Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
最近,脳動静脈奇形及び転移性脳腫瘍など一部の脳腫瘍に対して積極的にradiosurgeryが行われ,その有効性が多数報告されている10,20).この照射方法は,線量の集中度が極めて高く,周囲正常脳組織への影響が極めて少ない点が最大の特徴であるが,その適応と照射方法は,照射線量及び照射範囲の検討のみならず正常脳への影響を総合して判定する必要があり,その意味でradiosurgeryの正常脳に対する影響を検討することは,非常に重要であると思われる.しかし,従来の分割照射法に伴う放射線脳障害の解明が進むなかで,radiosur—geryに伴う脳障害については,現在までに一部の臨床例における報告6,12,21,25),あるいはマントヒヒ1,9),ラット7),ウサギ5)及びネコ18,19)を使用した動物モデルにおける主としで慢性期の病理組織学的な検討が行われているにすぎない.そこで,われわれはウサギを用いた照射モデルを作製し,dynamic CT(D-CT)で得られるパラメーター値の変動と,病理組織学的所見の両者を検討することで,linac stereotactic irradiation後の脳血流動態の変化及び,その原因について検討した.
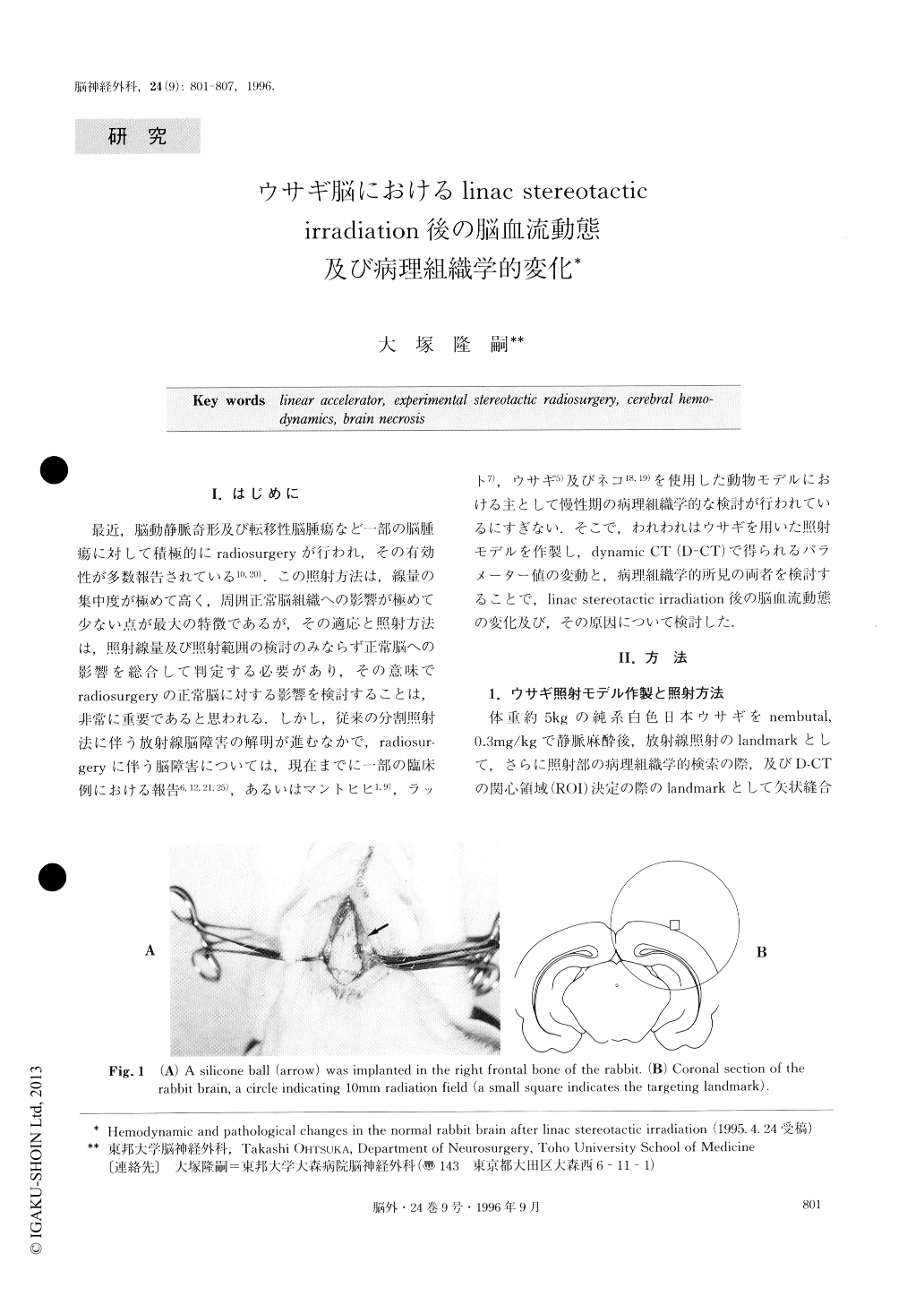
A number of clinical reports on stereotactic radiosur-gery using a linear accelerator have been published. So far, however, basic studies using the experimental animals have been comparatively few in number. Changes of cerebral hemodynamics and pathohistology in the animal brain after stereotactic, large dose irradia-tion was studied in this experiment. Fourteen pure im-bred Japanese white rabbits, weighing approximately 5kg, were used. As the landmark for irradiation target-ing, a small silicone ball, 2mm in diameter, was im-planted aseptically in the right frontal bone. A month after placing the landmark, stereotactic irradiation was given in a single dose of 100Gys by a linear accelerator with a 10mm collimator.
In all animals, dynamic CT was carried out before and immediately after irradiation, and thereafter, it was repeated at various intervals. Time density curve whichhas two parameters of peak-time (PT) and peak-height (PH), was drawn with the help of Sprine function. The ratios of PT, PH and CBF were calculated for their values in the irradiated area/values in the contralateral corresponding area. Two animals were sacrificed im-mediately, 1, 3, 7, 21, 90 and 180 days respectively after irradiation, and one animal was killed 1 year after radiation followed by another animal killed 2 years af-ter irradiation. Brains were removed and formalin-paraffin sections were made. All sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin and GFAP (glial fibrillary aci-dic protein).
In the brain of day 3, cerebral hemorrhage and an in-crease of astrocyte were demonstrated in the irradiated area. The increase of astrocyte had persisted for approx-imately 3 weeks. On the other hand, neurons and ves-sels appeared intact, even in the brain of day 90. In the brain of day 180, brain necrosis had developed in the irradiated area and necrosis had become wider and more prominent in the brains of 1 and 2 years after irradiation. Fibrinoid degeneration of capillaries was evident in the irradiated area and its adjacent areas. Regional cerebral blood flow (r-CBF) in the irradi-ated area decreased for 3 days and continued to remain at a lower level for a week. However, r-CBF increased thereafter again at 3 weeks. Then it gradually con-tinued to decrease and finally it became unmeasurable at 1 or 2 years after irradiation. To interpret the fact that there is a biphasic time course for r-CBF, the early decrease was attributed to local edema, and the later decrease was attributed to changes in the wall of ves-sels.
Copyright © 1996, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


