bronchiotracheal tree is not free from danger if safe dosage is exceeded. Lidocaine, at present the best possible anesthetic, is to be used below the maximum permissible dosis of 200mg. Toxic reactions associated with local anesthesia can be avoided by adequate premedication of vagolytic and psychotrophic drugs. For adult tonsilectomies local anesthesia is less hazardous with minimum bleeding and preferable over general anesthesia, because the latter has high mortality rate among the older age group.
To reduce the hemorrhage in the operative field, maintaining low venous pressure in the peripheral region is of utmost importance. In the head and neck region free venous drainage is more important than maintaining low systolic blood pressure. The use of α-blocker such as phenothiazine or butyrophenone derivatives is helpful in improving the peripheral circulation.
A comparative study of potentiated anesthesia, neuroleptanalgesia, propanidid, ketamine and acupuncture-anesthesia is composed of four elements constituting the anesthesia, that is hypnosis, analgesia, depression of reflexes and relaxation.
Copyright © 1974, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


