Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
偽膜性腸炎は,腸管上皮の急性壊死,および白血球,fibrin,壊死産物などから成る偽膜形成性の非特異的な炎症である.本症は19世紀末ごろ,最初に報告1)2)されて以来,消化管手術後にみられる術後合併症と考えられていた.その後1950年ごろより手術に関係なく,抗生剤投与後に発症することが知られ,にわかに注目を浴びるようになった.特に欧米を中心に,lincomycinおよびclindamycinが誘因と考えられる偽膜性大腸炎の発生は,既に多数報告されている3)~5).わが国でも抗生剤の多用により,その発生は比較的まれではなくなってきた.最近われわれは,amoxicillin(AM-PC)による偽膜性大腸炎の1例を経験したので,その概要について報告する.
A 51-year-old housewife was admitted to our hospital on September 7, 1979, with a week's history of watery diarrhea characterized by the passage of 20 to 30 bowel motions per day and fever. Two weeks prior to the development of these symptoms she had been given amoxicillin (AM-PC) 750mg daily for commoncold.
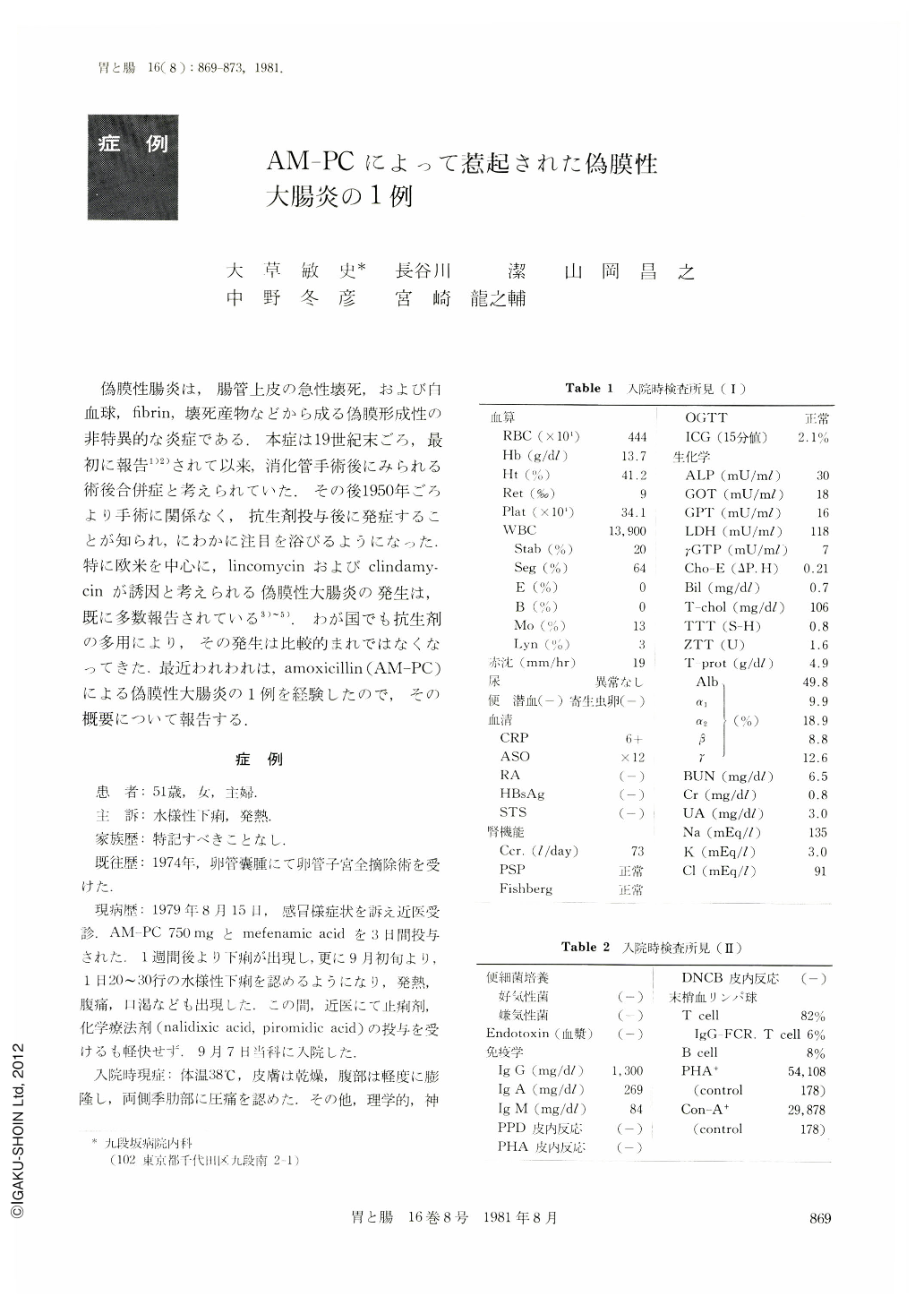
On admission she had fever of 38℃. The whitecell count was 13,900/mm3, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 19mm/hr, and CRP was positive. Stools were negative for occult blood. Repeated stool cultures were negative for enteric pathogens. Skin tests of PPD, PHA and DNCB were negative.
A barium enema was grossly abnormal showing “thumb-printing” in the entire colon but the small intestine was radiographically normal. Colonoscopy revealed a large number of thick, yellowish-white patches over the surface of the colon. Biopsy specimens were interpreted as consistent with pseudomembranous colitis.
A diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis after oral AM-PC therapy was made. After the patient was given CEX, the fever subsided promptly. White blood cell count became normal, but watery diarrhea contimed. After ten days of topical steroid therapy, diarrhea ceased. Skin tests of PPD and PHA became positwe.
AM-PC-associated pseudomembranous colitis is very rare. Stool cultures were negative for Clostridirrm diffrcile. Because there was no underlying abnormalities and immunologic reaction was decreased on admission, we suggest that immunologic mechanisms might have been operative in this case. The patient made a dramatic recovery by topical steroid therapy.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


