Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
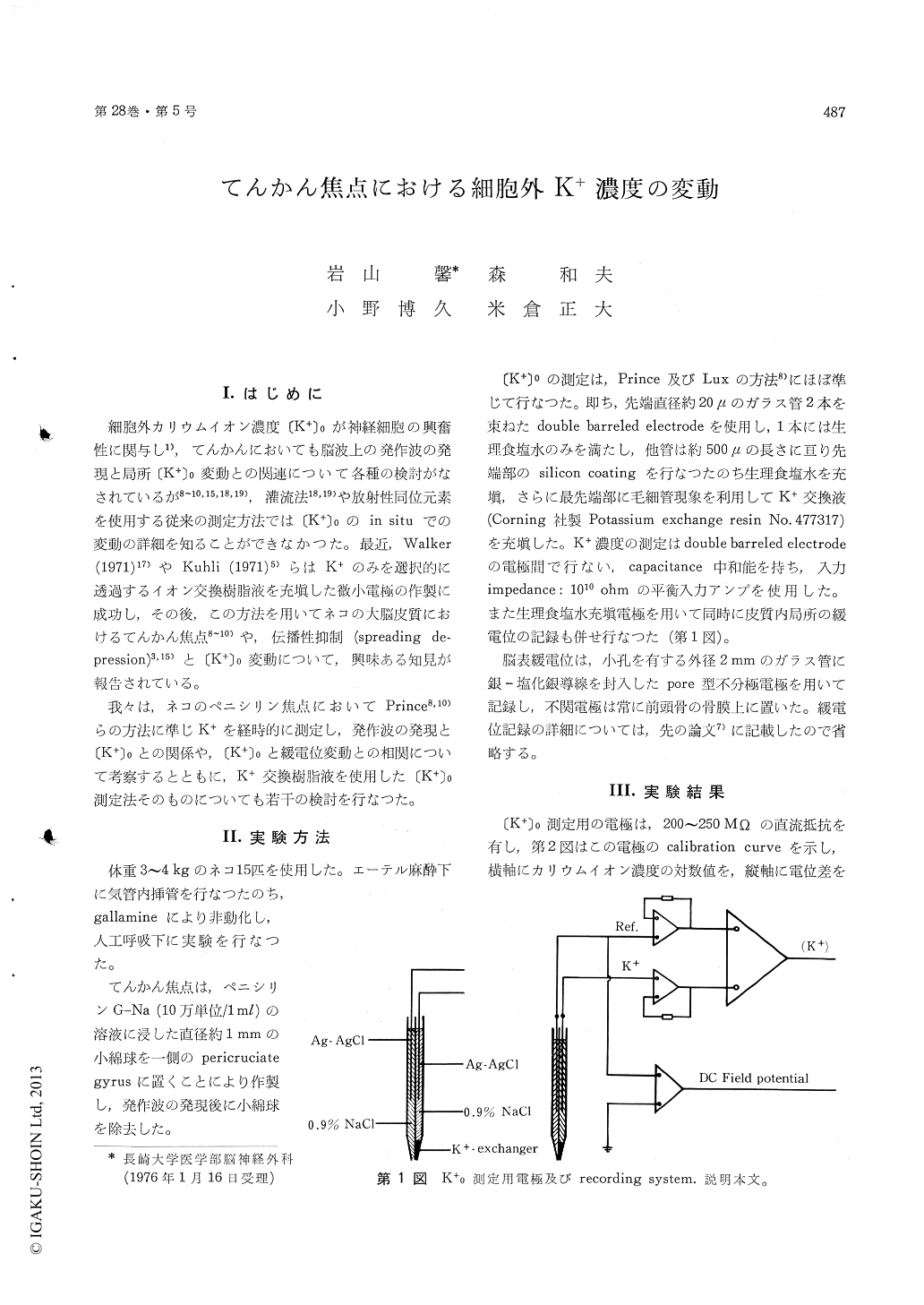
I.はじめに
細胞外カリウムイオン濃度〔K+〕0が神経細胞の興奮性に関与し1),てんかんにおいても脳波上の発作波の発現と局所〔K+〕0変動との関連について各種の検討がなされているが8〜10,15,18,19),灌流法18,19)や放射性同位元素を使用する従来の測定方法では〔K+〕0のin situでの変動の詳細を知ることができなかつた。最近,Walker(1971)17)やKuhli (1971)5)らはK+のみを選択的に透過するイオン交換樹脂液を充填した微小電極の作製に成功し,その後,この方法を用いてネコの大脳皮質におけるてんかん焦点8〜10)や,伝播性抑制(spreading de—pression)3,15)と〔K+〕0変動について,興味ある知見が報告されている。
我々は,ネコのペニシリン焦点においてPrince8,10)らの方法に準じK+を経時的に測定し,発作波の発現と〔K+〕0との関係や,〔K+〕0と緩電位変動との相関について考察するとともに,K+交換樹脂液を使用した〔K+〕0測定法そのものについても若干の検討を行なつた。
Direct measurements of changes in extracellularpotassium concentration were made by using apotassium-sensitive microelectrode. Epileptogenicfocus was produced by the topical application ofpenicillin G on the pericruciate gyrus in cats. EEGand steady potential (SP) shift were also recordedsimultaneously.
(1) Spontaneous interictal epileptiform eventsappeared after topical application of penicillin with-out any remarkable increase of baseline (K+)0 value.It was suggested that an increase of (K+)0 mightnot be a critical factor in the initiation of electro-graphic epileptiform events.
(2) Shortly after the initiation of epileptiformevents, each surface EEG discharge began to as-sociate with transient increase in (K+)0 of up to5.0mM. During the tonic-clonic ictal events, (K+)0showed a smooth rise, reaching a peak at the endof the tonic phase and then stabilized at the levelof 5.5-8.0mM throughout the period of the clonicphase.
One of the most significant finding was that anincrease in (K+)0 associated with any EEG par-oxysm, was limited within a value of approximately8mM and never exceeded from this range. Thisfinding suggested that a regulatory mechanism ofstabilizing (K+)0 was preserved in the epileptogenicfocus and that the termination of seizure was notdue to excess of (K+)0 which might result in andepolarizing inactivation.
(3) Simultaneous recording of the intracorticalsteady potential and (K+)0 concentration disclosedthat there existed some temporal dissimilarities be-tween the time course of the negative SP shiftand increase in (K+)0 associated either with isolatedor sustained EEG paroxysms. Some authors havepointed out that SP shift associated with paroxysmscould be explainable, at least in part, by changesin glial membrane potentials which were intimatelyrelated to (K+)0. It was suggested, however, fromthe present experiment that SP shift did not solelydue to changes in (K+)0.
Copyright © 1976, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


