Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
本邦においては結核罹患率の低下に伴い,脳内結核腫は稀な疾患となってきたが,われわれは治療に難渋した多発性脳内結核腫の1例を経験したので,文献的考察を加え報告する.
A 48-year-old woman complained of fever, headache and nausea in October, 1994. Because polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was positive for mycobacterium tuber-culosis in her cerebrospinal fluid, she was administered anti-tuberculous drugs. Steroid hormone was also admi-nistered for her symptoms of intracranial hypertension. However, multiple intracerebral masses appeared on CT and MRI 2 months later, and have increased in number and size. Cessation of the steroid homone was impossible as her intracranial hypertension had been deteriorated. She was transferred to our clinic on Octo-ber 23, 1995. On neurological examination she was drowsy and showed papilledema, weakness of bilateral lower extre-mities, left cerebellar sign, and bilateral Babinski's re-flexes. Enhanced CT and MRI revealed multi-locular le-sions in the right fronto-temporal, left temporal and left cerebellar regions. On November 7,1995 she was oper-ated on. Right fronto-temporal and left cerebellar mas-ses were partially removed. Pathological examination and PCR of the surgical specimens demonstrated tuber-culoma.
Postoperatively, her consciousness disturbance im-proved and the residual tuberculomas decreased in size under the influence of anti-tuberculous drugs and cessa-tion of the use of steroid hormone. Recently, tuberculosis is common neither in Japan nor in Western countries. Intracerebral tuberculoma is also very rare. The tuberculosis in our patient with multiple intracerebral tuberculomas resistant to anti-tuberculous drugs was thought to have been induced by decreased resistance to the infection due to the administration of the steroid hormone.
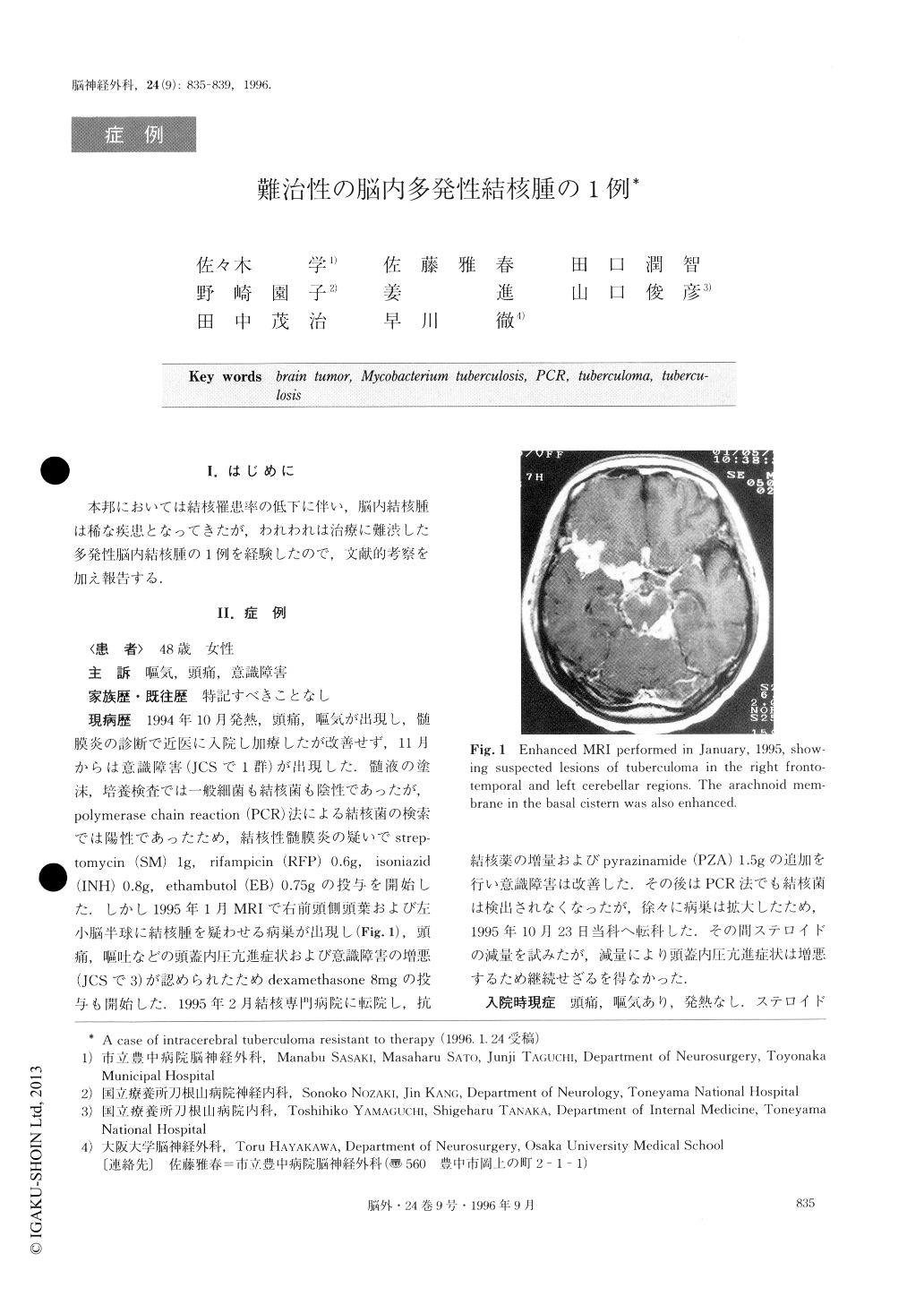
Copyright © 1996, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


