Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
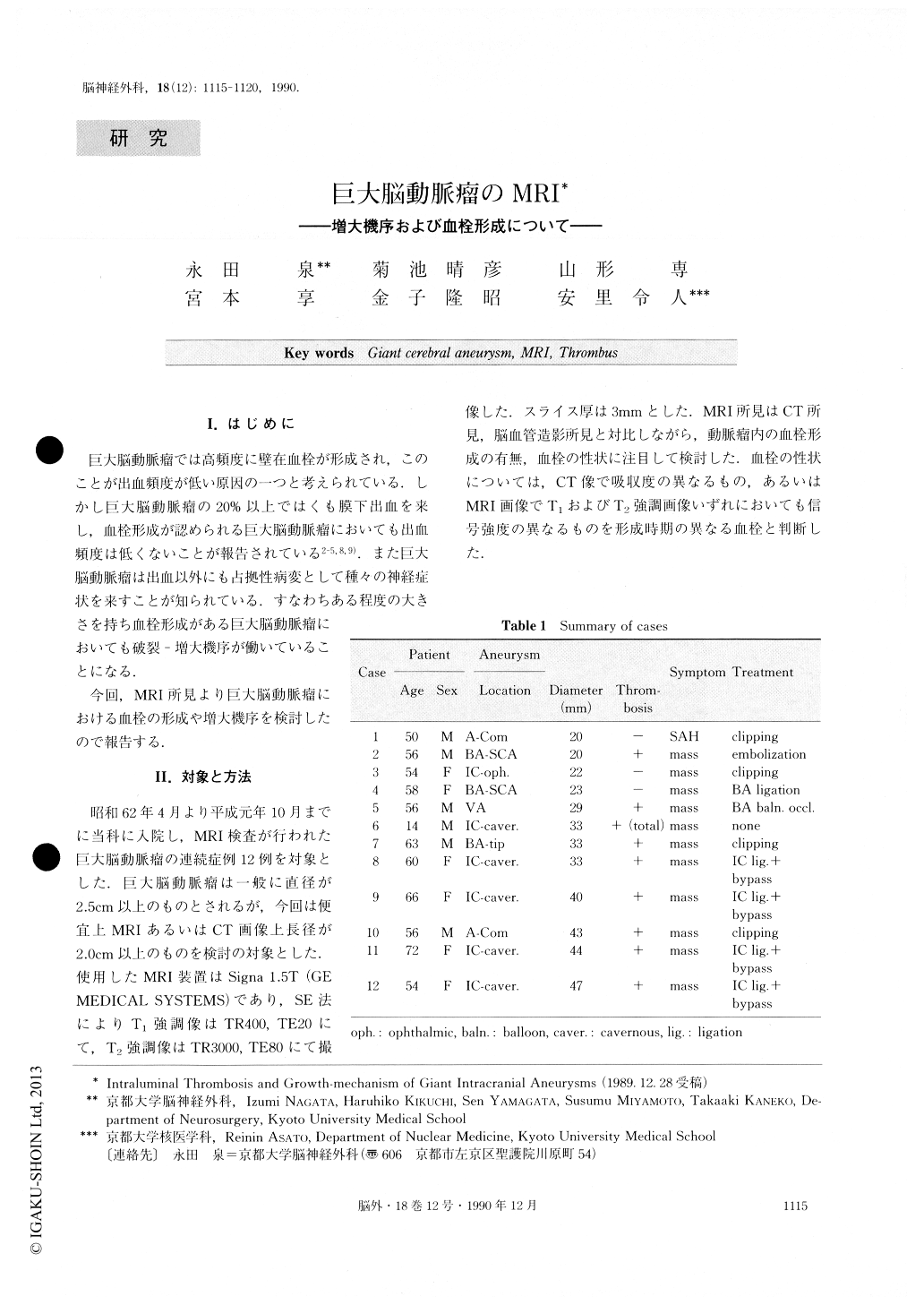
巨大脳動脈瘤では高頻度に壁在血栓が形成され,このことが出血頻度が低い原因の一つと考えられている.しかし巨大脳動脈瘤の20%以上ではくも膜下出血を来し,血栓形成が認められるい巨大脳動脈瘤においても出血頻度は低くないことが報告されている2-5,8,9).また巨大脳動脈瘤は出血以外にも占拠性病変として種々の神経症状を来すことが知られている.すなわちある程度の大きさを持ち血栓形成がある巨大脳動脈瘤においても破裂—増大機序が働いていることになる.
今回,MRI所見より巨大脳動脈瘤における血栓の形成や増大機序を検討したので報告する.
12 giant intracranial aneurysms were studied byMRI. Intraluminal thrombosis was observed in 9 aneurysms. Thrombosis was found more frequently in larger aneurysms. Thrombi were formed posteriorly or inferiorly in the lumen of 4 among 5 IC-cavernous aneurysms. Location of the neck of the aneurysms and stagnation of blood flow influenced by gravity may be causative factors determining the location of thrombi. In 6 aneurysms intraluminal thrombi were in-homogeneous on MRI, suggesting that the thrombi had been formed at different times. New thrombi were formed between the aneurysmal wall and the old thrombus in 3 cases. Dissection of the aneurysmal wall by residual blood flow in the lumen or hemorrhage in the aneurysmal wall may he one of the growth mecha-nisms of giant intracranial aneurysms.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


