Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
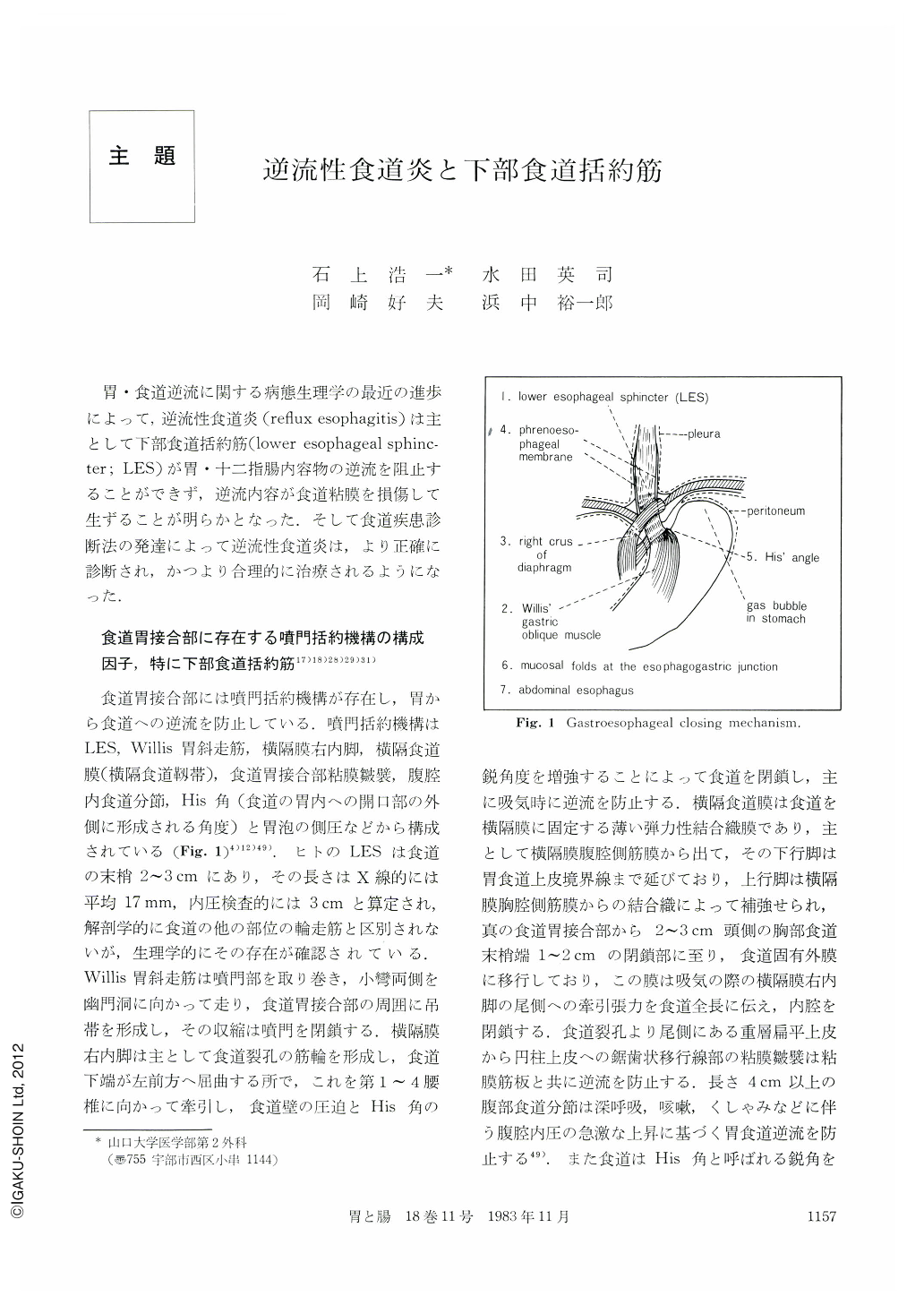
胃・食道逆流に関する病態生理学の最近の進歩によって,逆流性食道炎(refluxe sophagitis)は主として下部食道括約筋(lower esophageal sphincter;LES)が胃・十二指腸内容物の逆流を阻止することができず,逆流内容が食道粘膜を損傷して生ずることが明らかとなった.そして食道疾患診断法の発達によって逆流性食道炎は,より正確に診断され,かつより合理的に治療されるようになった.
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the Willis' gastric oblique muscle fibers, the right crus of the diaphragm, the phrenoesophageal membrane, mucosal folds at the esophagogastric junction, the intraabdominal segment of the esophagus and the angle of His play the major role in the cardiac closing mechanism in human beings. Most of the current evidence supports the concept that the LES is the main barrier that prevents gastroesophageal reflux. The changes in the gastroesophageal reflux pressure and the resting LES pressure (LESP) after destruction of the cardiac closing mechanism showed the same tendency in our experimental results in dogs. Regarding control of the cardiac closing mechanism, much attention has been paid to the effects of neural and humoral factors, such as the vagal nerve, gastrointestinal hormones and prostaglandins. Responses of the cardiac closing mechansim to exogenous gastrin were decreased in our experimental groups in dogs with division of the LES and the Willis' oblique muscle in the next place. Relationship between the LESP and serum gastrin level in various clinical conditions, influences of various kinds of endogenous and exogenous hormones on human LESP, and the factars which affect the LES tone were summarized. The pathogenesis of sphincter incompetence in patients with chronic reflux symptoms include gastrin deficiency, decreased sensitivity of the LES to endogenous gastrin, neural dysfunction, especially deranged function of the cholinergic neuron and the diseases and physiological defect of the LES muscle. Recently, the transient LES relaxations having no connection with swallowing action are given much attention in the pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis in the patients who showed normal LFSP. It was verified that taurocholate destroys the esophageal mucosal barrier, but such damage is not comparable to the pathohistological changes in the esophagitis. Effective drugs for esophagitis, such as antacids, bethanechol, metoclopramide, etc., increase the LES tone and promote the clearance of reflux contents in the esophagus.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


