Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
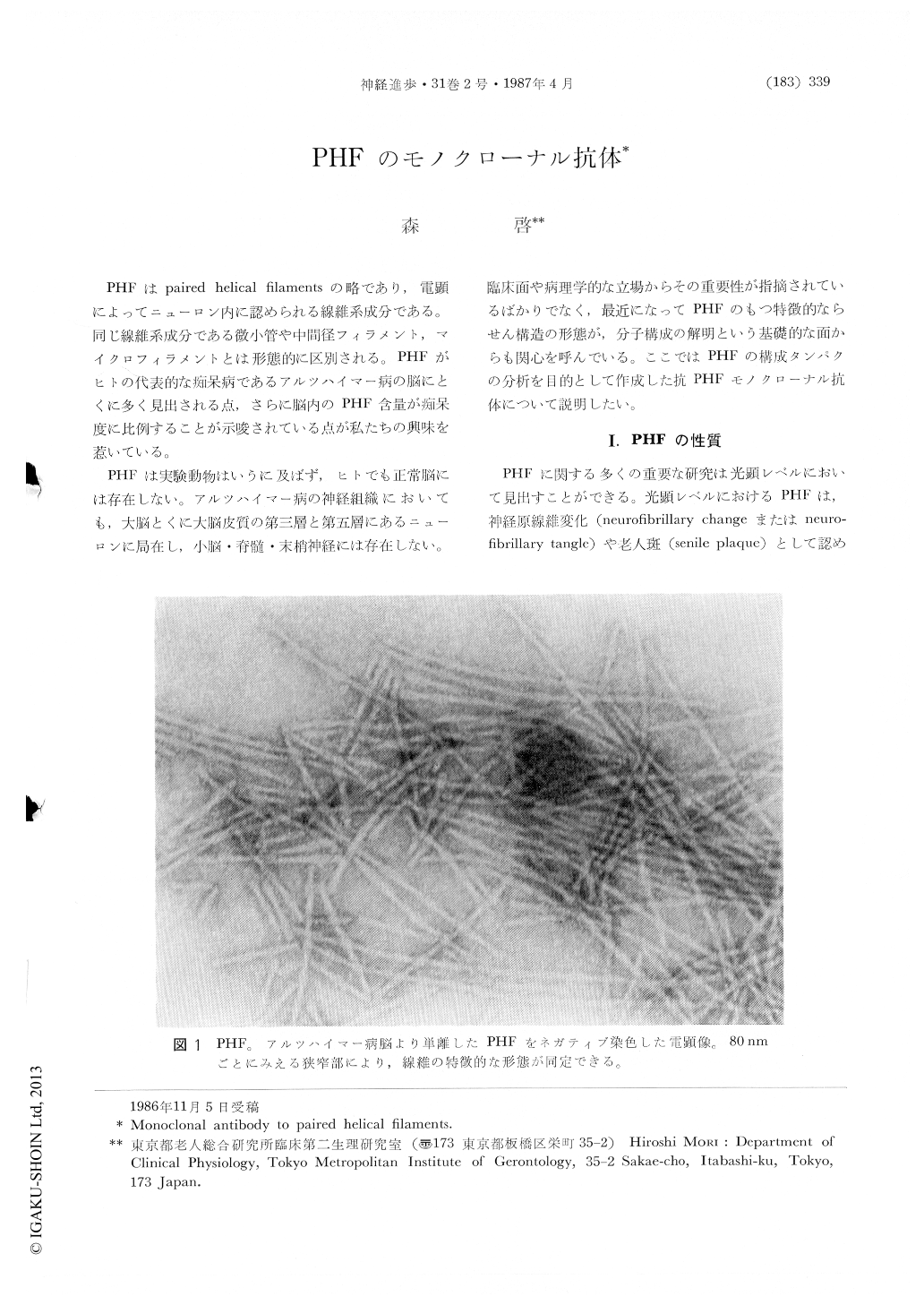
PHFはpaired helical filamentsの略であり,電顕によってニューロン内に認められる線維系成分である。同じ線維系成分である微小管や中間径フィラメント,マイクロフィラメントとは形態的に区別される。PHFがヒトの代表的な痴呆病であるアルツハイマー病の脳にとくに多く見出される点,さらに脳内のPHF含量が痴呆度に比例することが示唆されている点が私たちの興味を惹いている。
PHFは実験動物はいうに及ばず,ヒトでも正常脳には存在しない。アルツハイマー病の神経組織においても,大脳とくに大脳皮質の第三層と第五層にあるニューロンに局在し,小脳・脊髄・末梢神経には存在しない。臨床面や病理学的な立場からその重要性が指摘されているばかりでなく,最近になってPHFのもつ特徴的ならせん構造の形態が,分子構成の解明という基礎的な面からも関心を呼んでいる。ここではPHFの構成タンパクの分析を目的として作成した抗PHFモノクローナル抗体について説明したい。
Paired helical filaments (PHF), a distinct type of filaments, are the principal constituent of neurofibrillary tangles and neurites in senile plaques in the cerebral cortex of the subjects with Alzheimer's disease. The insolubility of PHF in various solvents enabled us to obtain highly purified PHF, but prevented the conventional analysis of their components. Here I reported that a hybridoma producing antibody (DF2) against PHF has been obtained after fusion between mouse myeloma and spleen cells from a Lewis rat immunized with purified PHF. DF2 has been found to recognize PHF and 5 kDa protein by the immunoblot study, suggesting that 5 kDa protein is a component of PHF. On the basis of immunoreactivity of DF2, antigenic 5 kDa protein was purified from human brain with molecular-sieving chromatography and HPLC. Purified 5 kDa protein was sequenced and proved to be ubiquitin. Vice versa, affinity-purified antibody to ubiquitin is found to decorate PHF at light and electromicroscopic level. Furthermore, ubiquitin sequence was directly identified in the proteolytic digestion of PHF. The epitope of DF2 was also determined by means of dot-immunobinding test using synthetic peptides and proteolytic fragments derived from ubiquitin. This epitope was found to occur near the /3 structure in the hydrophilic region by computer-aided hydrophobicity profile analysis and the secondary structure prediction.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


