Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
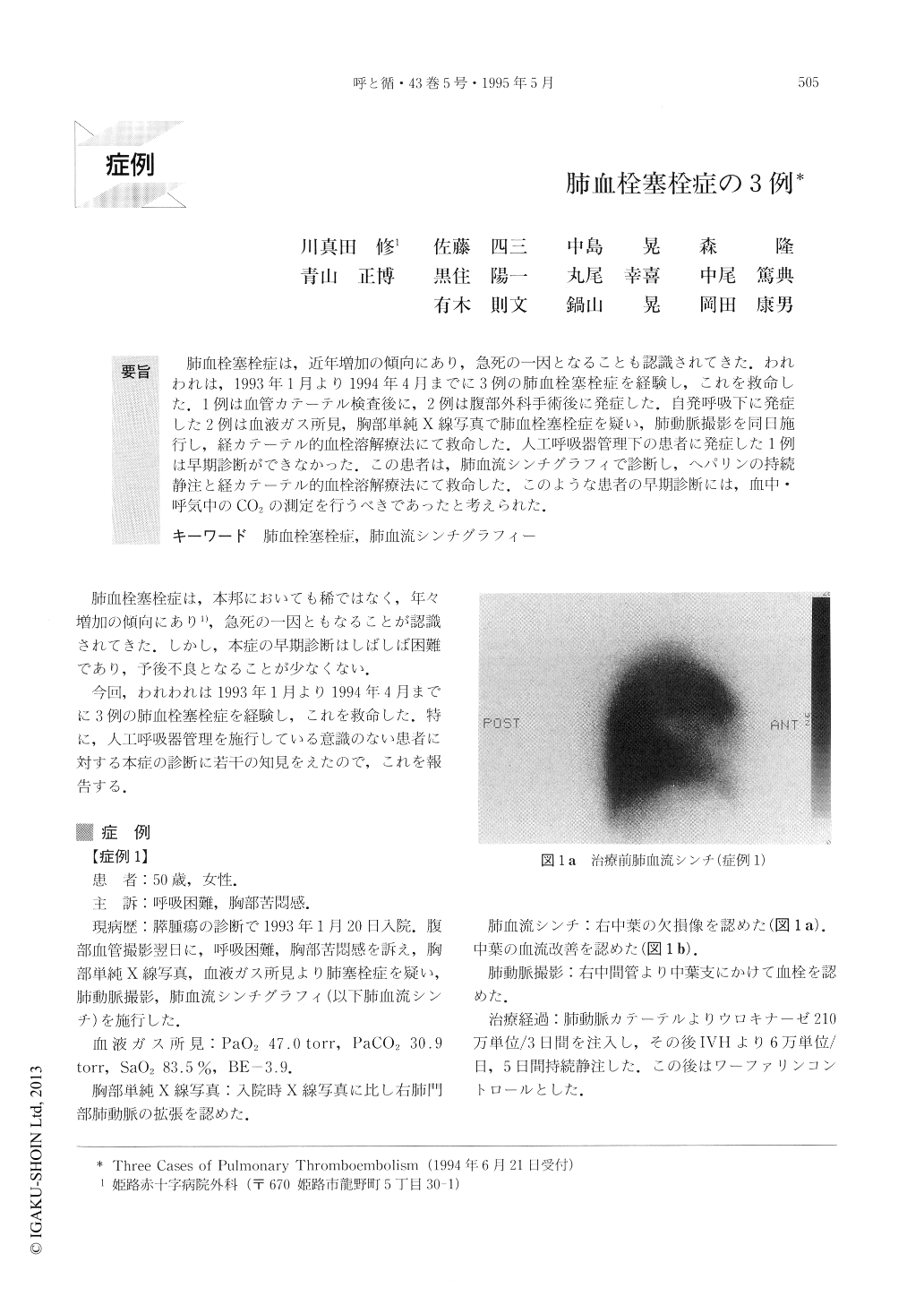
肺血栓塞栓症は,近年増加の傾向にあり,急死の一因となることも認識されてきた.われわれは,1993年1月より1994年4月までに3例の肺血栓塞栓症を経験し,これを救命した.1例は血管カテーテル検査後に,2例は腹部外科手術後に発症した.自発呼吸下に発症した2例は血液ガス所見,胸部単純X線写真で肺血栓塞栓症を疑い,肺動脈撮影を同日施行し,経カテーテル的血栓溶解療法にて救命した.人工呼吸器管理下の患者に発症した1例は早期診断ができなかった.この患者は,肺血流シンチグラフィで診断し,ヘパリンの持続静注と経カテーテル的血栓溶解療法にて救命した.このような患者の早期診断には,血中・呼気中のCO2の測定を行うべきであったと考えられた.
Pulmonary thromboembolism has been recognized as a cause of sudden death. We encountered three cases of pulmonary thromboembolism between January 1993 and April 1994 and saved all three. One occurred after catheter angiography while the others ocurred after abdominal surgery. In two cases, while the patient's respiration was still spontaneous , pulmonary throm-boembolism was suspected from blood gas analysis and plain chest x-p, which was confirmed by pulmonary artery angiography on the same day. Intrapulmonary infusion of urokinase cured the patients. In the other case, in which the patient was receiveing artificial respiration, an early diagnosis was not obtained, but a pulmonary perfusion scan gave the diagnosis and the patient was saved by continuous heparin injection and intrapulmonary infusion of urokinase. We considered that measurement of carbon dioxide concentration in blood and expiratory gas was most useful for obtaining an early diagnosis of pulmonary thromboembolism under artificial respirator management.
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


