Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
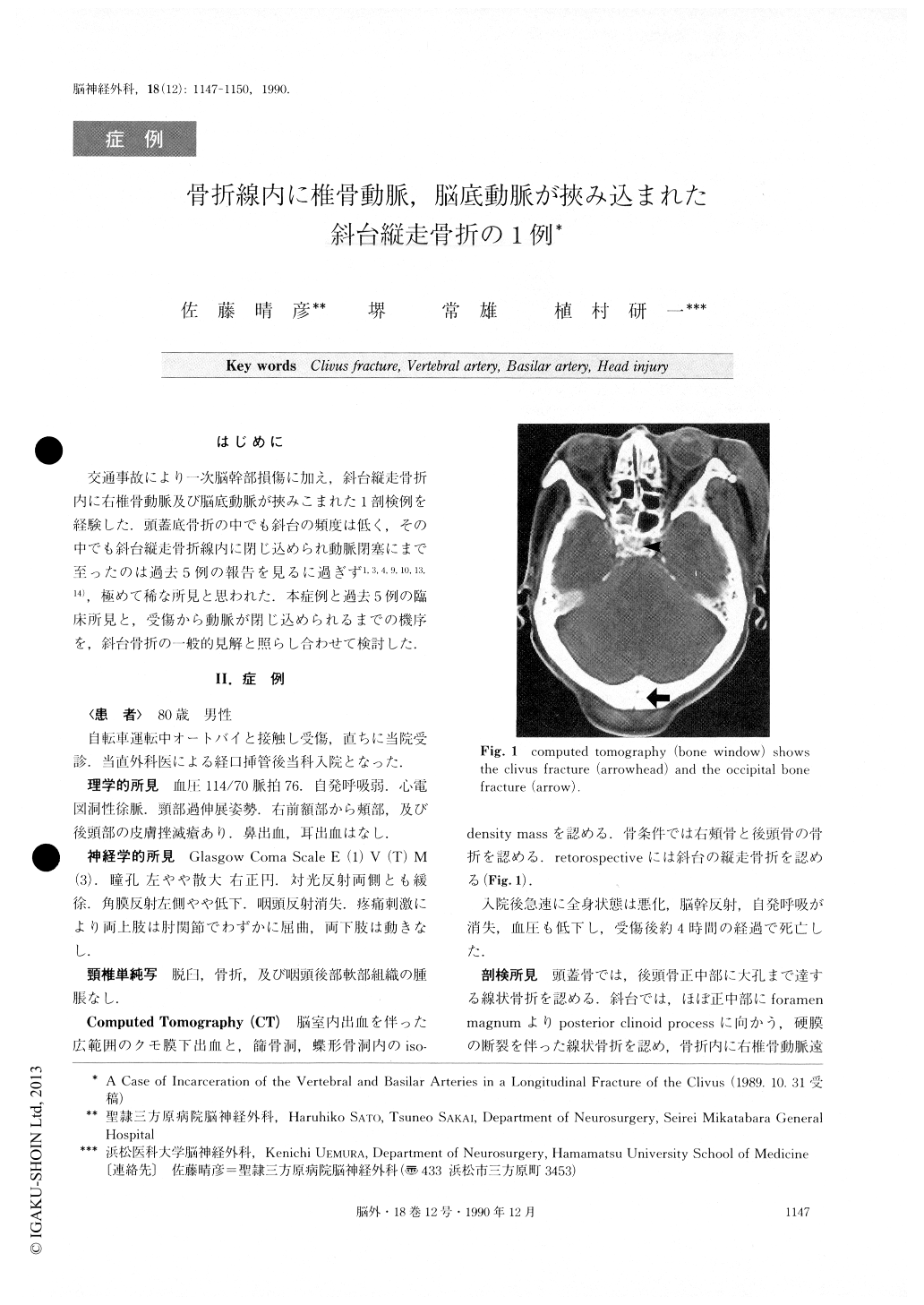
交通事故により一次脳幹部損傷に加え,斜台縦走骨折内に右椎骨動脈及び脳底動脈が挾みこまれた1剖検例を経験した.頭蓋底骨折の中でも斜台の頻度は低く,その中でも斜台縦走骨折線内に閉じ込められ動脈閉塞にまで至ったのは過去5例の報告を見るに過ぎず1,3,4,9,10,13,14),極めて稀な所見と思われた.本症例と過去5例の臨床所見と,受傷から動脈が閉じ込められるまでの機序を,斜台骨折の一般的見解と照らし合わせて検討した.
We report a case of incarceration of the right verte-bral and basilar arteries in a longitudinal fracture of the clivus.
A 80-year-old man was struck on the occiput in a traffic accident and was admitted to our hospital. He was in coma on admission. Neurological examination revealed that the left pupil was dilated, the light reflex was bilaterally sluggish, the left corneal reflex was ab-sent, and the pharyngeal reflex was absent. Computed tomography showed fractures in the occipital bone and clivus. His general condition rapidly deteriorated, and he died 4 hours after the injury. The autopsy revealed a longitudinal fracture of the clivus incarcerating the right vertebral artery together with the origin of the basilar artery. It also revealed primary brain stem injury.
We presented clinical features, mechanisms of the in-jury, and radiological findings for three types of clivus fracture ; longitudinal, transverse, and a fracture of the lower clivus extending into the occipital condyle. It is unusual to see incarceration of the basilar or the verte-bral artery in a longitudinal fracture of the clivus. We found only five reported cases. Each case presented a variety of brainstem dysfunctions. Three died of brain-stem infarction, and one died of aspiration pneumonia. The remaining patient is in a chronic vegetative state. In our case, the history and autopsy findings suggested that the patient died of the primary brainstem injury. We proposed two mechanisms of incarceration ; one is a midline occipital blow as in our case, and the other is axially transmitted force.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


