Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
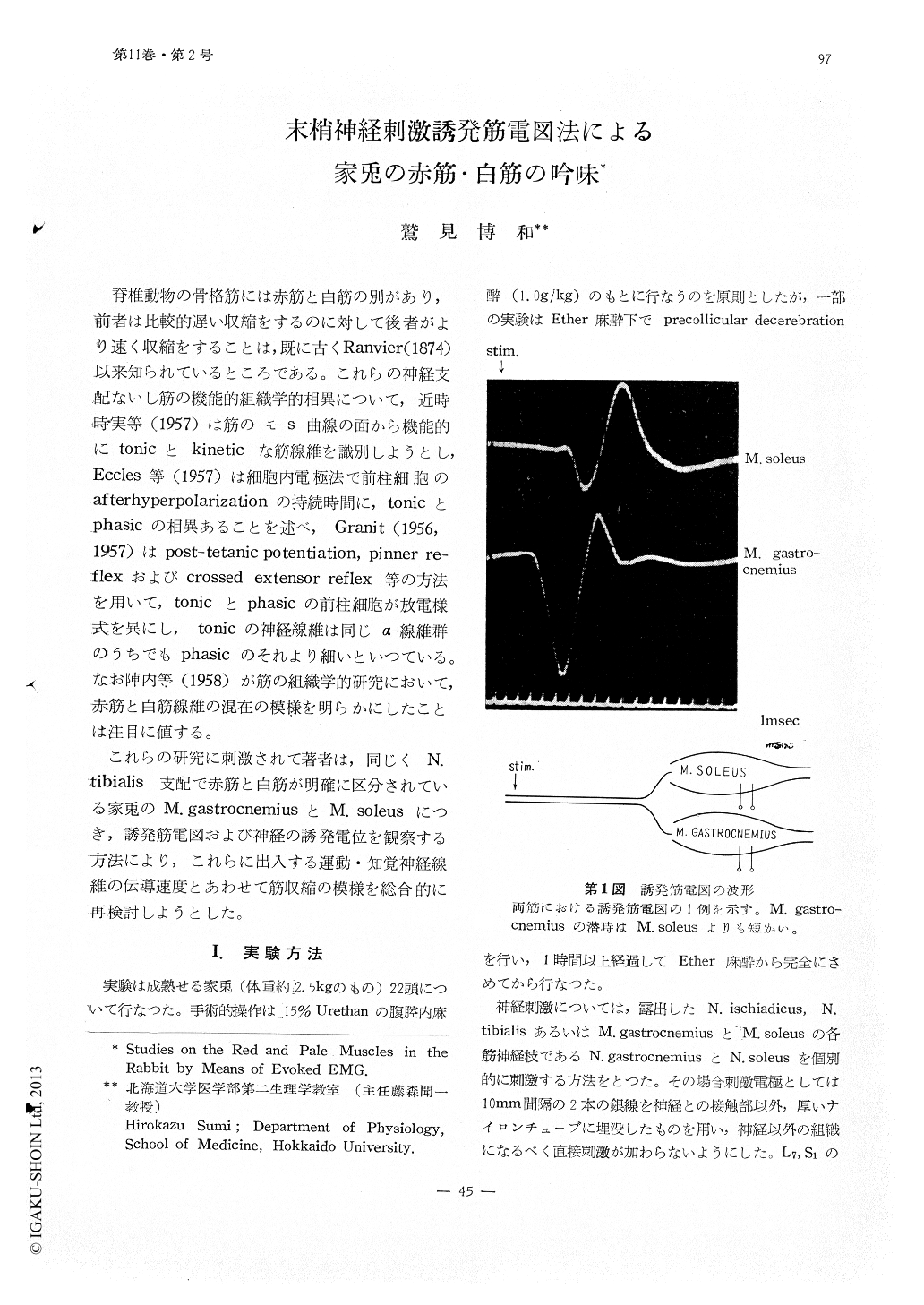
脊椎動物の骨格筋には赤筋と白筋の別があり,前者は比較的遅い収縮をするのに対して後者がより速く収縮をすることは,既に古くRanvier(1874)以来知られているところである。これらの神経支配ないし筋の機能的組織学的相異について,近時時実等(1957)は筋のモ-s曲線の面から機能的にtonicとkineticな筋線維を識別しようとし,Eccles等(1957)は細胞内電極法で前柱細胞のafterhyperpolarizationの持続時間に,tonicとphasicの相異あることを述べ,Granjt(1956,1957)はpost-tetanic potentiation,pinner reflexおよびcrossed extensor reflex等の方法を用いて,tonicとphasicの前柱細胞が放電様式を異にし,tonicの神経線維は同じα-線維群のうちでもphasicのそれより細いといつている。なお陣内等(1958)が筋の組織学的研究において,赤筋と白筋線維の混在の模様を明らかにしたことは注目に値する。
Evoked EMGs were recorded from the gastrocnemius (pale muscle) and soleus muscle (red muscle) in the rabbit, by stimulating the gastrocnemius and soleus nerve respectively at two different sites, and the maximal conduction velocity of gastrocnemius and soleus motorfibres was measured. Doubel-coaxial needle electrodes were used for picking up evoked EMG.
The maximal conduction velocity of the sensory and motor fibre both of gastrocnemius and soleus nerve was also compared picking up potential from the ventral and dorsal roots or respective muscle nerve.
1) The H_wave was difficult to recognize in these muscles.
2) The maximal conduction velocity of the motor fibre in the gastrocnemius muscle was faster than that of in soleus nerve in each case. Statistically there was significant difference, too.
3) The maximal conduction velocity of motor fibres in both muscles was a little faster than that of corresponding sensory fibres in both.
4) The latency of evoked EMGs in soleus muscle became longer by increasing degrees when the electrode was moved in muscle from proximal to distal, while in the gastrocnemius muscle they did not show so much difference.
Copyright © 1960, THE ICHIRO KANEHARA FOUNDATION. All rights reserved.


