Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
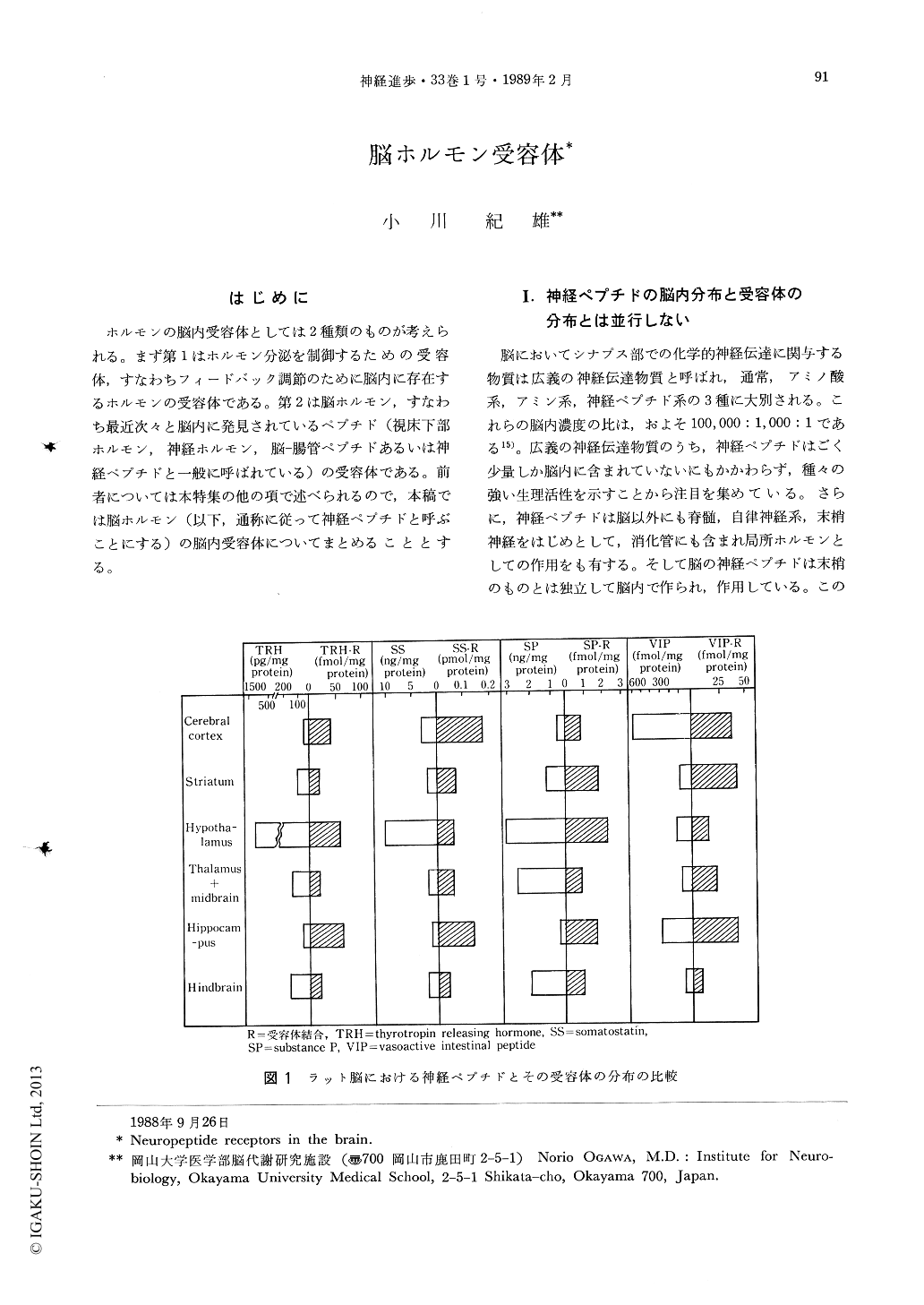
ホルモンの脳内受容体としては2種類のものが考えられる。まず第1はホルモン分泌を制御するための受容体,すなわちフィードバック調節のために脳内に存在するホルモンの受容体である。第2は脳ホルモン,すなわち最近次々と脳内に発見されているペプチド(視床下部ホルモン,神経ホルモン,脳—腸管ペプチドあるいは神経ペプチドと一般に呼ばれている)の受容体である。前者については本特集の他の項で述べられるので,本稿では脳ホルモン(以下,通称に従って神経ペプチドと呼ぶことにする)の脳内受容体についてまとめることとする。
Though the definition of brain hormones varies, they usually indicate neuropeptides or brain-gut peptides. Neuropeptides in the brain account for only 1/1,000 of biogenic amines but show marked physiological activity. The distribution of neuropeptides in the brain is not in parallel with that of their receptors with a 40-fold difference being observed in some areas. In biochemical studies of the brain, the amount of neuropeptides have been conventionally measured in an attempt to interpret all brain functions. However, the content of neuropeptides is the sum of their synthesis, storage and release, and there is a possibility that extremely small increases or decreases in their release are overlooked because of large amounts in storage. On the other hand, receptors are localized only in the synaptic area and sensitively reflect functional changes in this area. When release of a neuropeptide increases, the number of receptors decreases (down-regulation), whereas with long-term decreases in release, the number of receptors increases (up-regulation). Therefore, simultaneous measurements of the concentration of neuropeptides and their receptor bindings may provide more accurate information. Since the measurement of receptor binding more sensitively reflects changes in pathophysiological status and those due to drugs, it is essential for evaluation of brain function. In recent years, not only receptors but also the second messenger system has been actively studied. The second messenger system for neuropeptides includes, as with other neurotransmitters, the adenylate cyclase system and the inositol phospholipid system. Recently reciprocal regulation between neuropeptide receptors via the second messenger system has been demonstrated. In addition, reciprocal regulation between neuropeptide receptors and those of classical neurotransmitters have been shown. Interaction between receptors is, together with coexistence of neurotransmitters, an important theme to be solved.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


