Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
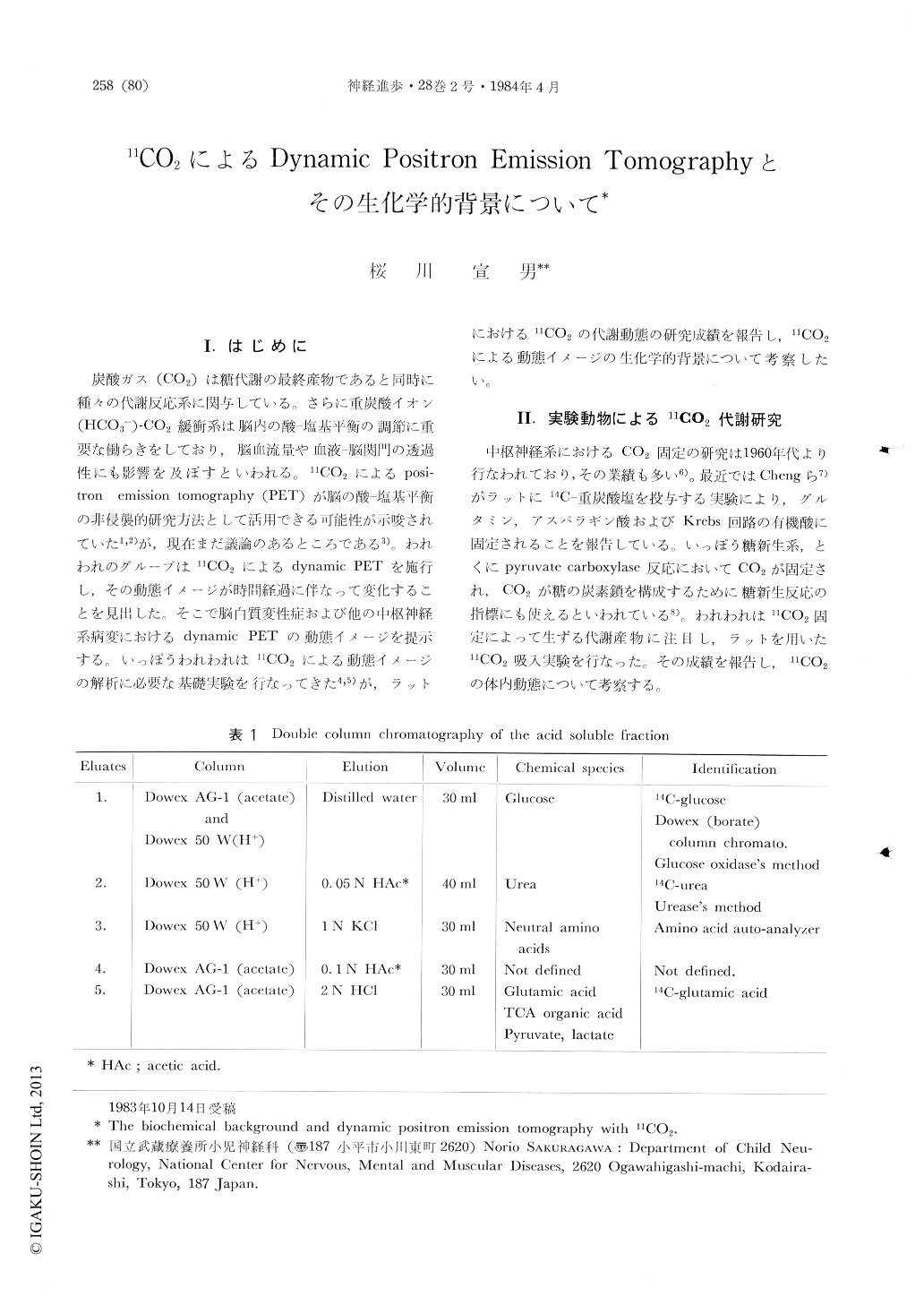
炭酸ガス(CO2)は糖代謝の最終産物であると同時に種々の代謝反応系に関与している。さらに重炭酸イオン(HCO3-)-Co2緩衝系は脳内の酸—塩基平衡の調節に重要な働らきをしており,脳血流量や血液—脳関門の透過性にも影響を及ぼすといわれる。11CO2によるpositron emission tomography(PET)が脳の酸—塩基平衡の非侵襲的研究方法として活用できる可能性が示唆されていた1,2)が,現在まだ議論のあるところである3)。われわれのグループは11CO2によるdynamic PETを施行し,その動態イメージが時間経過に伴なって変化することを見出した。そこで脳白質変性症および他の中枢神経系病変におけるdynamic PETの動態イメージを提示する。いっぽうわれわれは11CO2による動態イメージの解析に必要な基礎実験を行なってきた4,5)が,ラットにおける11CO2の代謝動態の研究成績を報告し,11CO2による動態イメージの生化学的背景について考察したい。
It has been still debatable if 11C-labeled carbon dioxide could be used in conjunction with positron emission tomography (PET) as an acid-base or metabolic tracer. Recently we found that dynamic PET with 11CO2 showed different dynamic images with time. In order to get some information about a biochemical basis of dynamic PET with 11CO2, we performed an experimental study on 11CO2 metabolism in rats with our special attention to 11CO2 fixation.
A Wistar rat (200~300 g) in a glass container was exposed to 11CO2 air (50~100 mCi) for 5 minutes and sacrificed soon or 20 minutes later.
Copyright © 1984, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


