Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
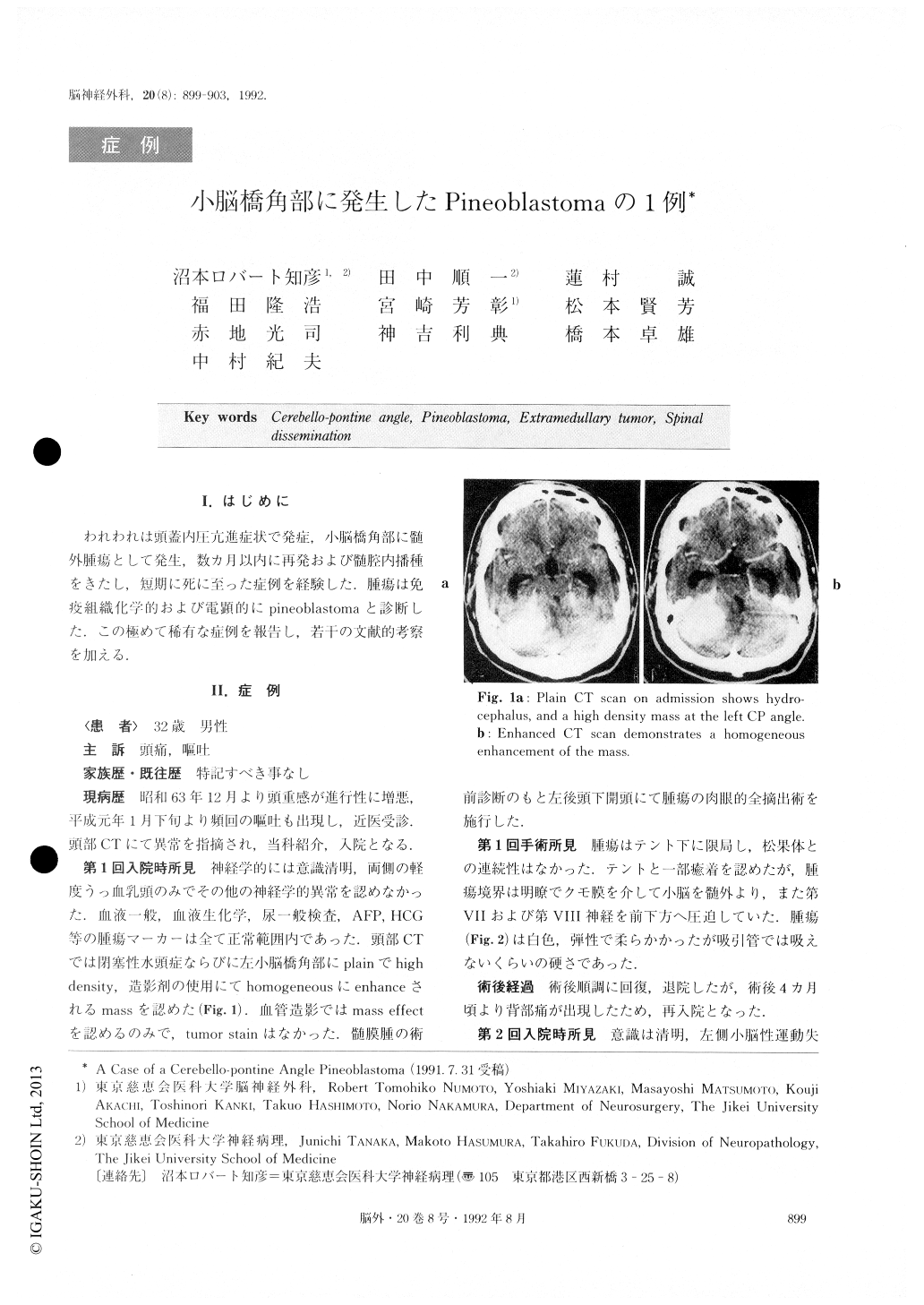
われわれは頭蓋内圧亢進症状で発症,小脳橋角部に髄外腫瘍として発生,数カ月以内に再発および髄腔内播種をきたし,短期に死に至った症例を経験した.腫瘍は免疫組織化学的および電顕的にpineoblastomaと、診断した.この極めて稀有な症例を報告し,若干の文献的考察を加える.
An extremely rare case of a left cerebello-pontine angle (CP angle) pineoblastoma has been reported.
The patient was a 32-year-old male whose initial manifestations were those of increased intracranial pressure. CT scan showed a large enhancing mass lo-cated at the left CP angle, associated with a moderate occlusive hydrocephalus. Left suboccipital craniectomy was performed. The mass was an extramedullary tumor which had compressed the left cerebellar hemisphere, and was easily separable from the adjacent tissue. The tumor was totally resected, and the patient had a tem-porary release from the symptoms. Recurrence and spinal dissemination were found within the ensuing few months. The tumor had invaded deeply through the left CP angle into the cerebellar parenchyme, and showed no anatomical connection with the pineal body. The tumor dissemination was also observed widely in the spinal subarachnoid space. No abnormalities at the pineal region were able to be confirmed using CT and MRI studies. Irradiation to the whole brain, to the localized left CP angle and to the spinal cord with addi-tional chemotherapy was given. The patient died half a year after the first operation. Autopsy was not per-formed.
Histopathologically, the tumor was delineated into lobular structures by reticulin fibrils and vimentin-positive interstitial tissue. Tumor cells were small in size, and had irregularly shaped hyperchromatic nuclei with increased mitotic figures, and formed various types of rosettes ; pineocytomatous, Flexner-Winter-Steiner, Homer-Wright and perivascular. Fine argyro-philic cell processes with club-shaped expansions were demonstrated inside the pineocytomatous rosettes. Some tumor cells contained PTAH and GFAP-positive bipolar fibers, and the others were immunocytochemi-cally positive for NFP, retinal S-protein and synap-tophysin.
Electron microscopic studies confirmed the histo-pathological results. Though synaptic structures were not visible, cells with occasional desmosome-like junc-tional devices were demonstrated.
According to the revised histologic WHO classifica-tion, this tumor was histologically diagnosed as a mixed pineocytoma / pineoblastoma, the predominant component of which was that of pineoblastic growth. There are old reports of “pinealomas” turning out to be “germinomas” at the CP angle, but there are no reports of true pineal parenchymal tumors. The tumor was thought to have had its origin at the ependymal lining of the recessus lateralis ventriculi quarti.
We suggest that immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy are invaluable for making a diagnosis of primitive tumors of the central nervous system.
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


