Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
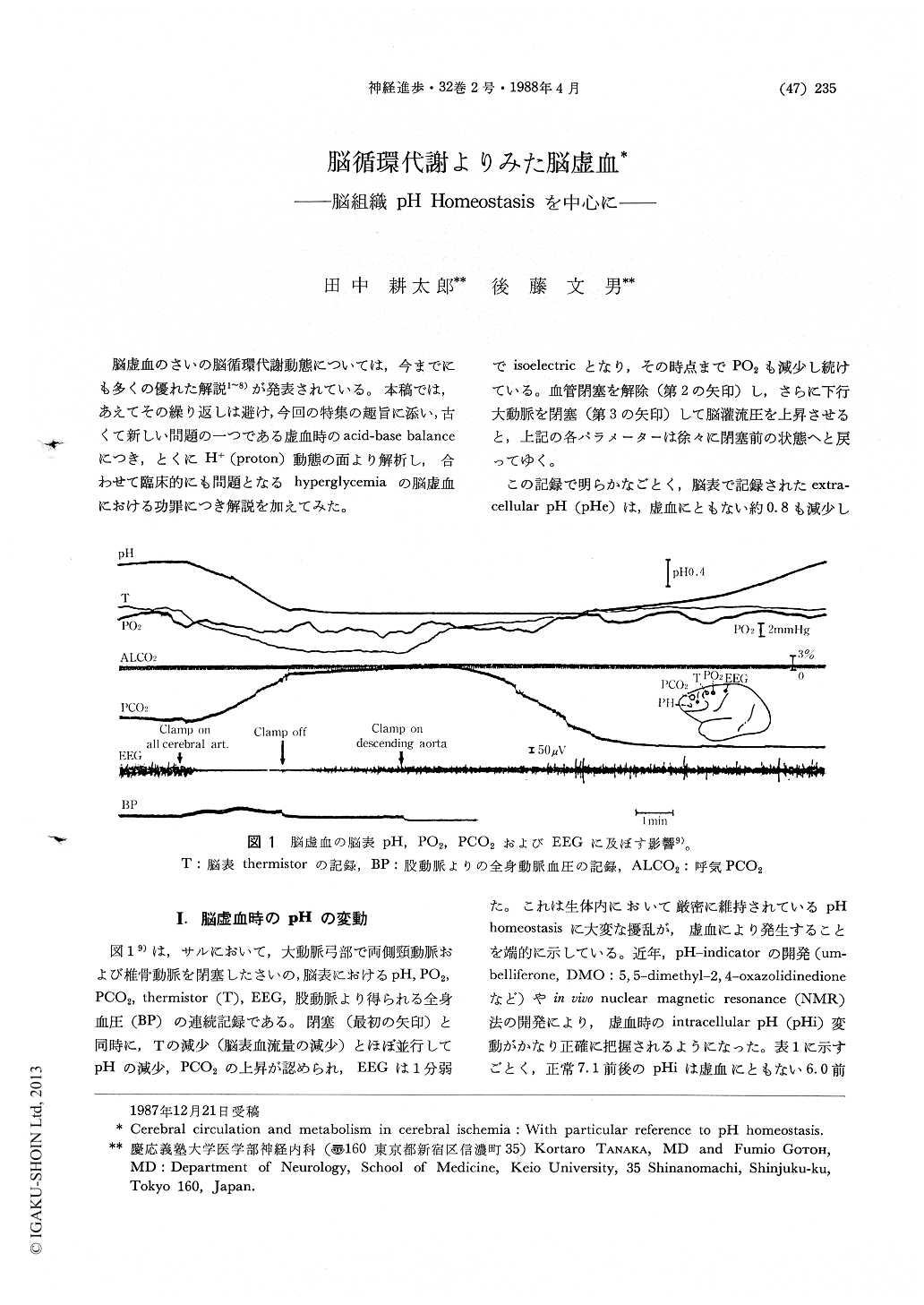
脳虚血のさいの脳循環代謝動態については,今までにも多くの優れた解説1〜8)が発表されている。本稿では,あえてその繰り返しは避け,今回の特集の趣旨に添い,古くて新しい問題の一つである虚血時のacid-base balanceにつき,とくにH+(proton)動態の面より解析し,合わせて臨床的にも問題となるhyperglycemiaの脳虚血における功罪につき解説を加えてみた。
The mechanism of pH homeostasis in braintissue and its derangement in brain ischemia were reviewed. The four major mechanisms contribute to the maintenance of pH in the normal brain : 1) production and consumption of H+ by brain metabolism, 2) physicochemical buffering, 3) transmembrane trantport of H+ and its equivalent, 4) compensatory adaptation of circulatory factors.
In brain ischemia, activation of anaerobic glycolysis together with hydrolysis of its product (ATP) is a major factor which produces H+ depending on intracellular pH. Consumption of H+ by metabolism of creatine phosphate and glycogen, or oxidation of lactate is almost negligible under ischemic condition.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


