Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
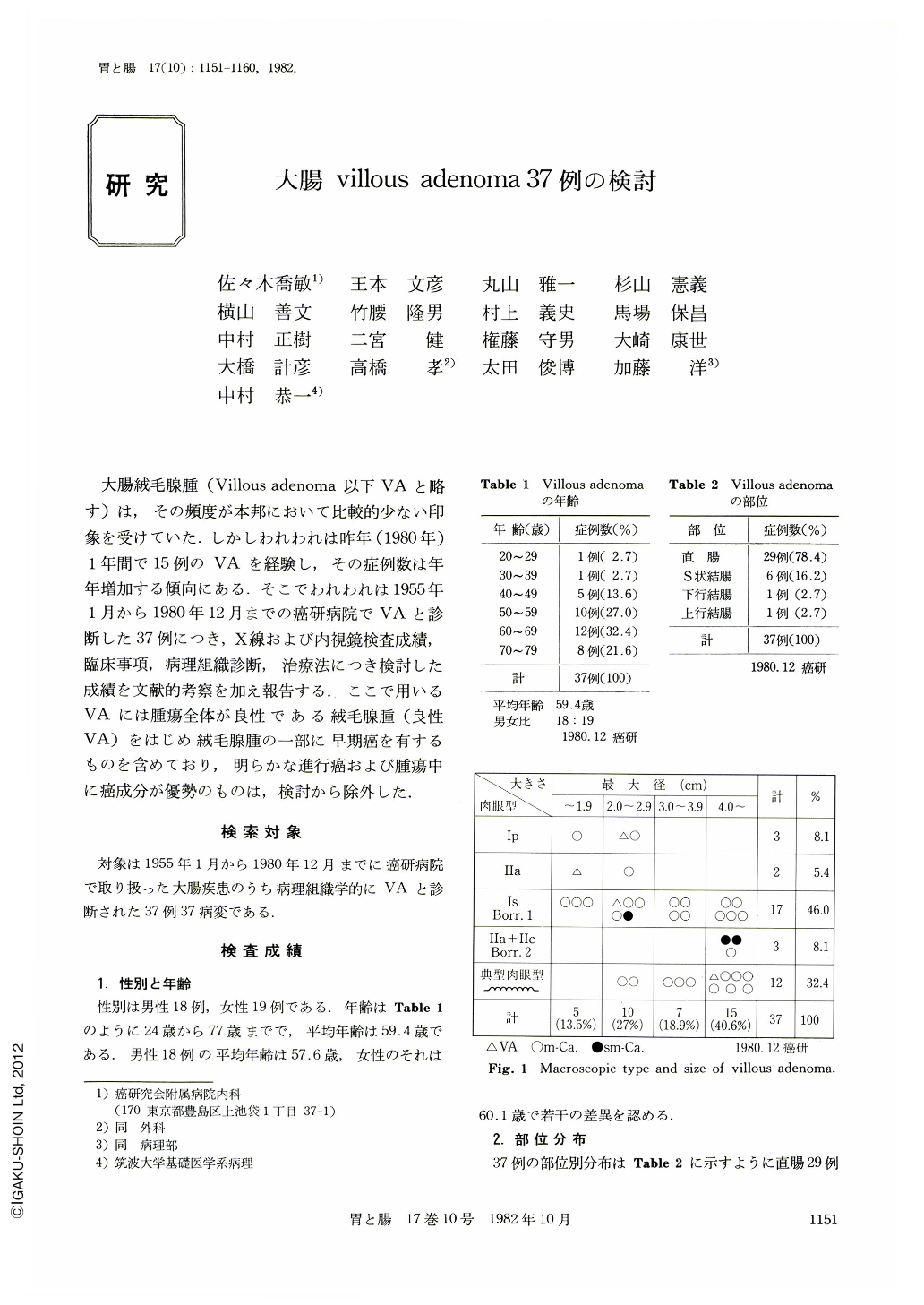
大腸絨毛腺腫(Villous adenoma以下VAと略す)は,その頻度が本邦において比較的少ない印象を受けていた.しかしわれわれは昨年(1980年)1年間で15例のVAを経験し,その症例数は年年増加する傾向にある.そこでわれわれは1955年1月から1980年12月までの癌研病院でVAと診断した37例につき,X線および内視鏡検査成績,臨床事項,病理組織診断,治療法につき検討した成績を文献的考察を加え報告する.ここで用いるVAには腫瘍全体が良性である絨毛腺腫(良性VA)をはじめ絨毛腺腫の一部に早期癌を有するものを含めており,明らかな進行癌および腫瘍中に癌成分が優勢のものは,検討から除外した.
Thirty-seven cases of villous adenoma which were examined and histo-pathologically diagnosed at Cancer Institute Hospital during the period of 26 years from January 1955 to December 1980 were studied.
They were classified into typical and atypical villous adenoma according to their macroscopic and radiologic findings. Radiologically typical villous adenoma was revealed as a cluster of granular elevations of the same size. Its margin was clearly discernible in some cases, but in other cases it was not. Added to this, there were cases with a cluster of elevations of various sizes' whose margin was comparatively clear.
Endoscopic examination by dye scattering method clearly revealed the margin of the lesions resulting in an effective observation of the granular elevations.
Of the 37 cases of villous adenoma, 33 cases, or 89.2%, were cancerous. The breakdown of this figure showed 29 carcinoma in villous adenoma and four invasive carcinoma. The result suggests that once the lesion is diagnosed as villous adenoma, clinically all the cases should be treated as malignant.
Surgical operation is the basic treatment for villous adenoma. Polypectomy is applicable only when the lesion is small enough for a total resection, or it is pedunculated villous adenoma.
Copyright © 1982, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


