Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
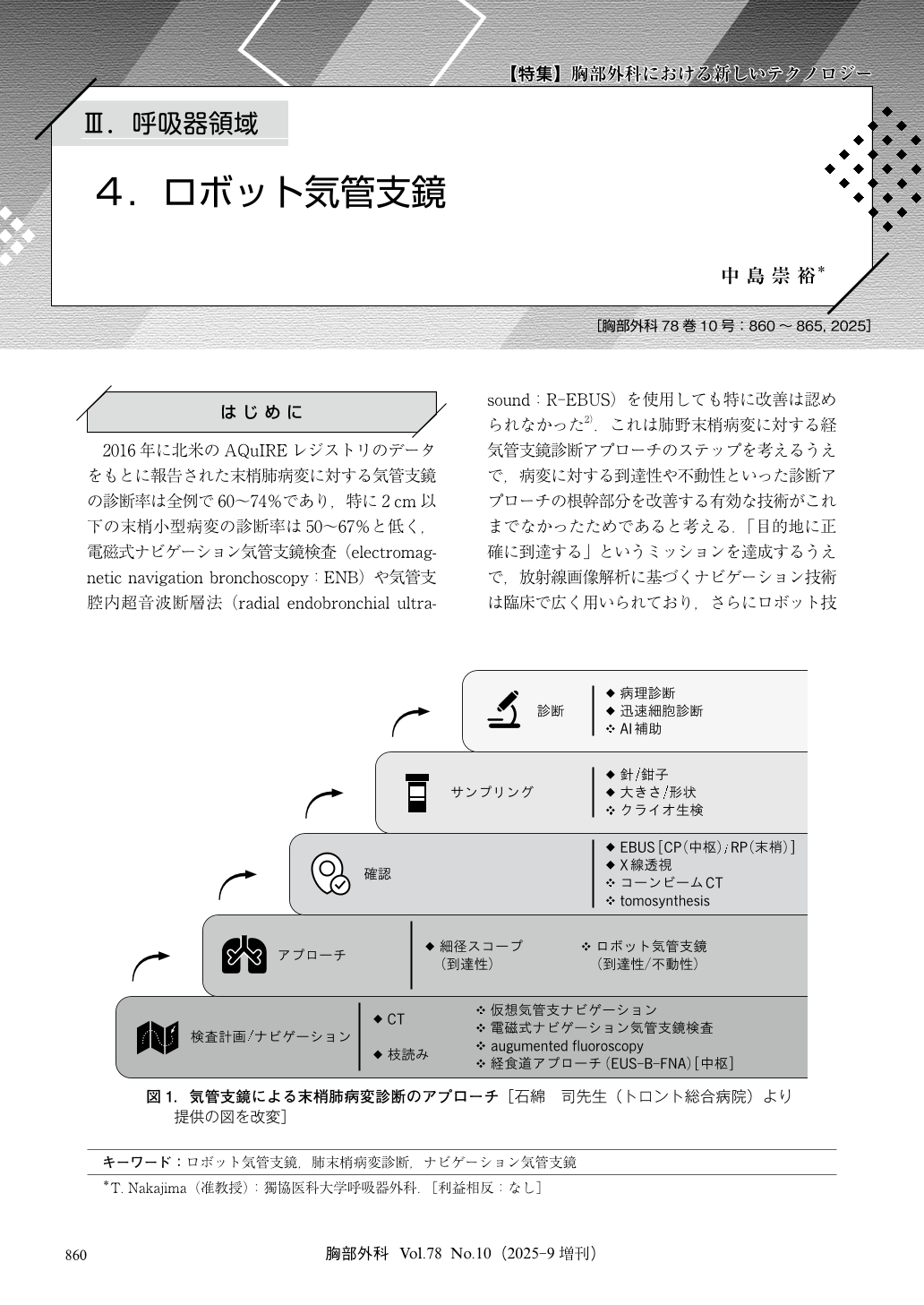
2016年に北米のAQuIREレジストリのデータをもとに報告された末梢肺病変に対する気管支鏡の診断率は全例で60~74%であり,特に2 cm以下の末梢小型病変の診断率は50~67%と低く,電磁式ナビゲーション気管支鏡検査(electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy:ENB)や気管支腔内超音波断層法(radial endobronchial ultrasound:R-EBUS)を使用しても特に改善は認められなかった2).これは肺野末梢病変に対する経気管支鏡診断アプローチのステップを考えるうえで,病変に対する到達性や不動性といった診断アプローチの根幹部分を改善する有効な技術がこれまでなかったためであると考える.「目的地に正確に到達する」というミッションを達成するうえで,放射線画像解析に基づくナビゲーション技術は臨床で広く用いられており,さらにロボット技術を組み合わせることで,高精度な末梢診断を行うために不可欠な「到達性」と「不動性」の両者を解決することができ,肺野末梢病変の診断率向上に寄与するだけでなく,将来の経気管支鏡的治療にも道を拓く重要な医療技術であると考えている.
Robotic bronchoscopy is an innovative bronchoscopic technique that combines advanced navigation systems with precise robotic control. This integration allows for highly accurate maneuvering and enhanced procedural safety, thereby contributing to further minimally invasive approaches in bronchoscopic diagnostics. In addition to diagnostic applications, its superior reach and stability suggest promising potential for future therapeutic interventions, such as bronchoscopic ablation. These developments indicate that a “one-stop shop” encompassing both diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer may soon become a reality. Although robotic bronchoscopy has not yet been introduced in Japan, its adoption is rapidly progressing in North America. Furthermore, other regions are also witnessing increased regulatory approvals and implementation of robotic-assisted bronchoscopic systems. As technological advancements continue and clinical evidence accumulates, the global dissemination of robotic bronchoscopy is expected to accelerate, potentially transforming the landscape of pulmonary medicine.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2025


