Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
一般に硬膜動静脈瘻(以下dural AVF)の症状として血管性雑音,頭蓋内圧亢進症状や脳内出血などが知られている11)が,痴呆は極めて稀である.こうした痴呆は治療により改善できることから,treatable dementiaとして最近注目を浴びている12).今回われわれは,記銘力の障害を主徴とし,失認,計算力の低下などの痴呆症状で急性に発症したdural AVFの1例を経験したので,病態メカニズムや責任病巣を中心に,若干の文献的考察を加えて報告する.
We report here a unique case of acute-onset dementia caused by a posterior fossa dural arteriovenous fistula (AVF), which was successfully treated by surgical re-section of the isolated transverse-sigmoid sinus com-bined with endovascular procedures.
A 70-year-old female was admitted to our hospital with acute-onset dementia and pulsatile tinnitus on the left side. CT scan revealed a low-density area in the parieto-temporal region. Cerebral angiography revealed a dural AVF of the transverse-sigmoid sinus with re-trograde drainage into cerebral cortical veins. After transarterial endovascular embolization of the dural AVF, a xenon-CT scan revealed increased cerebral blood flow. Four months postoperatively, however, she was admitted to our hospital again with seizure and aphasia due to recanalizaion of the dural AVF. After trans-arterial embolization, transvenous embolization was attempted, but was unsuccessful due to inaccessi-bility of the isolated sinus segment. Since this patient could not be cured by endovascular embolization, an open surgical resection of the isolated sinus segment was performed. Following this, CT scans revealed that the low density area present on the first admission had disappeared. The patient's dementia resolved postoper-atively.
We discuss the pathophysiological mechanism by which venous ischemia due to dural AVF can cause re-versible dementia.
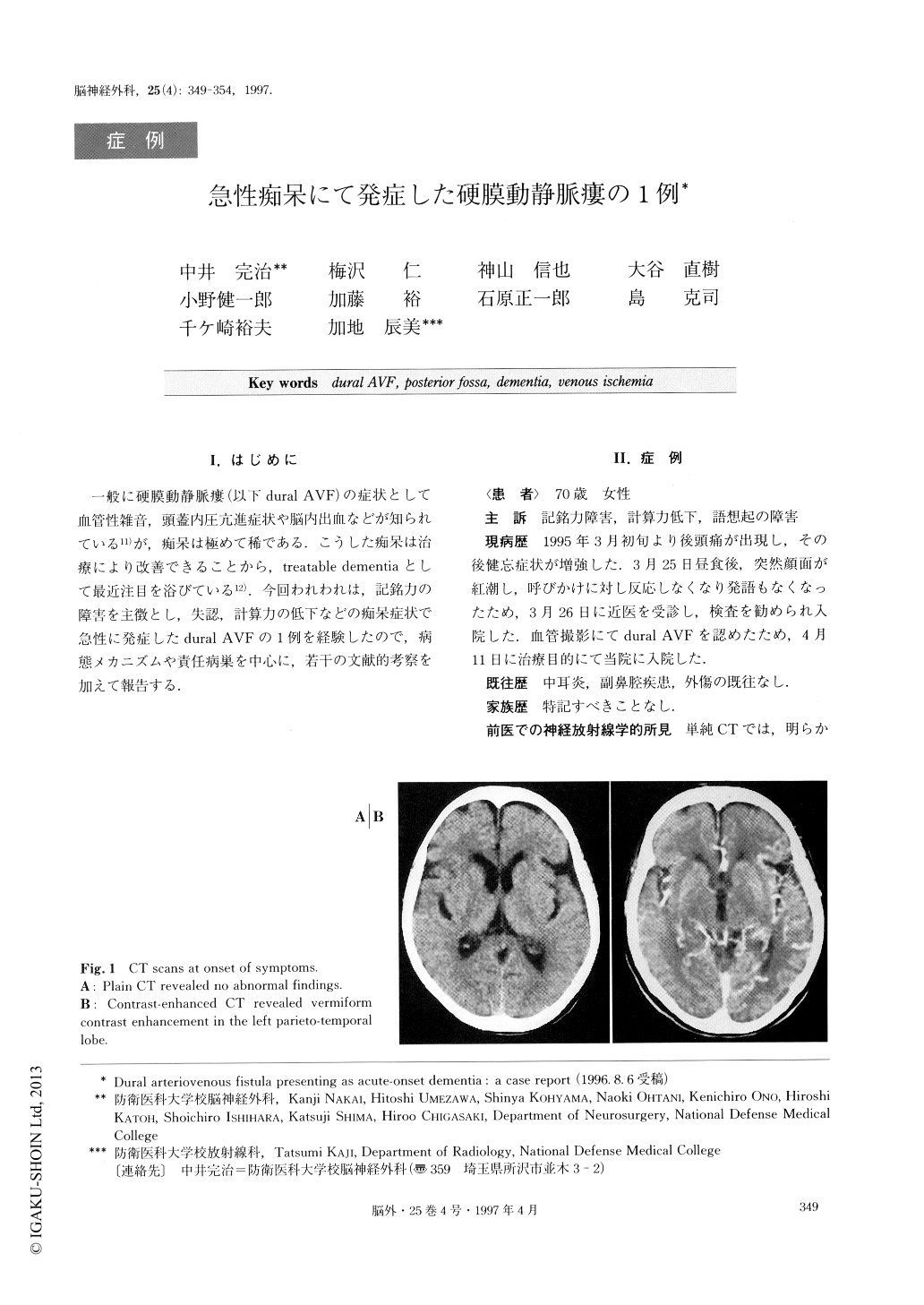
Copyright © 1997, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


