Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
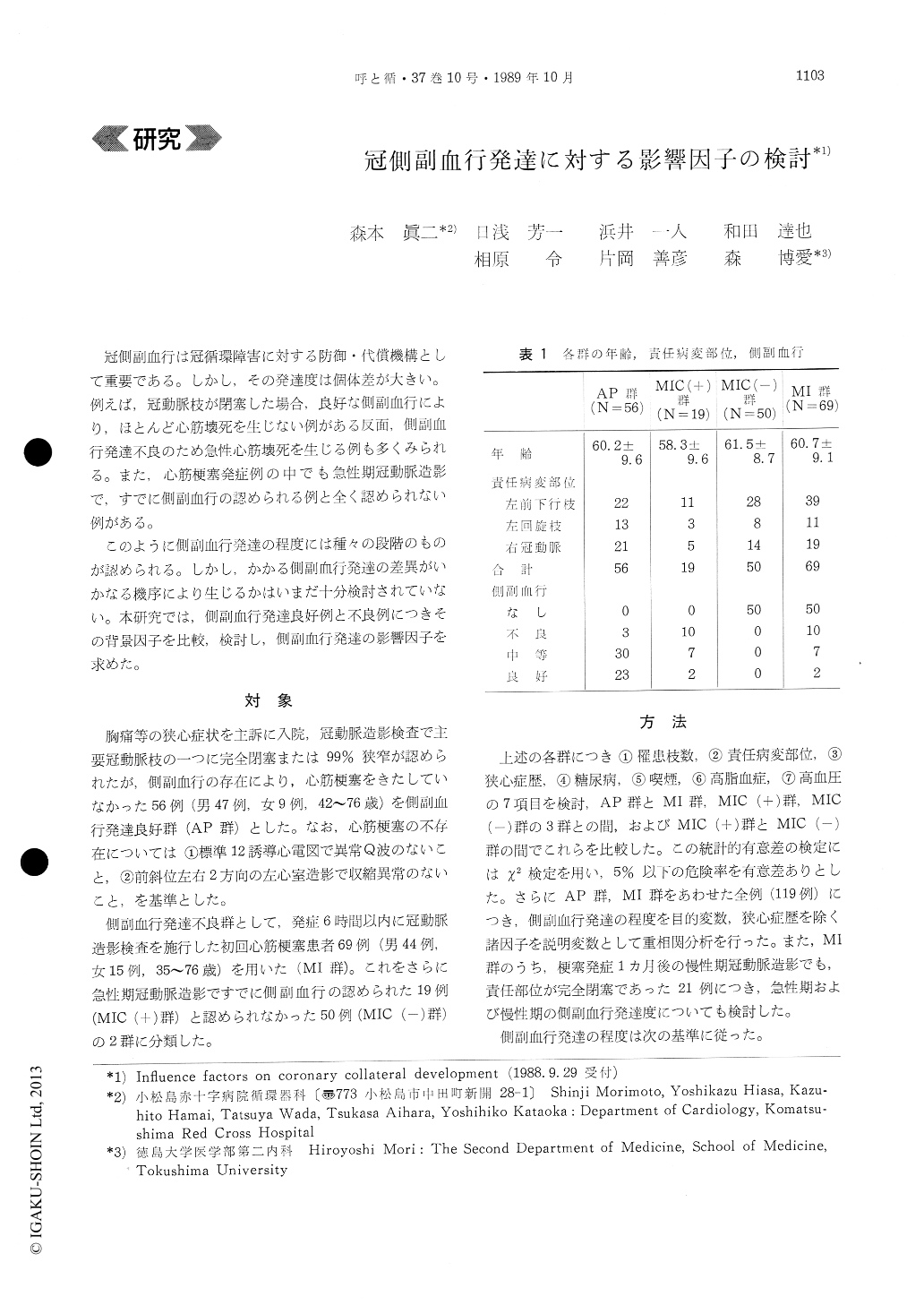
冠側副血行は冠循環障害に対する防御・代償機構として重要である。しかし,その発達度は個体差が大きい。例えば,冠動脈枝が閉塞した場合,良好な側副血行により,ほとんど心筋壊死を生じない例がある反面,側副血行発達不良のため急性心筋壊死を生じる例も多くみられる。また,心筋梗塞発症例の中でも急性期冠動脈造影で,すでに側副血行の認められる例と全く認められない例がある。
このように側副血行発達の程度には種々の段階のものが認められる。しかし,かかる側副血行発達の差異がいかなる機序により生じるかはいまだ十分検討されていない。本研究では,側副血行発達良好例と不良例につきその背景因子を比較,検討し,側副血行発達の影響因子を求めた。
In order to evaluate the influence factors on coro-nary collateral development, we compared various factors between two groups. Group I consisted of the 69 patients performed coronary angiography within 6 hours after the onset of acute myocardial infarction (MI) and Group II consisted of the 56 patients without MI because having good callateralsnevethless whose one coronary artery was totally occluded or had a 99% stenosis.
Group I (24/69, 35%) had a higher frequency of Diabetes mellitus than Group If (11/56, 20%) and had a lower frequency (30/69, 43%) of multi-vessel disease than Group II (39/56, 70%). The patients having angina duration more than 6 months were more in Group IF (37/56, 60%) than in Group I (18/69, 26%). No significant differences existed between these two groups in age, smoke, hyperlipi-demia and hypertension.
In conclusions, the patients with good collateral have high frequency of multivessel disease and long history of angina pectoris. Diabetes mellitus is a inhibit factor on coronary collateral development.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


