Japanese
English
原著
L-DOPA投与量と大脳皮質第一次視覚野,連合野,および小脳皮質虫部の光誘発電位
Doses of L-DOPA and photically evoked responses in the primary visual, association and cerebellar vermal cortices
門林 岩雄
1
,
三上 正嗣
2
,
加藤 仲勝
1
Iwao KADOBAYASHI
1
,
Masatsugu MIKAMI
2
,
Nobukatsu KATO
1
1京都府立医科大学精神医学教室
2京都第二日本赤十字病院中央検査室
1Department of Psychiatry, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine
2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Kyoto 2nd Red Cross Hospital
pp.326-331
発行日 1976年4月10日
Published Date 1976/4/10
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1431903840
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
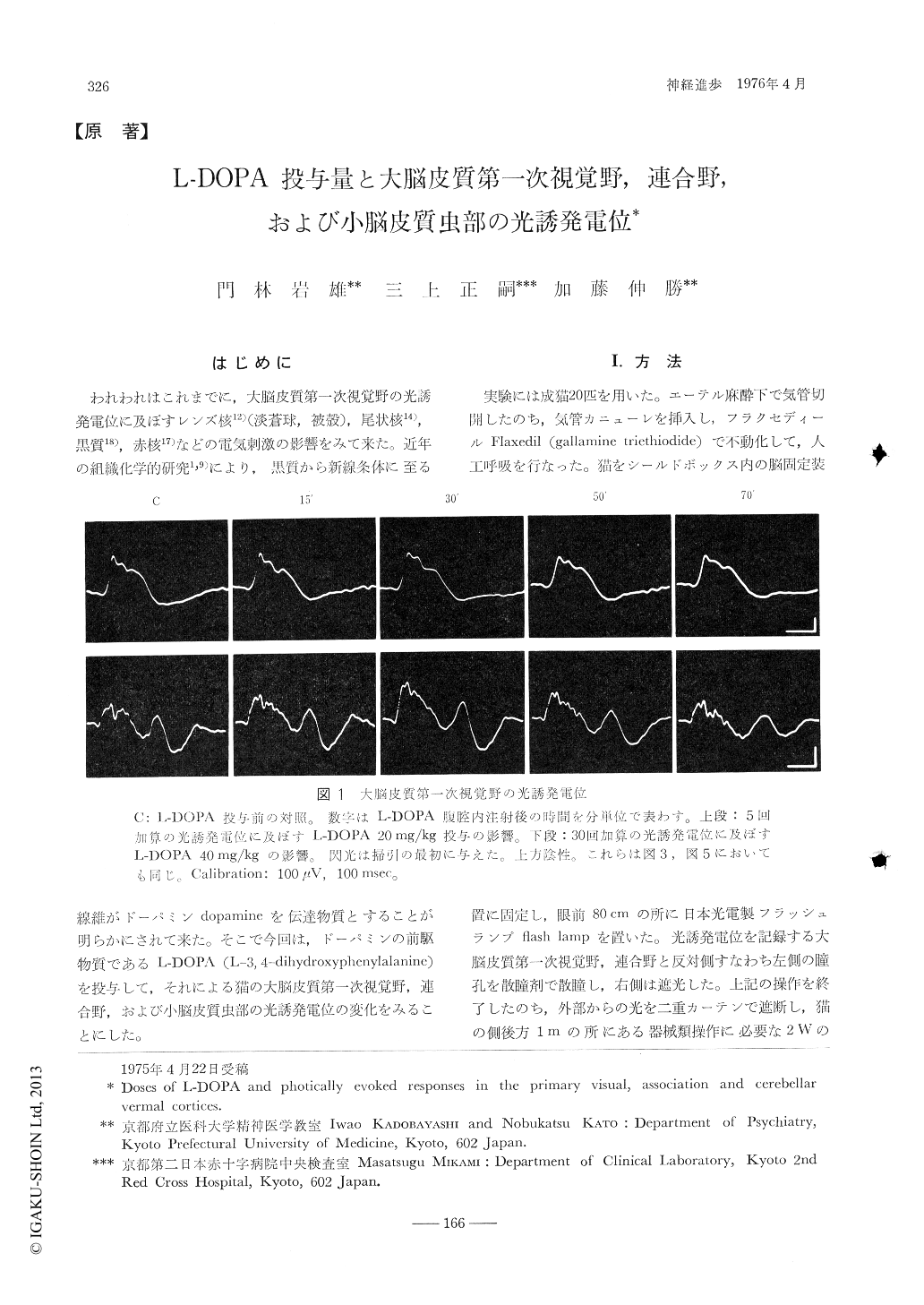
はじめに
われわれはこれまでに,大脳皮質第一次視覚野の光誘発電位に及ぼすレンズ核12)(淡蒼球,被殻),尾状核14),黒質18),赤核17)などの電気刺激の影響をみて来た。近年の組織化学的研究1,9)により,黒質から新線条体に至る線維がドーパミンdopamineを伝達物質とすることが明らかにされて来た。そこで今回は,ドーパミンの前駆物質であるL-DOPA(L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine)を投与して,それによる猫の大脳皮質第一次視覚野,連合野,および小脳皮質虫部の光誘発電位の変化をみることにした。
Different doses of L-DOPA were administered intraperitoneally to cats immobilized with gallamine triethiodide, and their effects on photically evoked responses in the primary visual, association, and cerebellar vermal cortices were observed. Injection of L-DOPA 10 mg/kg soon resulted in marked reduction in amplitude of the responses, but that of 20 mg/kg produced a lesser reduction, lasting for a longer time.
Copyright © 1976, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


