Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
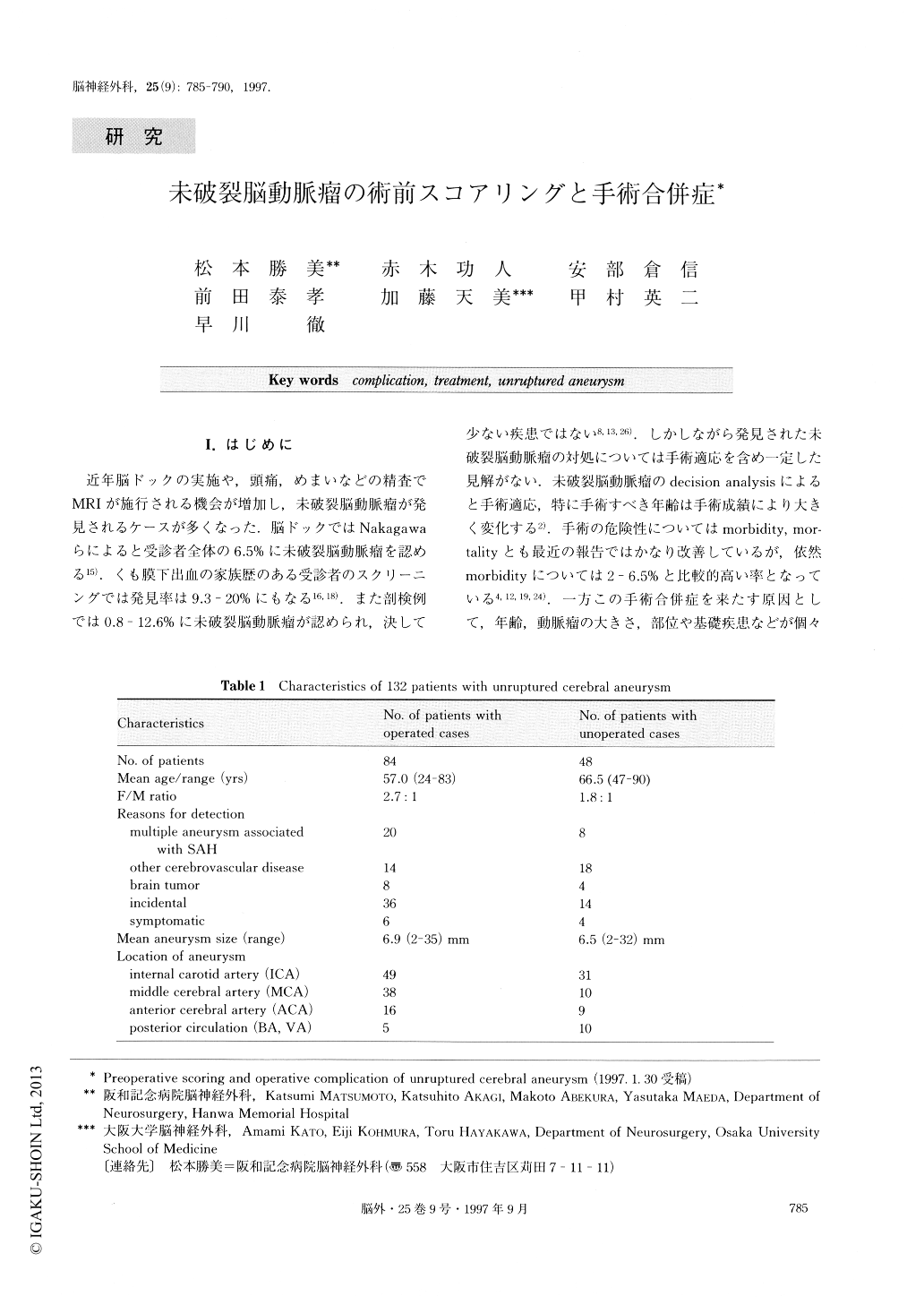
近年脳ドックの実施や,頭痛,めまいなどの精査でMRIが施行される機会が増加し,未破裂脳動脈瘤が発見されるケースが多くなった.脳ドックではNakagawaらによると受診者全体の6.5%に未破裂脳動脈瘤を認める15).くも膜下出血の家族歴のある受診者のスクリーニングでは発見率は9.3-20%にもなる16,18).また剖検例では0.8-12.6%に未破裂脳動脈瘤が認められ,決して少ない疾患ではない8,13,26).しかしながら発見された未破裂脳動脈瘤の対処については手術適応を含め一定した見解がない.未破裂脳動脈瘤のdecision analysisによると手術適応,特に手術すべき年齢は手術成績により大きく変化する2).手術の危険性についてはmorbidity,mor—talityとも最近の報告ではかなり改善しているが,依然morbidityについては2-6.5%と比較的高い率となっている4,12,19,24).一方この手術合併症を来たす原因として,年齢,動脈瘤の大きさ,部位や基礎疾患などが個々に検討されているが,実際はこれらの多くの要素が多方面で関与し合併症を誘引すると考えられる.今回,経過観察例,手術例および合併症を来たした症例について多方面の要素をスコアリングし,手術適応の決定ならびに手術合併症の予測が可能かどうかをretrospectiveに検討した.
Low risk of mortality and morbidity are necessary pre-conditions for surgical treatment of unruptured cere-bral aneurysms. We assessed retrospectively 132 pa-tients with angiographically confirmed cerebral aneurysms using an unruptured aneurysm score. Among them, 84 patients were treated surgically. The score consists of the sum of scores for the following factors: associated disease (none: 0, one: 1, two or more: 2); aneurysm size (below 14mm: 0,15- 24mm: 1, 25mm or more: 2); location (anterior cir-culation: 0, carotid cave: 1, posterior circulation: 2); and multiplicity (single: 0, two or more: 1). Eleven patients had complications and the morbidity rate in-cluding asymptomatic lesions was 13.1%. Five patients had permanent neurologic deficits (final morbidity rate 5.9%). The majority of patients with scores less than 1 underwent operations and the morbidity rate was low, whereas patients with scores between 2 and 4 had a higher morbidity rate. Preoperative scoring is useful for predicting surgical risks associated with unruptured cerebral aneurysm.
Copyright © 1997, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


