Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
近年,脊髄疾患の画像診断は,めざましい発展を遂げている。その原動力は,非イオン性水溶性造影剤の開発と,X線CTの進歩であり,MRIによってさらに加速されたといえよう。
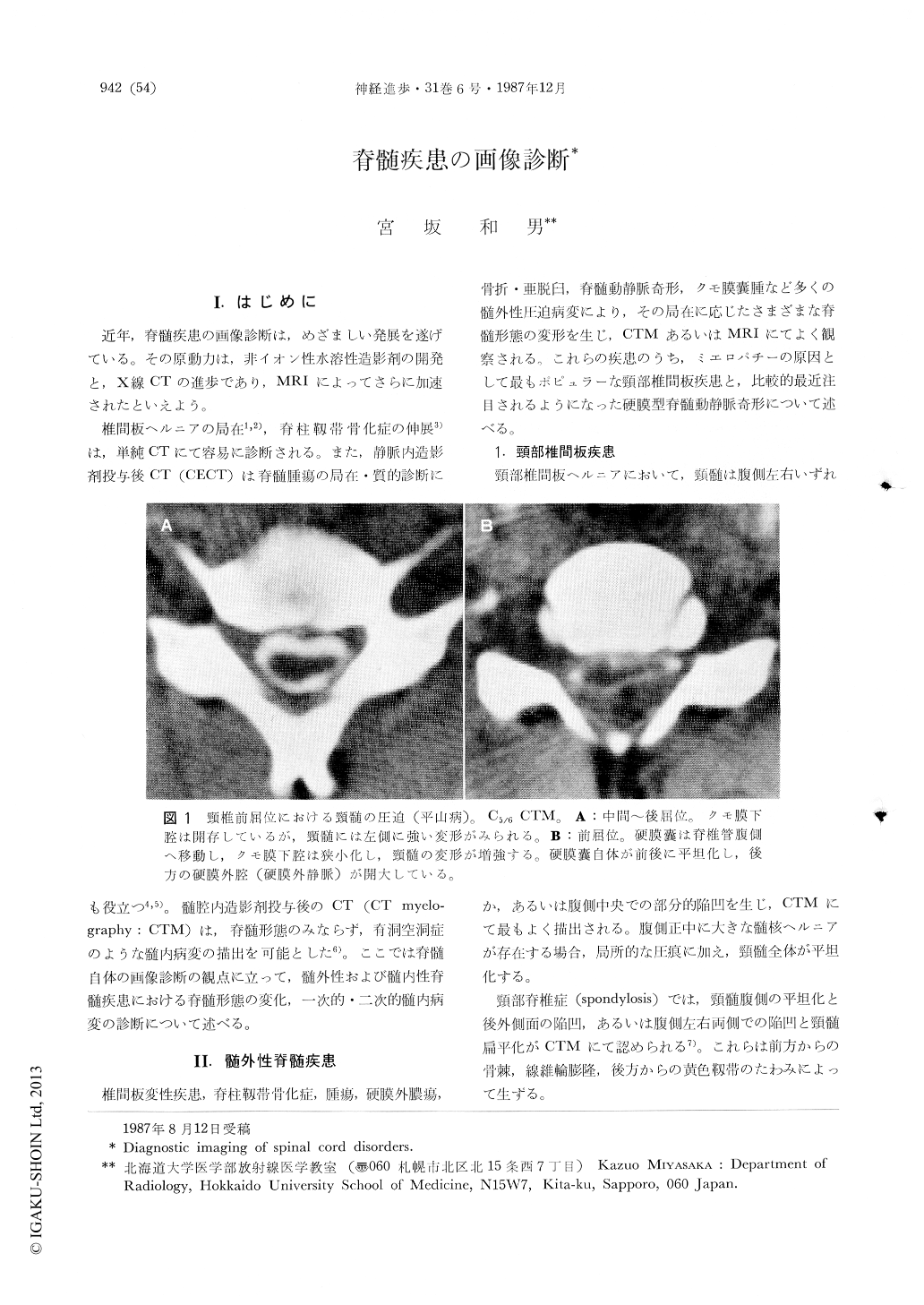
椎間板ヘルニアの局在1,2),脊柱靱帯骨化症の伸展3)は,単純CTにて容易に診断される。また,静脈内造影剤投与後CT(CECT)は脊髄腫瘍の局在・質的診断にも役立つ4,5)。髄腔内造影剤投与後のCT(CT myelography:CTM)は,脊髄形態のみならず,脊洞空洞症のような髄内病変の描出を可能とした6)。ここでは脊髄自体の画像診断の観点に立って,髄外性および髄内性脊髄疾患における脊髄形態の変化,一次的・二次的髄内病変の診断について述べる。
With recent refinements of CT and MRI, anatomical and pathological delineation of the spinal cord has been much improved. The subject of this article was to image morphological and parenchymatous changes of the spinal cord in such cases as cervical disc diseases, dural type of spinal arteriovenous malformations (AVM), syringomyelia, intramedullary neoplasms, and myelitis and demyelinating processes of the spinal cord. In cervical disc diseases, CTM showed various shapes of spinal cord deformity attributed to the location of disc protrusion and osteophytic ridge, and infolding of the ligamentum flava as well. Intramedullary penetration of contrase medium was observed in 12% of the cases with spondylotic myelopathy and may suggest cavitation within the spinal cord associated with repeative minor trauma and ischemia. In dural type of spinal AVM, MRI showed swelling and abnormality of signal intensity of the spinal cord which probably consistent with edema and softening provoked by venous congestion. Syringomyelia and intramedullary neoplasms were well demonstrated by MRI. Differentiation of the both conditions was discussed. In some, demyelinating lesion of the spinal cord was also depicted by MRI directly. Enhanced MRI using Gd-DTPA located not only intramedullary tumor nodules but also myelitis and demyelinating lesion.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


