Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
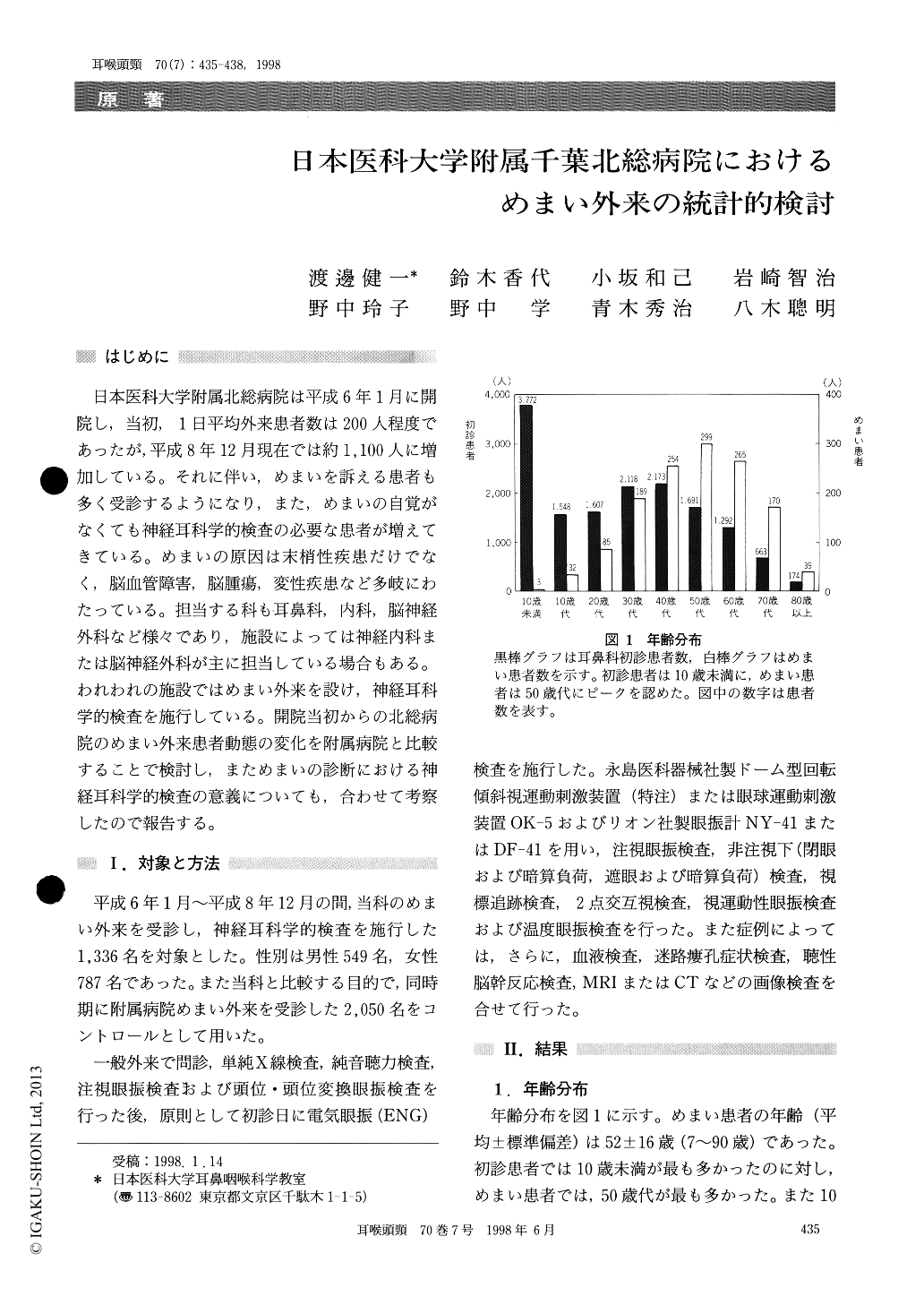
日本医科大学附属北総病院は平成6年1月に開院し,当初,1日平均外来患者数は200人程度であったが,平成8年12月現在では約1,100人に増加している。それに伴い,めまいを訴える患者も多く受診するようになり,また,めまいの自覚がなくても神経耳科学的検査の必要な患者が増えてきている。めまいの原因は末梢性疾患だけでなく,脳血管障害,脳腫瘍,変性疾患など多岐にわたっている。担当する科も耳鼻科,内科,脳神経外科など様々であり,施設によっては神経内科または脳神経外科が主に担当している場合もある。われわれの施設ではめまい外来を設け,神経耳科学的検査を施行している。開院当初からの北総病院のめまい外来患者動態の変化を附属病院と比較することで検討し,まためまいの診断における神経耳科学的検査の意義についても,合わせて考察したので報告する。
We performed statistical analysis of patients who visited vertigo clinic. Compared patients in 1994 with those in 1996, the ratio of patients who visited vertigo clinic in the first medical examination ofotolarygology increased to 170%. Peripheral dis-eases were most frequently observed and it's ratio increased gradually. In the peripheral diseases the horizontal-rotatory nystagmus was observed fre-quently and in the central diseases the horizontal or vertical nystagmus were observed. The ratio of abnormal signs in the eye tracking test and opto-kinetic pattern test was about 1% in the peripheral diseases, however, 30~40% in the central diseases.
Copyright © 1998, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.