Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
脳静脈洞血血栓症は,頭頸部感染症に続発するもの以外に,各種疾患の合併症および薬剤の副作用として発生するが,原因不明のものも少なくない2,7,10,16).
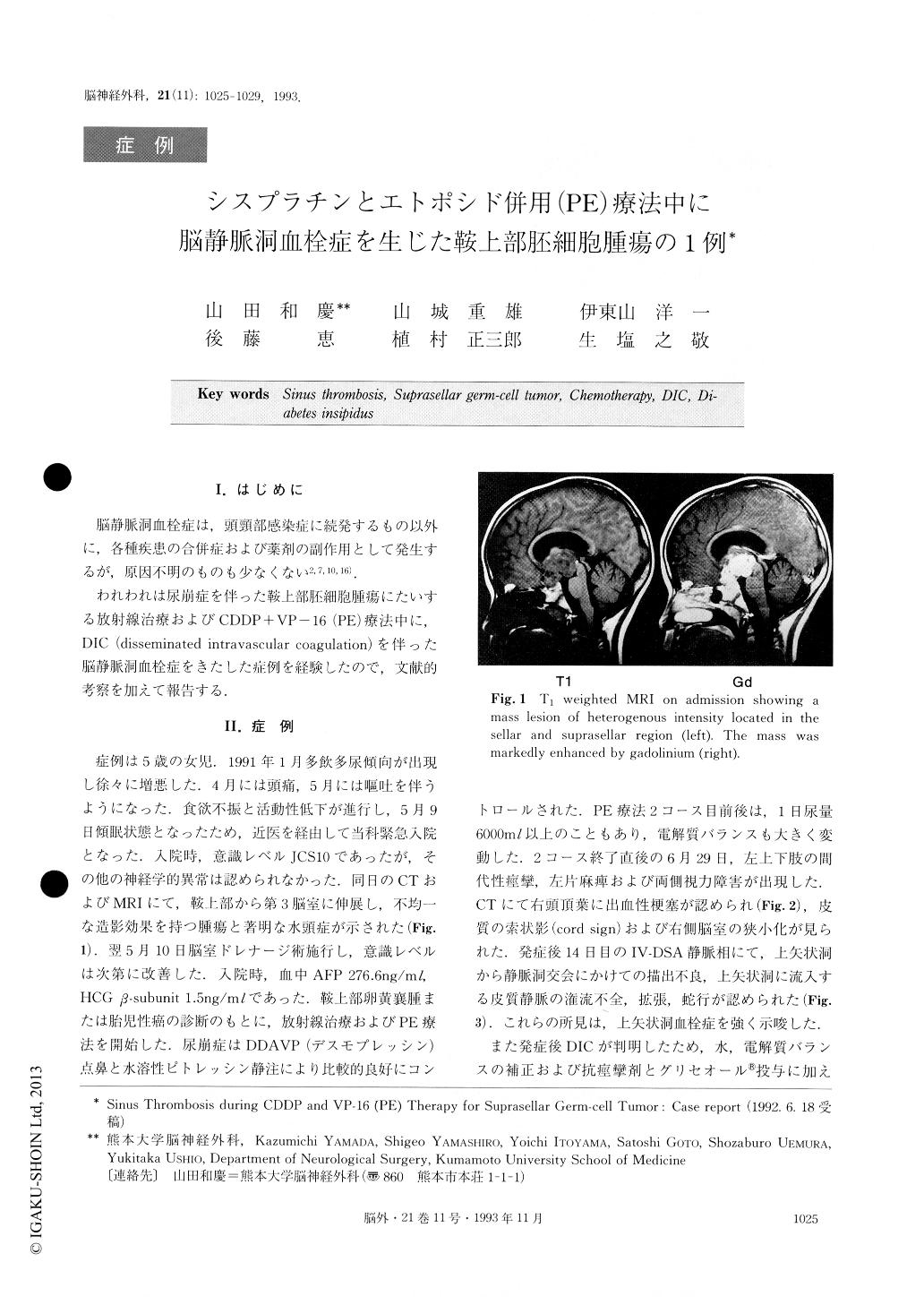
われわれは尿崩症を伴った鞍上部胚細胞腫瘍にたいする放射線治療およびCDDP+VP−16(PE)療法中に,DIC(disseminated intravascular coagulation)を伴った脳静脈洞血栓症をきたした症例を経験したので,文献的考察を加えて報告する.
A case of sinus thrombosis occurring during combina-tion chemotherapy with CDDP and VP-16 (PE) for a suprasellar germ-cell tumor is presented. A 5-year-old girl developed polyuria, polydipsia and headache in April, 1991 and became unconscious on May 10, 1991, when MRI and CT demonstrated a suprasellar tumor and marked hydrocephalus.
After a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt operation, radiothe-rapy and two courses of PE therapy were carried out. Serum NSE was measured and analyzed in relation to the level of consciousness (Japan Coma Scale) upon admission, the modified Araki's classification, the presence or ab-sence of skull fracture, findings from computed tomogra-phy (CT) scans and the prognosis according to the Glas-gow outcome scale. Differences were compared by t-test to determine significance. When the level of conscious-ness was compared with the serum NSE level upon admission, the NSE level was significantly higher in pa-tients showing a three digit code disturbance of con-sciousness than in the other patients (p < 0.005). When NSE was analyzed in relation to the modified Araki's classification, the NSE level for the prolonged type with focal signs was higher than the NSE level for any other type (p < 0.0001 compared to the transient type). The NSE level was significantly higher in patients with skull fracture than in patients without skull fracture (p<0.01). The NSE level was significantly higher in patients show-ing contusion on CT scans than in patients without con-tusion (p< 0.005). When NSE was analyzed inrelation to the prognosis, the NSE level was significantly higher in patients who later died or fell into a vegetative state than in the other patients (p < 0.0001). These results suggest that serum NSE level provides useful information for assessing the severity of injury to the brain parenchyma and prognosis.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


