Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
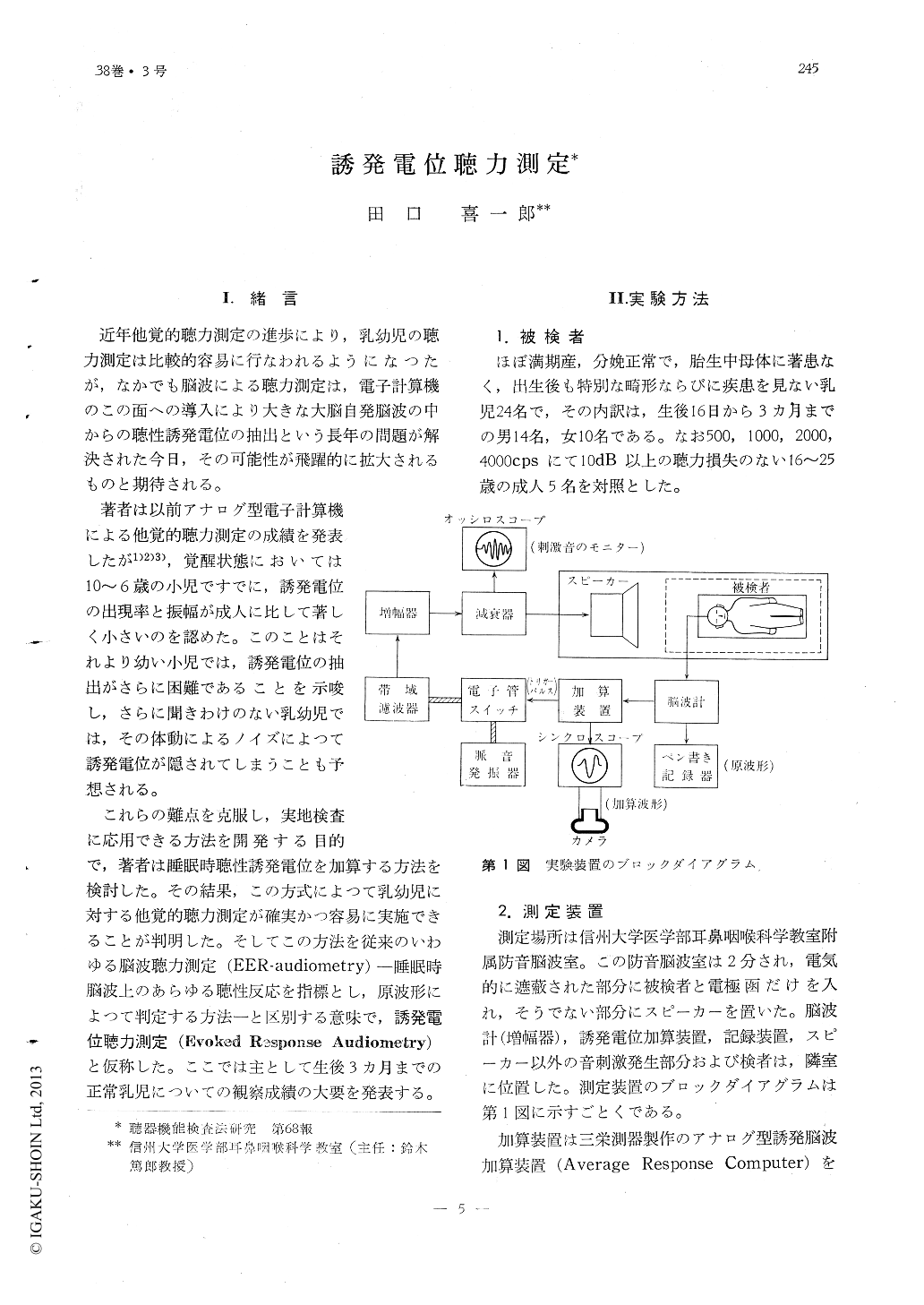
Ⅰ.緒言
近年他覚的聴力測定の進歩により,乳幼児の聴力測定は比較的容易に行なわれるようになつたが,なかでも脳波による聴力測定は,電子計算機のこの面への導入により大きな大脳自発脳波の中からの聴性誘発電位の抽出という長年の問題が解決された今日,その可能性が飛躍的に拡大されるものと期待される。
著者は以前アナログ型電子計算機による他覚的聴力測定の成績を発表したが1)2)3),覚醒状態においては10〜6歳の小児ですでに,誘発電位の出現率と振幅が成人に比して著しく小さいのを認めた。このことはそれより幼い小児では,誘発電位の抽出がさらに困難であることを示唆し,さらに聞きわけのない乳幼児では,その体動によるノイズによつて誘発電位が隠されてしまうことも予想される。
By means of electrical response computer electro-encephalographic reponse during sleep in infant children to sound stimulation was obtained with following results: There were triphasic waves noted namely, negative, positive and negative with corres-ponding peaks recorded at 270 300 msec, 500-520msec and 710 770msec.
The rate at which evoked response appea-red at 30dB SPL was 62.5%, at 50 dB SPL it was 95.8% and at 60dB SPL it was 100%.
The amplitude of the wave of evoked res-ponse was smaller than those that were ob-tained from adults but much larger than those taken from sucking infants in their full wa-king state.
This amplitude reached its maximum at the stage 3; and as the degree in which the depth of sleep increased the latent peak be-came proportionately delayed.
Copyright © 1966, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


