Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
髄液の化学的組成に関する研究は,Magendie14)によつて1842年に始めて行なわれて以来,絶え間なく続けられている。髄液の代謝は主として水の代謝であると考えられるが,水と電解質とは密接な関係を保つて移動するので,電解質ぬきで髄液の代謝を考えることはできない。したがつて髄液の電解質に関しては,多くの臨床的,実験的研究がなされて来た。しかしこれらの多くは,個々の電解質単独の分布あるいは移動に関するもので,電解質相互間,およびその他の髄液の要累と電解質との相互関係を論じたものは,きわめて少ない。
われわれは100例の脳神経外科患者から採取した髄液の電解質,とくにNa,K,C1およびHCO3についてこのような点を検討し,髄液の電解質代謝の特性およびその意義を明らかにしようと試みた。
Concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride andbicarbonate were measured in lumbar and ventric-ular cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) taken from 100 neuro-surgical patients. Distribution of these electrolytesin CSF was statistically analyzed in relation to (1)CSF pressure, (2) CSF protein concentration, (3)other electrolytes. and (4) plasma concentrations ofcorresponding solutes. The results were as follows:
1) The mean concentrations of Na. K, Cl, andHCO3 in normal CSF were 146.7, 2.82, 123.8, and22.3 mEq/l respectively, and the mean ratios forteach electrolyte between CSF and plasma were0.96, 0.63, 1.12, and 0.81 in above order.
2) The concentrations of these four electrolytesin ventricular fluid tended to be lower than thosein lumber CSF although the difference was notstatistically significant.
3) Abnormal values of the concentrations of theseelectrlytes in CSF, which were estimated statisticallyfrom the standard deviations of normal mean values,were not significantly correlated with a variety ofcentral nervous system disease, although somepatients with brain tumors showed abnormally highor low concetrations of Na and Cl in CSF.
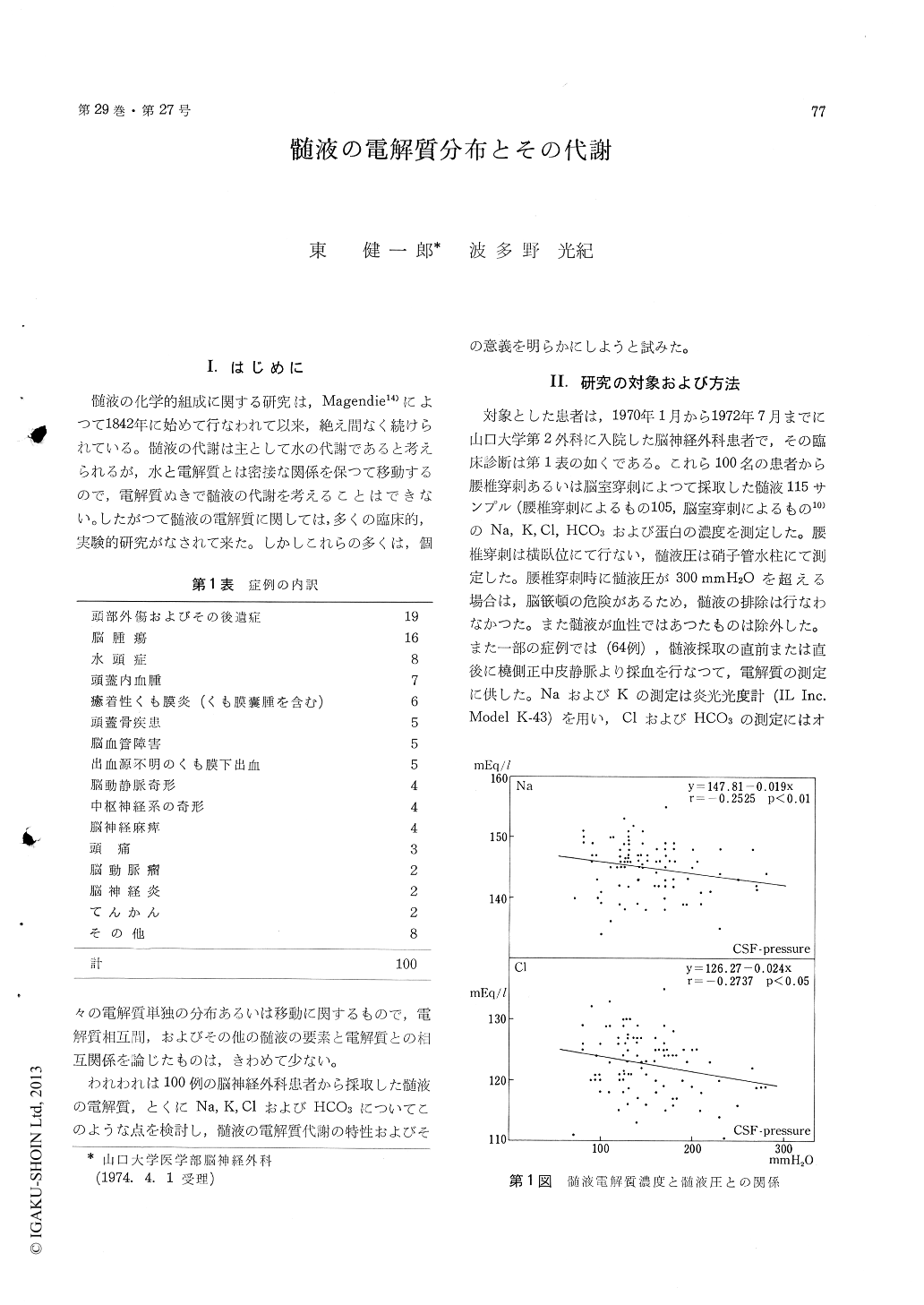
4) There were significant negative correlationsbetween concentrations of CSF-Na and Cl and CSFpressure.
5) There was a tendency toward significant nega-tive correlation between CSF-Cl and CSF-protein.
6) Regression analysis among distribution of fourelectrolytes showed significant correlations in fol-lowing four combinations; K vs Cl, Na vs cl, Navs K, and Cl vs HCO3.
7) The concentrations of Na, Cl and HCO3 inCSF varied with the plasma concentrations of cor-responding ions, while CSF-K was completely in-dependent of plasma concentration.
8) The ratio of concentrations of CSF-K, Cl, andHCO3 to plasma concentrations was inversely cor-related to the plasma concentrations of correspond-ing ions.
These results suggest that Na and Cl in CSFare dependent on plasma concentrations and arerelated to water transport between plasma and CSF,as well as being influenced to some extent by otherfactors such as CSF pressure. On the other hand,CSF-K is strictly regulated in order to maintaina constant level in CSF, probably through home-ostatic mechanism. Bicarbonate concentration inCSF may also be regulated in relation to changesin acid-base balance for stability of CSF-pH, al-though it is influenced to some extent by plasmalevel of this ion.
It is surmised that some of these ions are trans-ported in and out of the CSF compartment main-taining a mutual relationship, and thus playing animportant role in production and absorption of CSF.
Copyright © 1975, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


