Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
脳血管の水分透過性に関与する可能性のある中枢性arginine vasopressin(AVP)について,延髄網様体(MORF)の電気刺激前後の髄液および損傷脳白質におけるAVPの変化について雑種成猫57頭を用いて実験的に検討した。髄液および血漿中AVPの正常値は,各々4.0±2.2,9.9±3.6pg/mlであった。正常脳にMORF刺激を80分間加えた群では,髄液中AVPは,進行性に増加し,刺激終了時には前値に比し,約1.7倍の有意な上昇を示した。凍結損傷後約17時間経過した浮腫脳に同様のMORF刺激を加えた群では,約2.2倍とさらに有意な上昇を示した。浮腫脳に高血圧を負荷した群では,有意な変化を認めなかった。血漿中AVPおよび血漿浸透圧は各群とも有意な変化を認めなかった。一方,組織中AVPは,損傷側,非損傷側とも各群間で有意差を認めなかった。下位脳幹の電気刺激によって,正常脳,浮腫脳ともに中枢性(髄液中)AVPが増加することが明らかとなった。
It has been reported that after 40 minutes of stimulation of the medullary reticular formation (MORF) , widespread significant increase by 1. 4% to 2.8% in brain water content occurs in white matter of the injured hemisphere. Recent studies indicate that centrally released arginine vasopressin (AVP) influences water permeability of the brain in both normal and pathological conditions. The pres-ent study was carried out to clarify the effect of electrical stimulation of MORF on centrally released AVP.
The cats were divided into three groups. In group A (16 cats) , electrical stimulation of MORF (lmsec, 5V, 50Hz) was carried out for 80 minutes in normal cats. In group B (11 cats) , stimulation was started17 hours after cold injury under the same conditions and carried out for 80 minutes. In group C (10 cats) , angiotensin II was administered to elevate blood pressure to the same degree as during MORF stimu-lation 17 hours after cold injury. AVP concentra-tions in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), plasma and brain tissue of the injured and non-injured white matter were measured by radioimmunoassay. Plasma osmolality was also determined by the freezing point depression method. Normal values (means ±S. D.) of CSF and plasma AVP were 4. 0 ± 2.2 and 9.9 ± 3.6 pg/m/ respectively. Plasma AVP and osmolality did not show significant changes before and at the end of experiments in all groups. There were no significant changes in CSF AVP by induced hypertension for 80 minutes (Group C). Stimulation of the medullary reticular formation resulted in significant and progressive increase in CSF AVP in normal and injured brain (Group A, B). The mean values of CSF AVP became approximately two times the prestimulation level after 80 minutes of stimulation in injured brain (Group B). There were no significant differences in tissue AVP both in the injured and in the non-injured hemisphere in all groups. These results suggest that stimulated condition of MORF increases in centrally released AVP, which may facilitate the production of vasogenic brain edema.
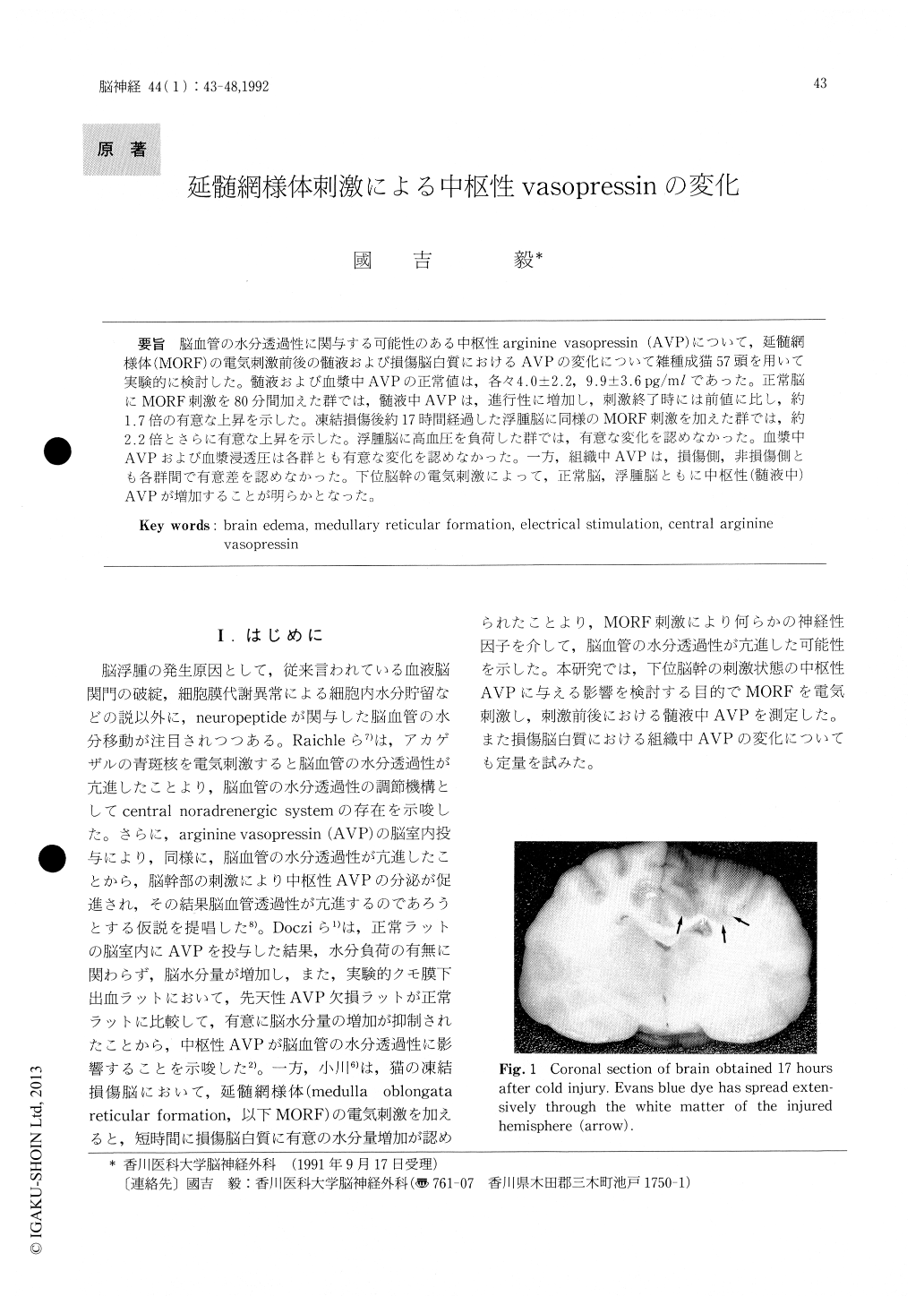
Copyright © 1992, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


