Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
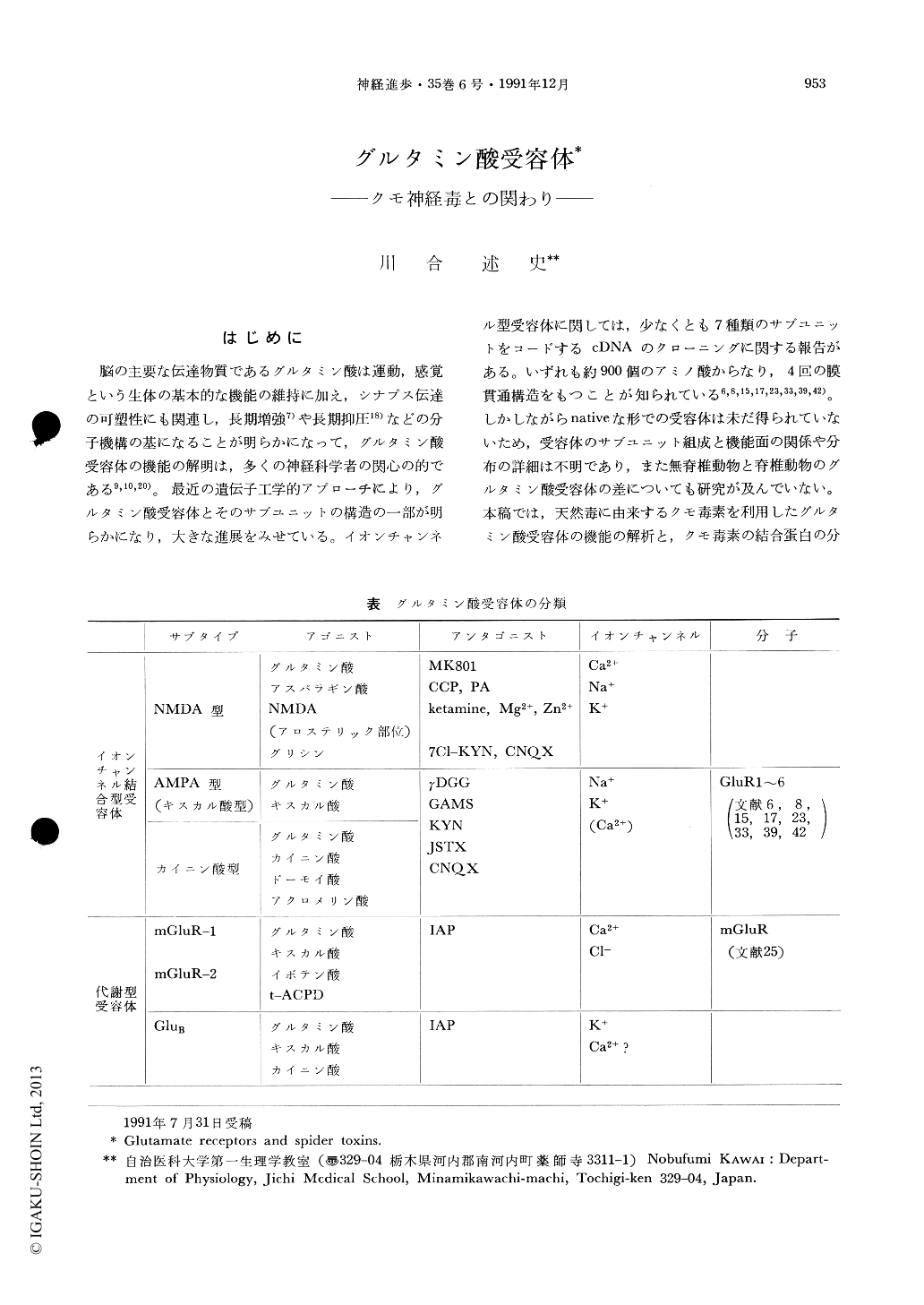
脳の主要な伝達物質であるグルタミン酸は運動,感覚という生体の基本的な機能の維持に加え,シナプス伝達の可塑性にも関連し,長期増強7)や長期抑圧18)などの分子機構の基になることが明らかになって,グルタミン酸受容体の機能の解明は,多くの神経科学者の関心の的である9,10,20)。最近の遺伝子工学的アプローチにより,グルタミン酸受容体とそのサブユニットの構造の一部が明らかになり,大きな進展をみせている。イオンチャンネル型受容体に関しては,少なくとも7種類のサブユニットをコードするcDNAのクローニングに関する報告がある。いずれも約900個のアミノ酸からなり,4回の膜貫通構造をもつことが知られている6,8,15,17,23,33,39,42)。しかしながらnativeな形での受容体は未だ得られていないため,受容体のサブユニット組成と機能面の関係や分布の詳細は不明であり,また無脊椎動物と脊椎動物のグルタミン酸受容体の差についても研究が及んでいない。本稿では,天然毒に由来するクモ毒素を利用したグルタミン酸受容体の機能の解析と,クモ毒素の結合蛋白の分離の研究,さらにシナプス前膜に局在する新しい型の代謝型グルタミン酸受容体について解説する。
Characterization of glutamate receptors have been employed using a specific blocker derived from the venom of spider Nephila clavata. The toxin (JSTX) preferentially blocks quisqualate type glutamate receptors in crustacean neuromuscular synapse, squid giant synapse and mammalian brain synapses. Following determination of the structure of JSTXs, a main component JSTX-3 with its analog were chemically synthesized and used for the study of structure-activity relationships. Labeled spider toxins were synthesized for the histological and biochemical studies of the glutamate receptors. 125I labeled JSTX-3 and biotinylated JSTX-3 were used for visualization of glutamate receptors in crustacean muscle and mammalian brain. Using affinity purification, JSTX-3-binding proteins were isolated from bovine brain. The purified protein was reconstituted into giant liposomes and channel activities in-duced by glutamate in the patch pipet was blocked by JSTX. By use of JSTX and pertussis toxin, a novel type of glutamate receptor-GluB receptor was found in crustacean neuromuscular synapse. While the postsynaptic glutamate receptor was blocked by JSTX, GluB receptor was insensitive to JSTX but it was blocked by pertussis toxin indicating the involvement of inhibitory GTP-binding protein. Injection of GTPrS in the presynaptic axon mimicked the presynaptic glutamate potentials and caused presynaptic inhibitory action which is concluded by quantal analysis of excitatory postsynaptic currents. GluB receptors thus exert presynaptic inhibitory effect and regulate transmitter release in the crustacean neuromuscular synapse.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


