Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
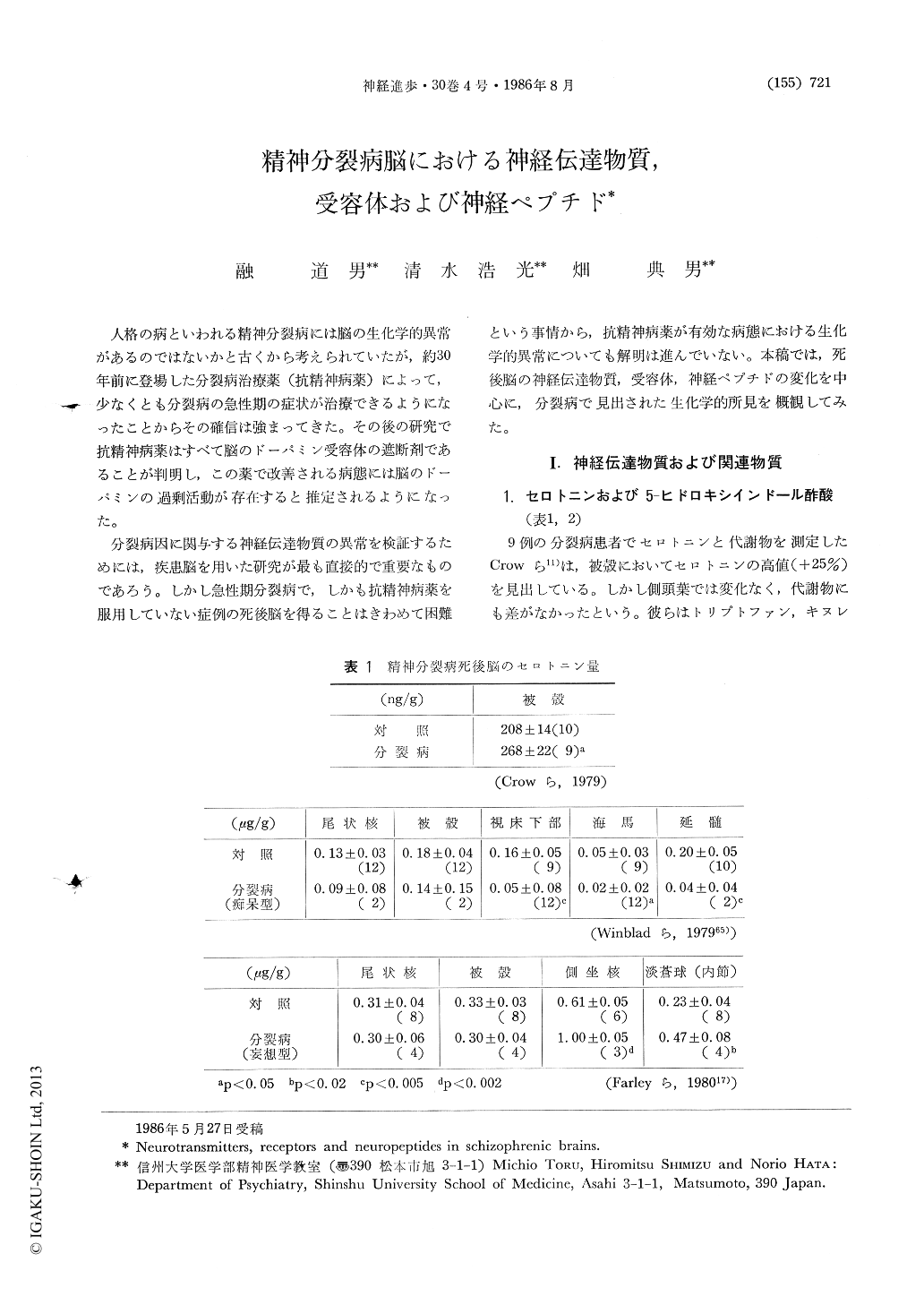
人格の病といわれる精神分裂病には脳の生化学的異常があるのではないかと古くから考えられていたが,約30年前に登場した分裂病治療薬(抗精神病薬)によって,少なくとも分裂病の急性期の症状が治療できるようになったことからその確信は強まってきた。その後の研究で抗精神病薬はすべて脳のドーパミン受容体の遮断剤であることが判明し,この薬で改善される病態には脳のドーパミンの過剰活動が存在すると推定されるようになった。
分裂病因に関与する神経伝達物質の異常を検証するためには,疾患脳を用いた研究が最も直接的で重要なものであろう。しかし急性期分裂病で,しかも抗精神病薬を服用していない症例の死後脳を得ることはきわめて困難という事情から,抗精神病薬が有効な病態における生化学的異常についても解明は進んでいない。本稿では,死後脳の神経伝達物質,受容体,神経ペプチドの変化を中心に,分裂病で見出された生化学的所見を概観してみた。
It has been hypothesized about the etiology of schizophrenia that abnormalities in central neuro-transmitter system is involved. Much evidence has indicated an important role for dopamine in the brain, especially in acute states. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that antipsychotic drugs play their role in close relation to their antidopa-minergic potency.
In this review paper, we collected biochemical findings mainly obtained from post-mortem schizo-phrenic brains. The focus is first on the classical neurotransmitters, second on the neurotransmitter receptors and third on the neuropeptides.After we reviewed the data of serotonin, noradrenaline, choline acetyltransferase, γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamic acid, dopamine system was examined. In our analysis of ten or more post-mortem brains from chronic schizophrenic patients, dopamine concentrations of schizophrenics did not differ from those of controls in the n. caudatus, putamen, n. ruber and n. subthalamicus. A significantly increased homovanillic acid level was observed in the putamen and substantia nigra. A most important finding is that tyrosine hydroxylase was measured to be increased in the n. caudatus, putamen and substantia nigra.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


