Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
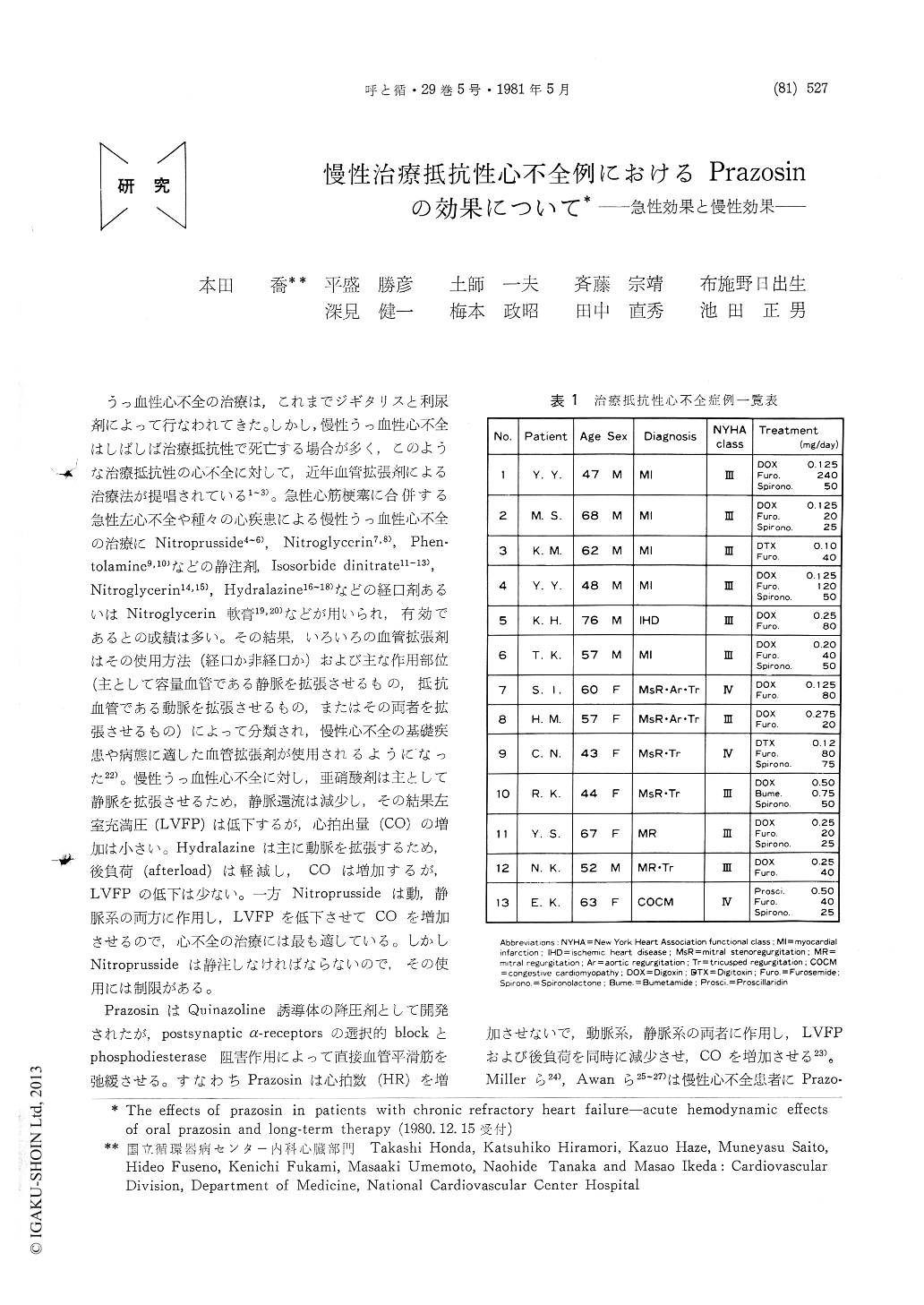
うっ血性心不全の治療は,これまでジギタリスと利尿剤によって行なわれてきた。しかし,慢性うっ血性心不全はしばしば治療抵抗性で死亡する場合が多く,このような治療抵抗性の心不全に対して,近年血管拡張剤による治療法が提唱されている1〜3)。急性心筋梗塞に合併する急性左心不全や種々の心疾患による慢性うっ血性心不全の治療にNitroprusside4〜6),Nitroglycerin7,8),Phen—tolamine9,10)などの静注剤,Isosorbide dinitrate11〜13),Nitroglycerin14,15),Hydralazine16〜18)などの経口剤あるいはNitroglycerin軟膏19,20)などが用いられ,有効であるとの成績は多い。その結果,いろいろの血管拡張剤はその使用方法(経口か非経口か)および主な作用部位(主として容量血管である静脈を拡張させるもの,抵抗血管である動脈を拡張させるもの,またはその両者を拡張させるもの)によって分類され,慢性心不全の基礎疾患や病態に適した血管拡張剤が使用されるようになった22)。
The hemodynamic effects of oral prazosin were investigated in 13 patients with chronic refrac-tory heart failure. A single dose of prazosin (2-4 mg) decreased mean systemic arterial pressure and left ventricular filling pressure by 16 mmHg (-17%, p<0.05) and 6 mmHg (-33%, p<0.05), respectively, and increased cardiac index by 0.52L/min/m2 (+23%, p<0.05) without any significant changes in heart rate. It also decreased systemic vascular resistance and pulmonary vas-cular resistance by 22% (p<0.01) and 42% (p< 0.01), respectively. These effects of prazosin on left ventricular function appeared in the first hour, reached its maximum at 3.2 hour and lasted for the entire 6 hour period of observation.
Hemodynamics were further studied during supine exercise in 4 patients. The extent of in-crease in heart rate and pressure-rate product were significantly less (p<0.05) and stroke index significantly greater (p<0.05) with prazosin.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


