Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
胸部X線写真は肺高血圧の診断に重要な手がかりを与えてくれる。兼本ら1)は,原発性肺高血圧症の胸部X線写真から種々の所見を定量化し報告している。
しかしながら,肺高血圧を呈する基礎疾患は種々存在するため,これらの所見が果して肺高血圧症に共通の所見であるか否かを検討することは有意義であると考えられる。
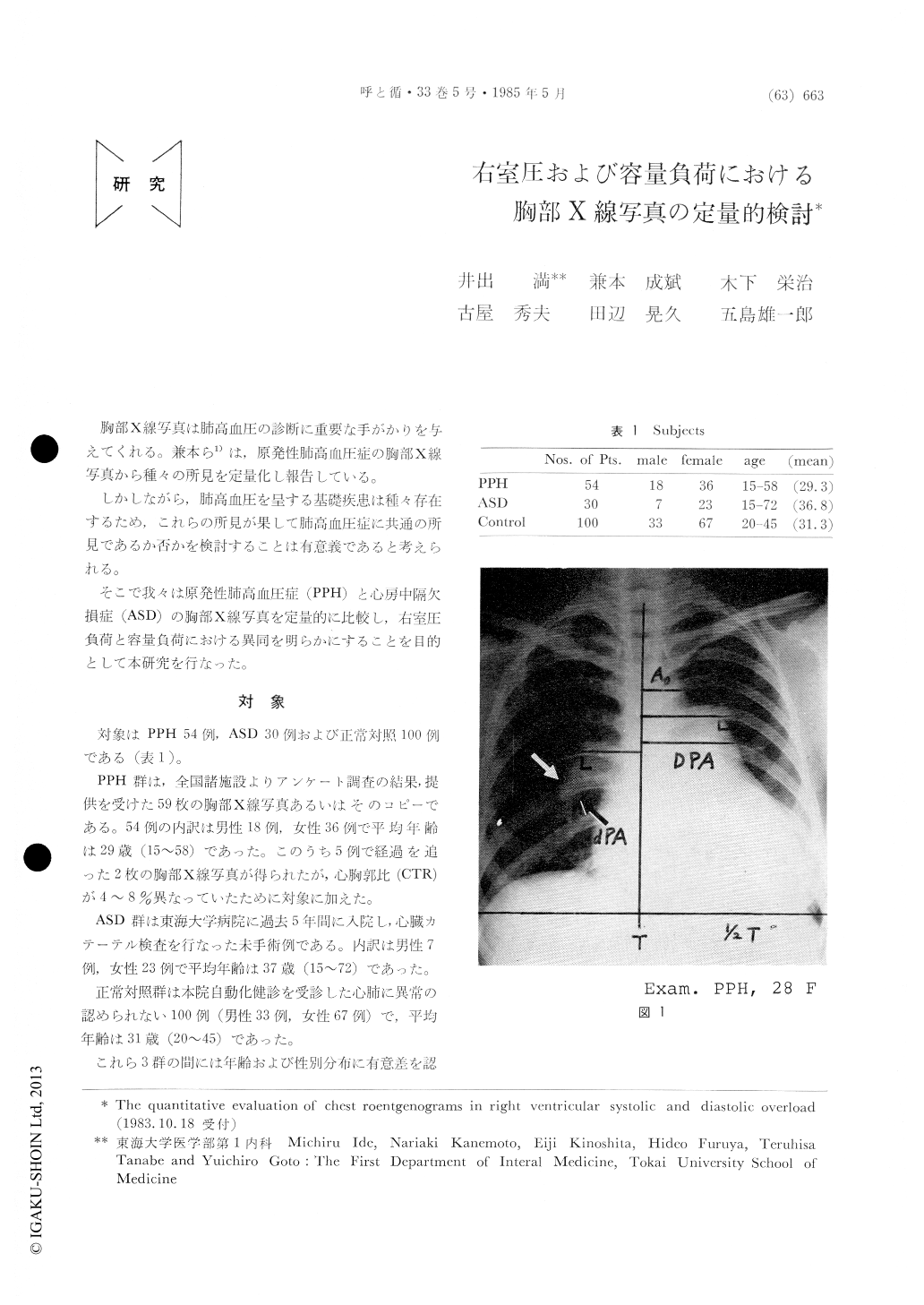
Chest roentgenograms were taken in 30 patients (pt) with atrial septal defect (ASD, mean 37 y/o), 54 pt with primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH 29 y/o) and 100 normals (31 y/o) as control. The method used consisted of measurement of the following 5 items on posteroanterior chest roentgenograms ob-tained by routine method. (1) Ao : width of the aortic knob from the midline, (2) DPA : width of the pulmonary artery from the midline, (3) PL : the point of union of the external border of the upper lobe artery with the pars interlobaris was identified as point L and the sum of horizontal distance of the right and left L to the midline was defined as PL, (4) dPA : width of the descending branch of the right pulmonary artery (PA), (5) maximum transverse dia-meter of the heart. (1) and (2) was divided by a half thoracic diameter (T/2) and (3) and (5) by (T). Cor-relation of these items and pulmonary hemodynamics was also examined.
In Ao/(T/ 2), ASD showed significantly smaller value compared with other groups. All other para-meters took greater values in disease groups. DPA /(T/2) and PL/T correlated positively with PA pressure in both pt groups and in addition dPA in ASD. Pt with dPA≧30mm revealed mean PA pressure 30mmHg.
We conclude that chest roentgenogram can afford useful information for the diagnosis and noninvasive detection of pulmonary hemodynamics.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


