Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
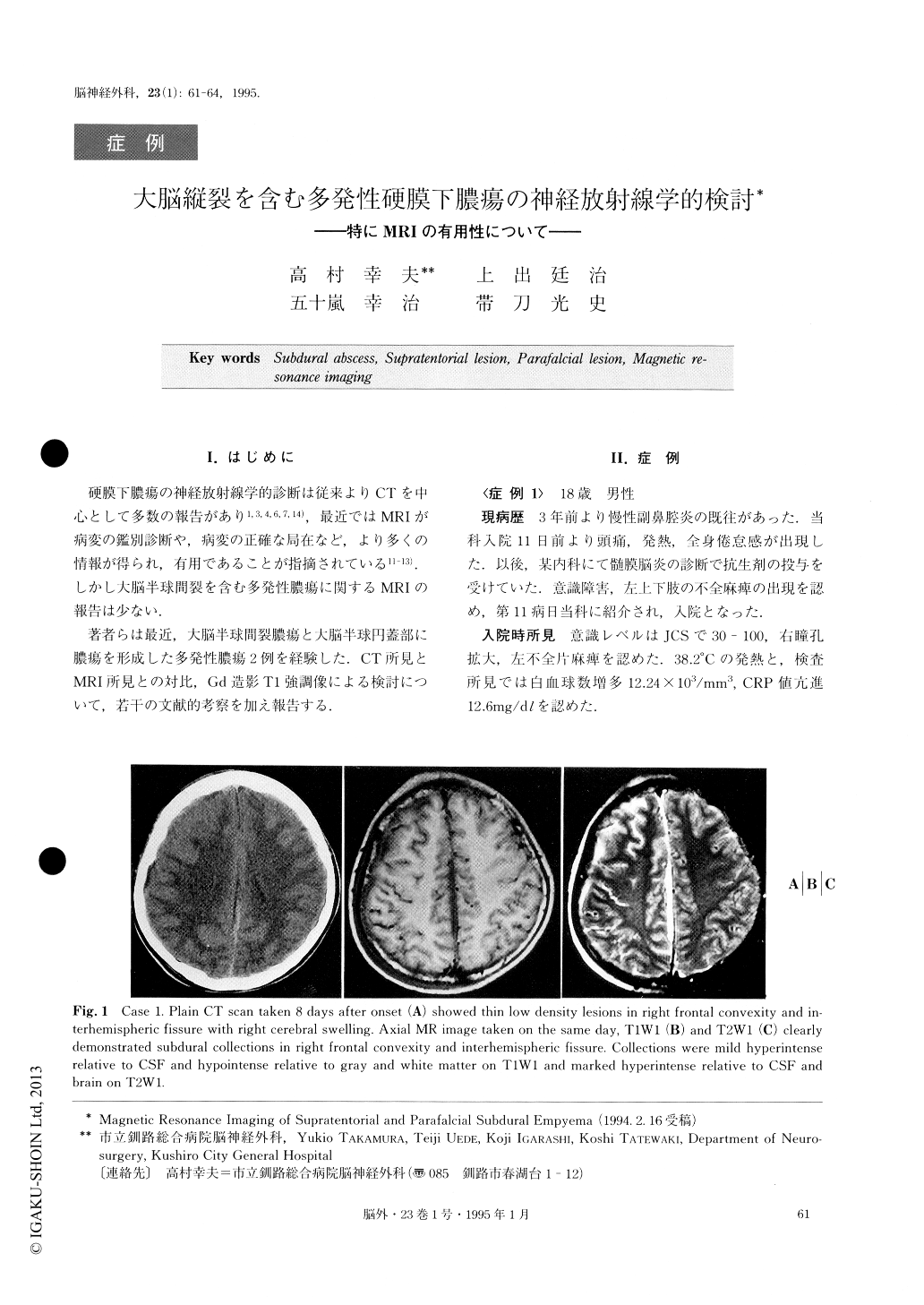
硬膜下膿瘍の神経放射線学的診断は従来よりCTを中心として多数の報告があり1,3,4,6,7,14),最近ではMRIが病変の鑑別診断や,病変の正確な局在など,より多くの情報が得られ,有用であることが指摘されている11-13).しかし大脳半球間裂を含む多発性膿瘍に関するMRIの報告は少ない.
著者らは最近,大脳半球間裂膿瘍と大脳半球円蓋部に膿瘍を形成した多発性膿瘍2例を経験した.CT所見とMRI所見との対比,Gd造影T1強調像による検討について,若干の文献的考察を加え報告する.
The authors report the MR imaging of two patients with mutltiple subdural empyemas, including one in the interhemispheric fissure.
MRI demonstrated convexity and interhemispheric collections which were mild hyperintense relative to CSF, hypointense relative to gray and white matter on T1W1, and marked hyperintense relative to CSF, and brain on T2W1. On the basis of signal intensity differ-ences, MRI can distinguish subdural empyemas from most sterile effusions and chronic subdural hematomas with similar CT appearances. MRI was found to be clearly more sensitive to subdural empyemas than CT, though such lesions missed on CT were considered to be relevant. MR was superior to CT in demonstrating the nature, presence, and extent of these lesions. In both cases, the capsule of the lesions demonstrated en-hancement, and connection between each lesion was obvious on contrast-enhanced MRI. It seems that con-rast-enhanced MR image may detect encapsulation of an abscess which can not be detected from conrast-enhanced CT.
We emphasized that the most significant factor in the successful surgical management of multiple subdural empyema, particularly including interhemisperic collec-tions is the accurate location of pus. This can be reli-ably achieved with MR imaging.
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


