Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
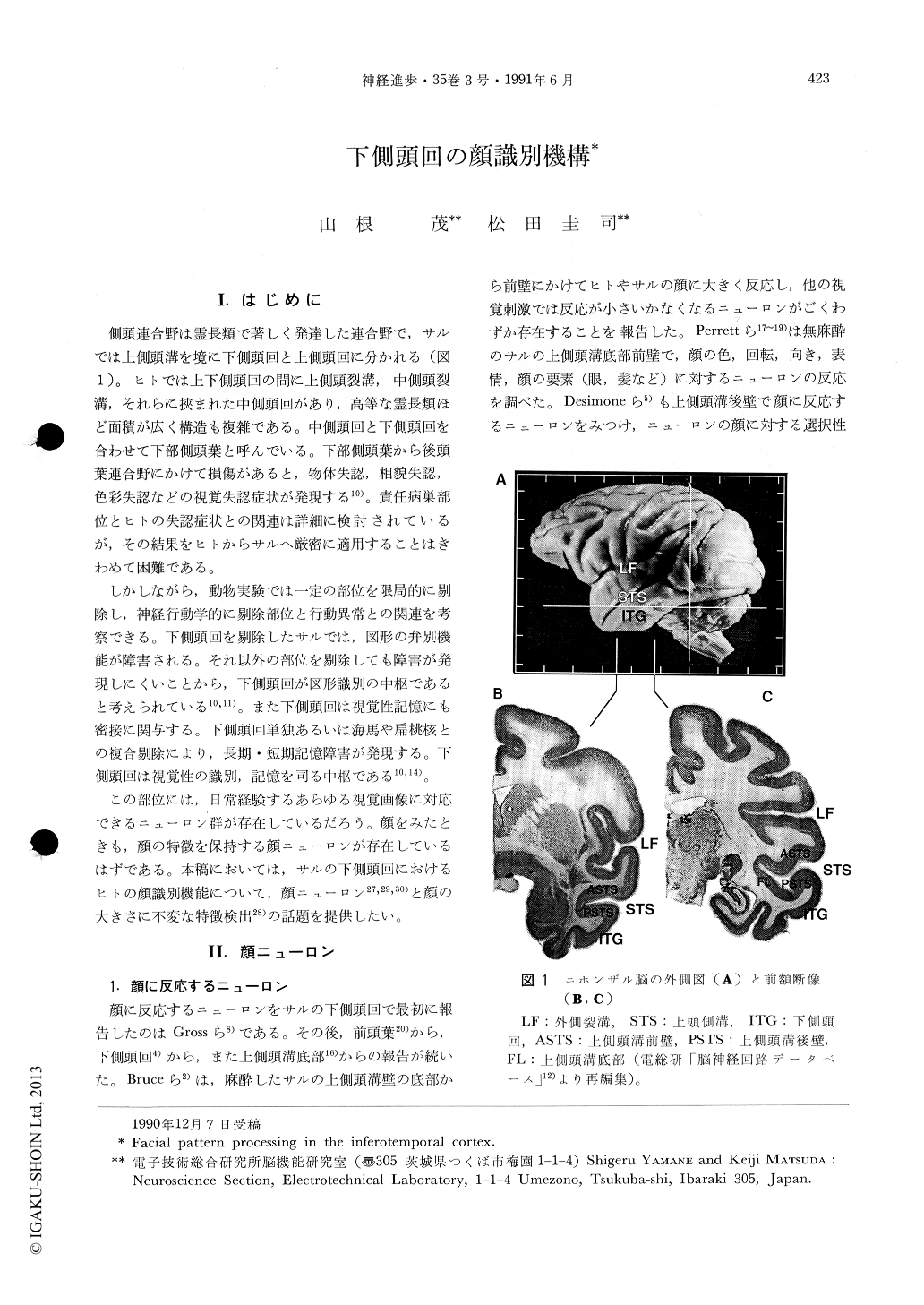
側頭連合野は霊長類で著しく発達した連合野で,サルでは上側頭溝を境に下側頭回と上側頭回に分かれる(図1)。ヒトでは上下側頭回の間に上側頭裂溝,中側頭裂溝,それらに挾まれた中側頭回があり,高等な霊長類ほど面積が広く構造も複雑である。中側頭回と下側頭回を合わせて下部側頭葉と呼んでいる。下部側頭葉から後頭葉連合野にかけて損傷があると,物体失認,相貌失認,色彩失認などの視覚失認症状が発現する10)。責任病巣部位とヒトの失認症状との関連は詳細に検討されているが,その結果をヒトからサルへ厳密に適用することはきわめて困難である。
しかしながら,動物実験では一定の部位を限局的に剔除し,神経行動学的に剔除部位と行動異常との関連を考察できる。下側頭回を剔除したサルでは,図形の弁別機能が障害される。それ以外の部位を剔除しても障害が発現しにくいことから,下側頭回が図形識別の中枢であると考えられている10,11)。また下側頭回は視覚性記憶にも密接に関与する。下側頭回単独あるいは海馬や扁桃核との複合剔除により,長期・短期記憶障害が発現する。下側頭回は視覚性の識別,記憶を司る中枢である10,14)。
The inferotemporal cortex of monkeys plays an important role in visual pattern discrimination. Responses of neurons in the inferotemporal cortex and superior temporal sulcus were recorded while the monkey was performing the human face discrimination task. Out of 850 neurons, 115 were re-sponded to faces. Each of them showed graded responses to different faces, i.e., some faces gave large responses but some other faces gave small responses. The selectivity to faces was different from neuron to neuron.
The relationships between facial features and the responses to faces were analyzed. Face neurons which detected the combination of distances between facial elements essential to faces were found in the inferotemporal cortex. We have studied size invariant processing of features in face neurons. The responses of face neurons to different faces were analyzed by a multiple correlation model expressed as a multiplicative equation of the power of distances between facial elements such as eyes, mouth, facial outline and hair. The dimension of the model is a spatial value. In order to assess the degree of size invariance of each face neuron, we defined a “spatial dimension tuning curve” calculated from the model using response magnitudes to faces at different image sizes. Some face neurons had broad tuning against spatial dimension, and a few face neurons, which could be responding in a size invariant fashion, had sharp tuning at zero spatial dimention. The possible mechanism of this size invariant function is discussed.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


