Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
抄録 14頭のラット実験脳腫瘍(9L gliosarcoma)と3頭の正常ラットを用いて,25%または20%mannitolの内頸動注によるosmotic blood brain barrier disruptionの際,cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum(CDDP)の腫瘍または正常組織内への移行濃度について,CDDPの単なる動注,または静注群と比較して検討した。CDDPの各平均腫瘍内濃度は,単に,CDDPのみ内頸動注した場合48.0μg/gに対し,25%mannitol併用動注では100.9μg/g,20% mannitol併用で96.77と高張滲透圧溶液により約2倍にCDDPの腫瘍組織内濃度が増加した。腫瘍周辺正常脳組織内へのCDDP濃皮は,25% mannitol群では腫瘍組織内と同様高値であったが,20% mannitol群では比較的低値であった。しかし,CDDP静注群では腫瘍組織内濃度はいずれも低値で平均9.2μg/gであり,周辺正常脳も低値であった。化学療法剤の腫瘍組織内移行促進を目的としたosmotic blood brain barrier disruptionに用いられる高張滲透圧溶液としては20%mannitolが適切である。
The limited effect of chemotherapy on malig-nant brain tumors has been related to tumor cell insensitivity to the drugs and to their in-effectial delivery to the tumor4,25,30). The studies by Groothuis6) and Neuwelt et al19,20) have shown that the studies of tumor vessel permeability show considerable variability in different areas of tumors and between defferent tumor models.
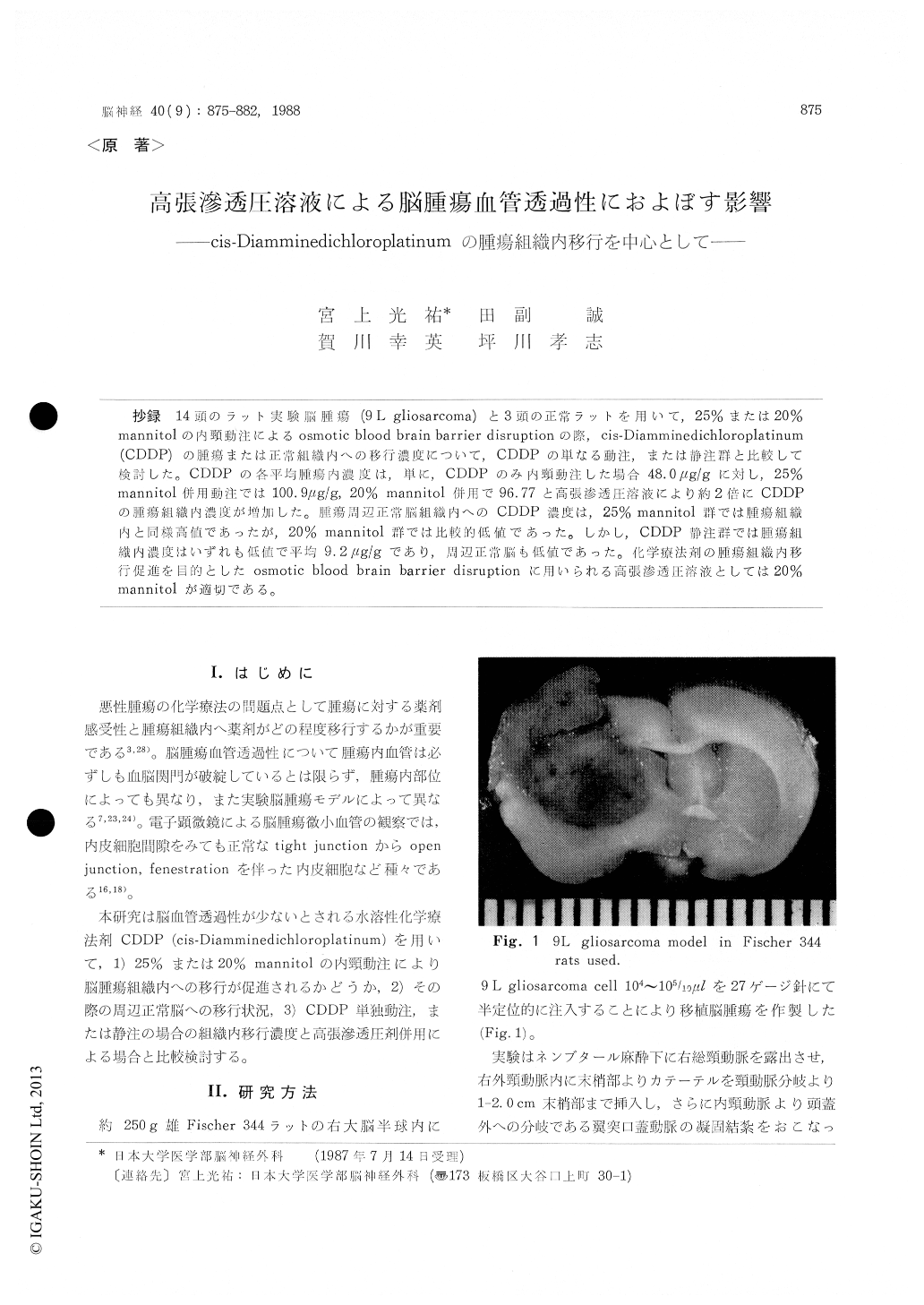
The present studies used the 9L gliosarcoma model in Fischer 344 rats to evaluate the increase of tumor vessel permeability by osmotic BBB open-ing on drug delivery to the tumor, brain adja-cent to tumor (BAT), and brain distant to tumor using cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (CDDP) as a chemotherapeutic agent which was watersoluble and rarely permeable to BBB. In addition the difference of delivery to normal brain and tumor tissue were studied on intravenous or in-tracarotid administration of cisplatin with or with-out intracarotid infusion of graded (20%, 25%) hyperosmolar mannitol.
Evans blue, which binds to plasma albumin, was used to provide a visual marker of BBB opening. 20% or 25% hyperosmolar mannitol infusion to right internal carotid artery for BBB disruption was done at 0.12 ml/sec for 30 sec with controlled re-spiration after temporally clipping of right com-mon carotid artery. Then cis-diamminedichloro-platinum (CDDP) was infused at 0.5 mg/ml/100 gr (body weight). In control studies isotonic saline instead of mannitol was infused to intracarotid artery at identical rate and volume.
In 14 9L gliosarcoma bearing rats and 3 normal rats cis-diamm inedichloroplatinum (CDDP) delivery to tumor and normal brain. CDDP concentration of the tumor tissues in ipsilateral hemisphere which infused with 25% mannitol was increased, varying from 36.2 to 192 μg/g (mean 100.9±56.37) as well as infusion of 20% mannitol having increase CDDP concentration from 63.9 to 141 μg/g (mean 96.77) in tumor tissues. In addition, tumor/serum raito of CDDP concentration demonstrated high values by either 25% mannitol or 20% mannitol infusion. However, in the intracarotid administra-tion of CDDP with saline instead of hyperosmolar mannitol, CDDP concentration of tumors was less,providing 48.0 μg/g in mean value, than that with 20% or 25% mannitol. Intravenous administration of CDDP showed low levels not only in normal brains but also in tumor tissues. In the brain around tumor and the brain distant from tumor infused with 25% mannitol intraarteally was re-vealed high CDDP concentration, whereas by in-traarterial infusion of 20% mannitol CDDP con-centration in them did not increase.
These results might suggest that the CDDP de-livery to the tumor was increased in Fischer 144 rats with 9L gliosarcoma by osmotic blood brain barrier disruption with hyperosmolar mannitol. 20% mannitol should be used as hyperosmotic agent for blood brain barrier disruption in order to increase drug delivery to malignant brain tumor because drug penetration to normal brain with 20% mannitol was less than with 25% mannitol.
Copyright © 1988, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


