Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
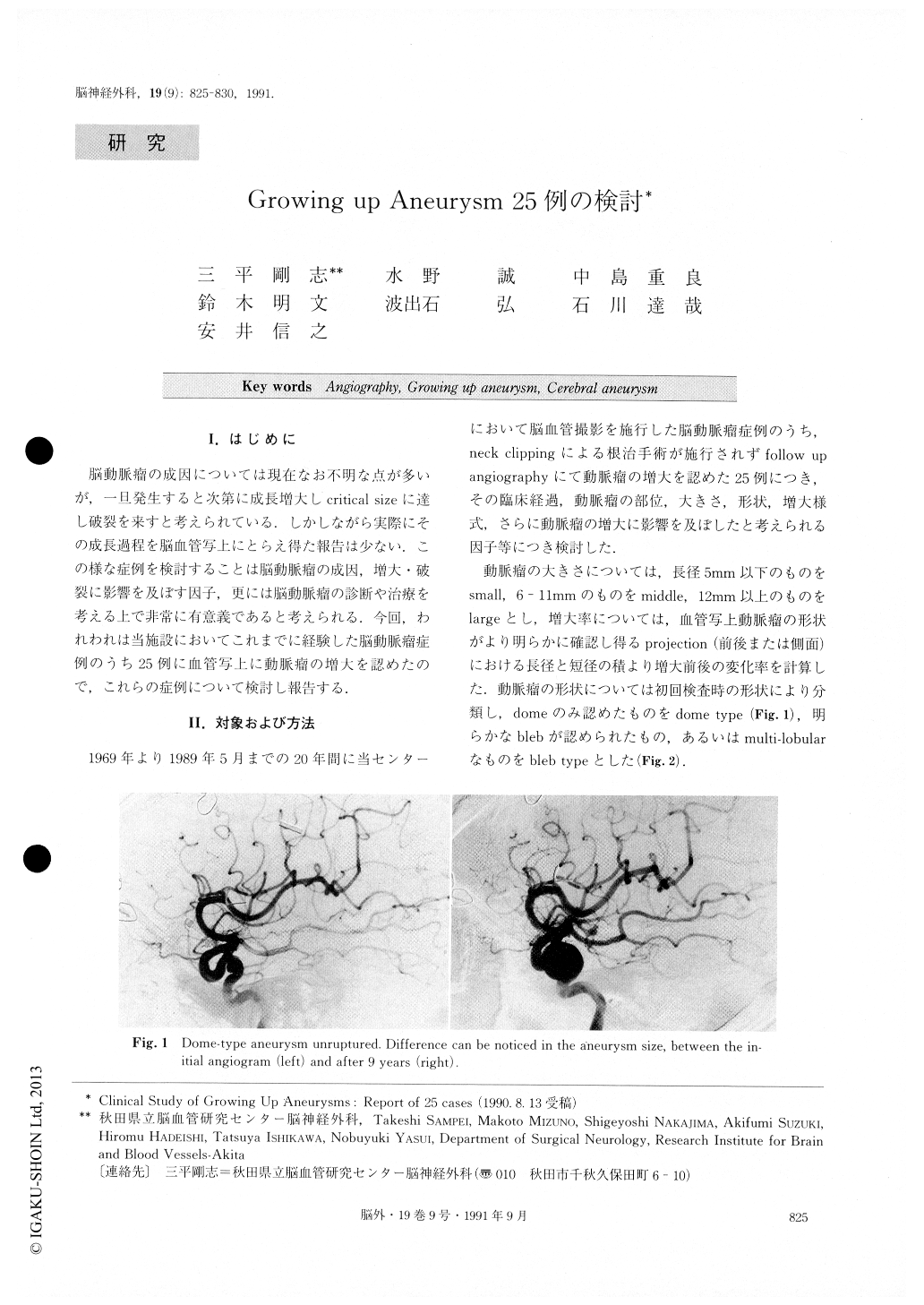
脳動脈瘤の成因については現在なお不明な点が多いが,一旦発生すると次第に成長増大しcritical sizeに達し破裂を来すと考えられている.しかしながら実際にその成長過程を脳血管写上にとらえ得た報告は少ない.この様な症例を検討することは脳動脈瘤の成因,増大・破裂に影響を及ぼす因子,更には脳動脈瘤の診断や治療を考える上で非常に有意義であると考えられる.今回,われわれは当施設においてこれまでに経験した脳動脈瘤症例のうち25例に血管写上に動脈瘤の増大を認めたので,これらの症例について検討し報告する.
Abstract
Twenty-five cases of patients with growing up aneurysms are reported. Growth of the aneurysm was confirmed by repeated angiography within 1 month in 11 cases (short-term group), and for over 1 month in the other 14 cases (long-term group) following the ini-tial angiography. Clinical history, shape and growth pattern of aneurysms, as well as hemodynamic factors that effect the growth were investigated in each group. The aneurysms were classified according to the shape into dome-type (smooth contour) and bleb-type (irregular contour). In all cases of the short-term group, the first angiography was performed because of rupture of the aneurysm. In this group, 4 cases bled again because of enlargement or the development of an aneurysmal bleb. Growth rate and the initial size of the aneurysm did not effect the potential of re-rupture.
In the long-term group, 9 cases out of 14 (64.3%) had “non-ruptured aneurysm” at the time of first angiogra-phy. In the follow up, 5 cases were ruptured (two be-cause of re-bleeding and three for the first time) . In 3 out of these 5 cases, a bleb was demonstrated on initial angiography, and in another case, a bleb was demon-strated in follow-up angiography. Only one case rup-tured because of the growth of the aneurysmal dome. Most of the aneurysms that rupture, in the follow-up survey, showed a larger growth rate in comparison with aneurysms that did not rupture. Many cases of this long-term group were associated with hypertension or vascular abnormalities which would effect the aneurysmal growth. Also, 11 cases of this group showed multiple aneurysms (8 of which had more than 3 aneurysms).
The results of this study suggest that there is a diffe-rent mechanism for aneurysmal growth according to whether the patient was in the short-term group or the long-term group. A ruptured aneurysm may change its size and shape every moment in its acute phase as is shown in this study in the short-term group. The most important factors that influence the growth and risk of rupture of aneurysms in the long-term group are the in-itial shape, hemodynamic factors, and also the predis-position of the patients.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


