Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
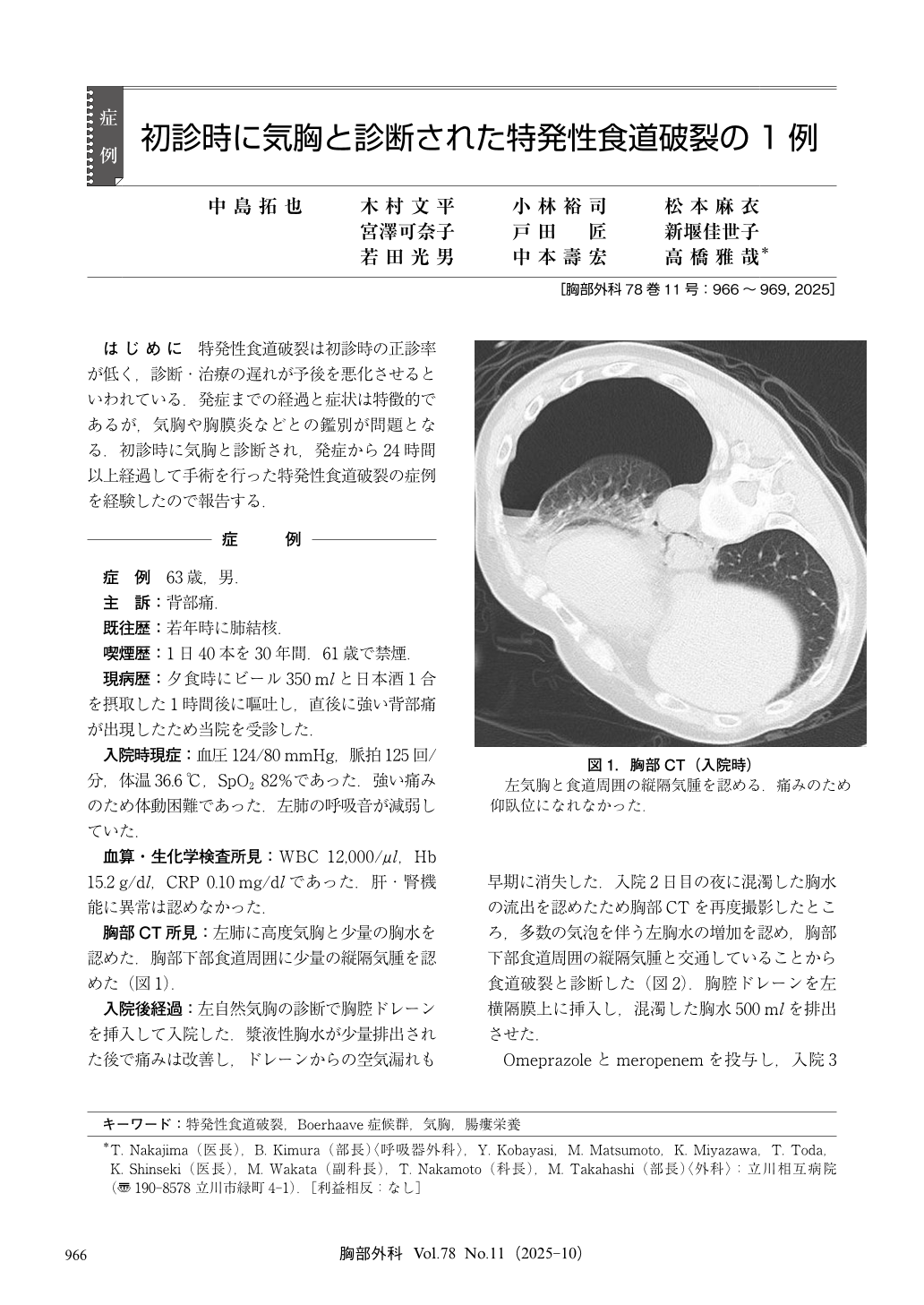
はじめに 特発性食道破裂は初診時の正診率が低く,診断・治療の遅れが予後を悪化させるといわれている.発症までの経過と症状は特徴的であるが,気胸や胸膜炎などとの鑑別が問題となる.初診時に気胸と診断され,発症から24時間以上経過して手術を行った特発性食道破裂の症例を経験したので報告する.
We experienced a case of idiopathic esophageal rupture, which can easily become severe. The patient was a 63-year-old man. At the initial visit, he was diagnosed with pneumothorax, but computed tomography (CT) showed mediastinal emphysema and esophagography showed perforation, which led to the diagnosis of the above disease. Surgery was performed more than 24 hours after the initial diagnosis. The perforation was closed with sutures and covered with mediastinal pleura. An enterostomy was added at the same time. Postoperatively, pneumonia and pleural effusion were observed, but the patient was discharged from the hospital without serious complications due to systemic management including measures against sepsis and respiratory complications and nutritional management. In the postoperative management of this disease, it is important to pay attention to systemic management such as nutritional management as well as countermeasures against infection and respiratory complications.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2025