Japanese
English
原著
耳鼻科全身麻酔1821例の検討
Statistical Analysis on 1821 Cases of General Anesthesia in the Otolaryngeal Surgeries
松井 雅之
1
,
佐藤根 敏彦
1
,
佐藤 裕
2
,
淀野 美砂子
2
Masayuki Matsui
1
1青森労災病院麻酔科
2弘前大学医学部麻酔科
1Department of Anesthesiology, Aomori Rosai Hospital
pp.443-446
発行日 1983年6月20日
Published Date 1983/6/20
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1492209620
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
従来から耳鼻咽喉科の手術はその大多数が気道付近に関与するため,麻酔および手術に伴う合併症の発生頻度が異常に高いと報告されている1,2)。これは術者と気道を共有するため,術者に手術しやすい術野を提供すると同時に,気道を確保しなければならない困難性があるためで,術前,術中,術後を通じての患者管理のあらゆる面で細心の注意が要求される理由がここにある。
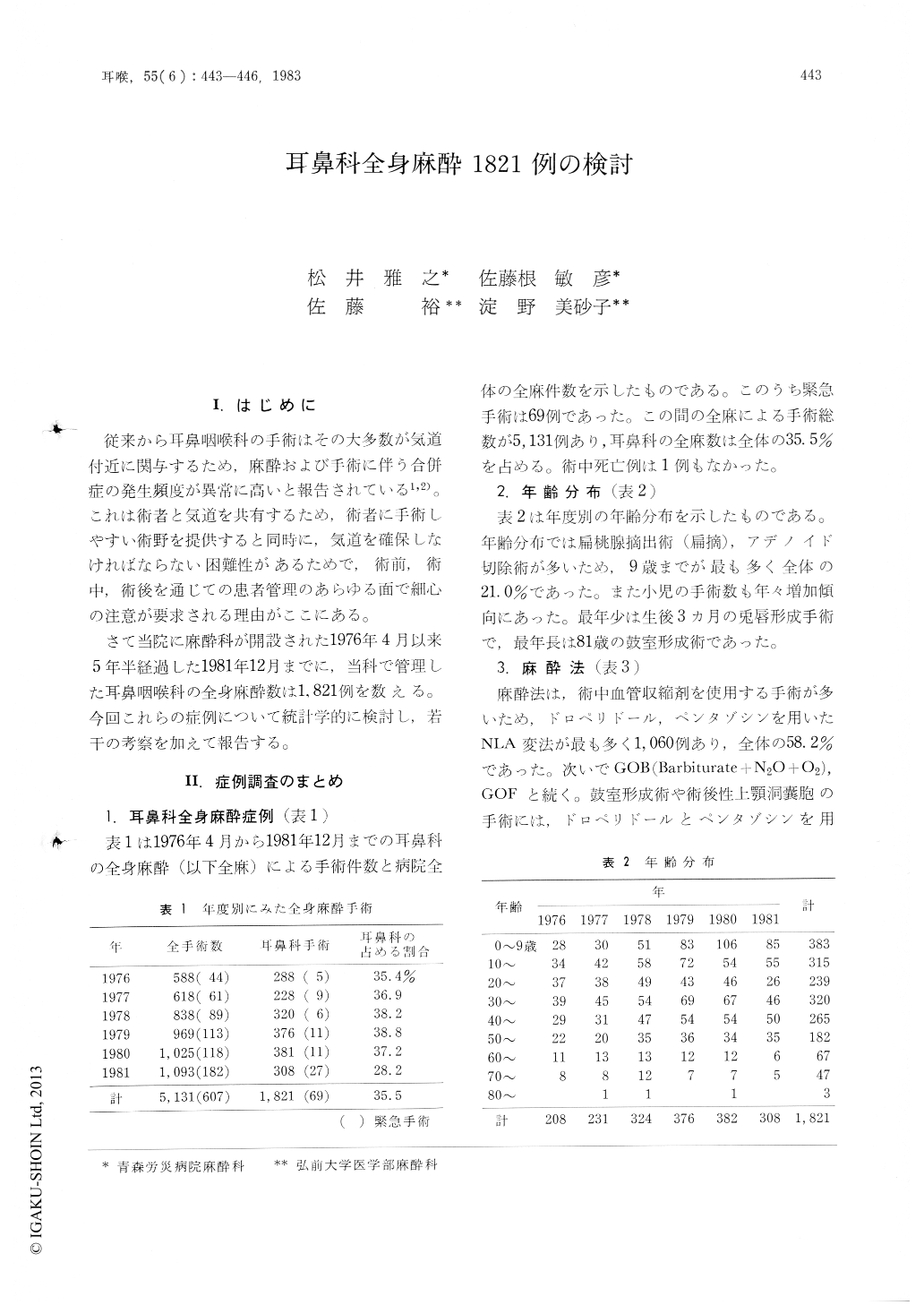
さて当院に麻酔科が開設された1976年4月以来5年半経過した1981年12月までに,当科で管理した耳鼻咽喉科の全身麻酔数は1.821例を数える。今回これらの症例について統計学的に検討し,若干の考察を加えて報告する。
From 1976 to 1981 general anesthesia was performed in 1821 otolaryngeal cases which comprised 35.5 per cent of all general anesthesia at that period.
The results were as follows :
1) The majority of the cases was tonsillectomy (524 cases or 28.8%).
2) 383 cases (21.0 per cent) were under 9 years of age.
3) The modified neuroleptanesthesia was used in most cases.
4) The emergency operations were performed in 69 cases.
Copyright © 1983, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


