Japanese
English
原著
亜急性甲状腺炎における超音波検査の意義
Clinical Significance of Sonography in Subacute Thyroiditis
山田 弘之
1
,
矢野原 邦生
1
,
宮本 良生
2
Hiroyuki Yamada
1
1山田赤十字病院耳鼻咽喉科
2山田赤十字病院放射線科
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yamada Red-Cross Hospital
pp.603-607
発行日 1988年7月20日
Published Date 1988/7/20
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1411200193
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.緒言
亜急性甲状腺炎は甲状腺炎症性疾患の一つであり日常臨床において時折経験する疾患ではあるが,内科的治療が行われるためわれわれ耳鼻咽喉科医が遭遇する機会は意外と少ない。
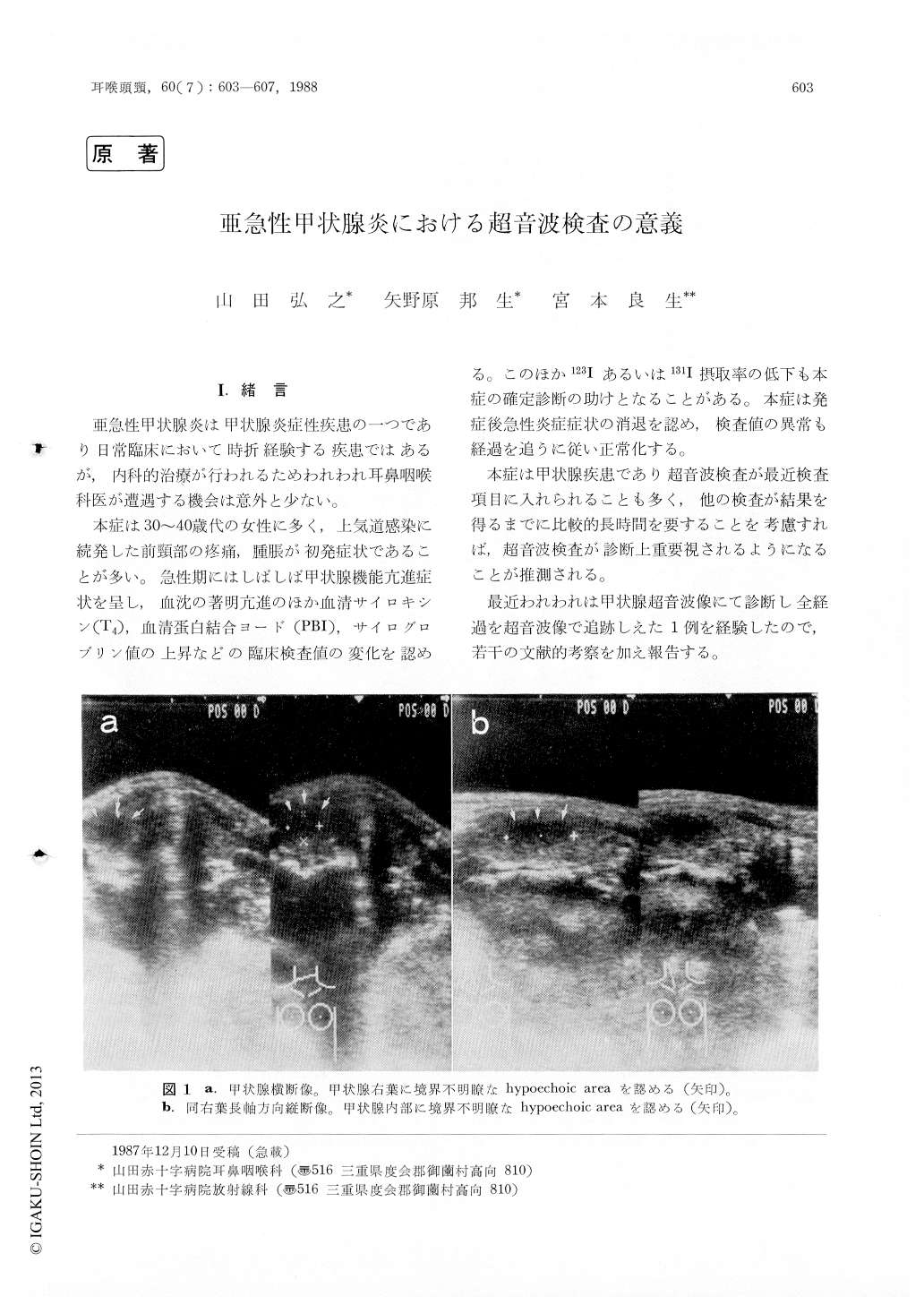
本症は30〜40歳代の女性に多く,上気道感染に続発した前頸部の1疼痛,腫脹が初発症状であることが多い。急性期にはしばしば甲状腺機能亢進症状を呈し,血沈の著明亢進のほか血清サイロキシン(T4),血清蛋白結合ヨード(PBI),サイログロブリン値の上昇などの臨床検査値の変化を認める、,このほか123Iあるいは131I摂取率の低下も本症の確定診断の助けとなることがある。本症は発症後急性炎症症状の消退を認め,検査値の異常も経過を追うに従い正常化する。
Sonographic characteristic in the active phase of subacute thyroiditis is unclear and heterogeneous hypoechoic area in the affected thyroid. The hypoechoic area will decreased in size by treatment. Sonography is more useful for diagnosis and for estimating cure of this disease compared with erythrocytes sedimentation rate and thyroid function.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


