Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
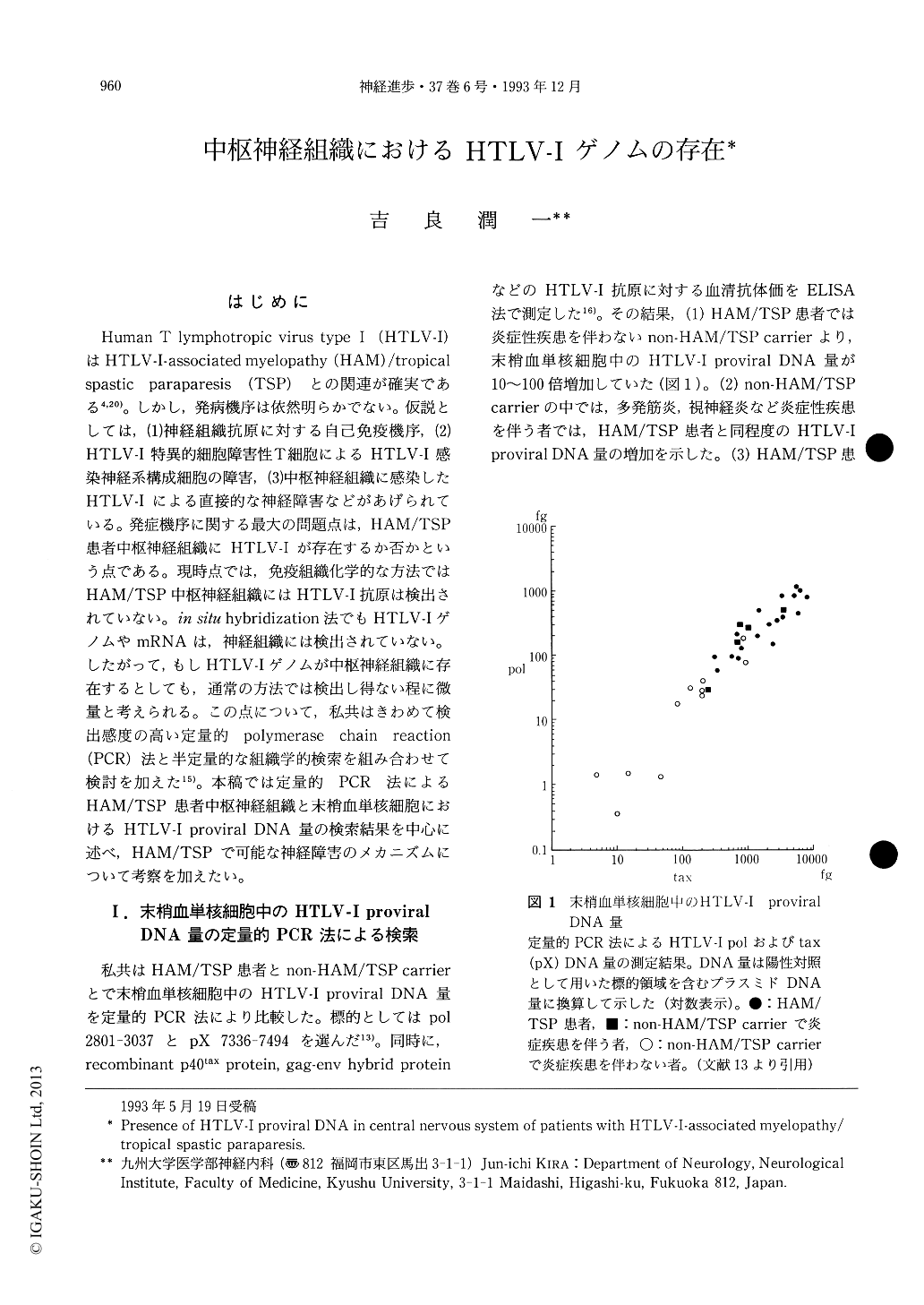
Human T lymphotropic virus type I(HTLV-I)はHTLV-I-associated myelopathy(HAM)/tropicalspastic paraparesis(TSP)との関連が確実である4,20)。しかし,発病機序は依然明らかでない。仮説としては,(1)神経組織抗原に対する自己免疫機序,(2)HTLV-I特異的細胞障害性T細胞によるHTLV-I感染神経系構成細胞の障害,(3)中枢神経組織に感染したHTLV-Iによる直接的な神経障害などがあげられている。発症機序に関する最大の問題点は,HAM/TSP患者中枢神経組織にHTLV-Iが存在するか否かという点である。現時点では,免疫組織化学的な方法ではHAM/TSP中枢神経組織にはHTLV-I抗原は検出されていない。in situ hybridization法でもHTLV-IゲノムやmRNAは,神経組織には検出されていない。したがって,もしHTLV-Iゲノムが中枢神経組織に存在するとしても,通常の方法では検出し得ない程に微量と考えられる。この点について,私共はきわめて検出感度の高い定量的polymerase chain reaction(PCR)法と半定量的な組織学的検索を組み合わせて検討を加えた15)。本稿では定量的PCR法によるHAM/TSP患者中枢神経組織と末梢血単核細胞におけるHTLV-I proviral DNA量の検索結果を中心に述べ,HAM/TSPで可能な神経障害のメカニズムにっいて考察を加えたい。
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to determine the presence and amounts of human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNCs) and central nervous system (CNS) tissues of patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (HAM) /tropical spastic paraparesis (TSP) . In PBMNCs, the HTLV-I proviral DNA was 10-to 100-fold higher in 18 patients with HAM/TSP and in 5 HTLV-I carriers without HAM/TSP who had autoimmune or inflammatory diseases than in 12 HTLV-I carriers without HAM/TSP and without autoimmune or inflammatory diseases. The patients who had had onset of myelopathy at a younger age (15 to 39 years) had an extremely high level of HTLV-I proviral DNA in the early phase, as compared with findings in those with a late onset of myelopathy (44 to 61 years) . The large increase in HTLV-I proviral DNA in PBMNCs increases the probability for HTLV-I-infected cells to enter into and make contact with constituent cells of the CNS, and therefore, contribute to the development of the disease. In formalin-fixed CNS tissues, HTLV-I pX and env but not pol DNA were detected in 5 of 6 patients with HAM/TSP. The CNS samples from 1 patient with adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) and CNS infiltration of leukemic cells were positive for pX, env, and pol DNA by PCR. None of the samples from 9 control subjects with other neurological disorders was consistently positive for HTLV-I by PCR, but all showed positive bands on β-globin PCR. Quantitative PCR combined with histological studies revealed the followings. (1) There was no correlation between HTLV-I proviral DNA amounts and extent of perivascular mononuclear cell infiltration in the HAM/TSP CNS. (2) The amounts of pX DNA were greater in the HAM/TSP samples than in the ATL sample, although the extent of mononuclear cell infiltration was far less in the HAM/TSP samples than in the ATL sample. Sequence analysis of the cloned PCR products identified the HTLV-I pX sequence. Therefore, all these observations suggest that in addition to infiltrating mononuclear cells, constituent cells of the CNS may harbor the HTLV-I genome in patients with HAM/TSP.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


