Japanese
English
原著
ACE阻害剤が原因として疑われた頭頸部血管性浮腫の1例
A Case of Angioedema Probably Related to the Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
佐伯 忠彦
1
,
清水 義貴
1
,
三和 秀輔
2
Tadahiko Saiki
1
1新日鐵広畑病院耳鼻咽喉科
2三和内科医院
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Nippon Steel Hirohata Hospital
pp.507-510
発行日 2000年7月20日
Published Date 2000/7/20
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1411902214
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
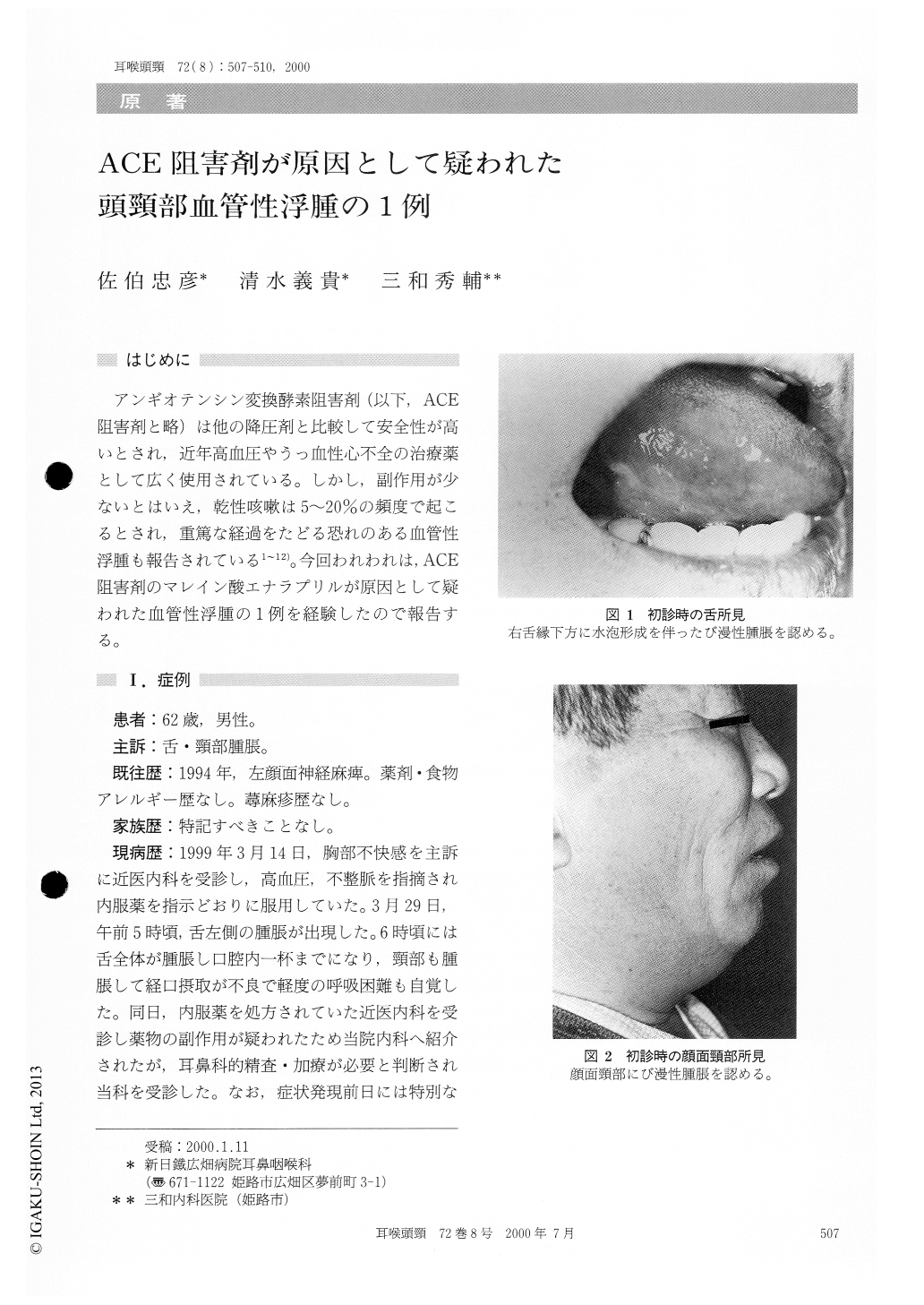
アンギオテンシン変換酵素阻害剤(以下,ACE阻害剤と略)は他の降圧剤と比較して安全性が高いとされ,近年高血圧やうっ血性心不全の治療薬として広く使用されている。しかし,副作用が少ないとはいえ,乾性咳嗽は5〜20%の頻度で起こるとされ,重篤な経過をたどる恐れのある血管性浮腫も報告されている1〜12)。今回われわれは,ACE阻害剤のマレイン酸エナラプリルが原因として疑われた血管性浮腫の1例を経験したので報告する。
A 62-year-old male complained of edema of the tongue, larynx, face and neck. The edema was occurred suddenly in the morning four days after administration of ACE inhibitor. The patient was admitted to hospital and treated with prednisolone, antiallergic drugs. Edema disappeared two days after the onset of symptoms.
Copyright © 2000, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.